ppt - UTK-EECS
... According to Haykin, S. (1994), Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, NY: Macmillan, p. 2: ...
... According to Haykin, S. (1994), Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, NY: Macmillan, p. 2: ...
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial
... an expanded role that glial cells might play in signaling, but neurons are still considered the basis of this function. Neurons are important, but without glial support they would not be able to perform their function. ...
... an expanded role that glial cells might play in signaling, but neurons are still considered the basis of this function. Neurons are important, but without glial support they would not be able to perform their function. ...
Animal Form and Function are Correlated at all levels of organization
... -Muscle tissue is the most abundant tissue in most animals -There are three types of muscle: Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth ...
... -Muscle tissue is the most abundant tissue in most animals -There are three types of muscle: Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth ...
Nervous System
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
The Nervous System
... Consists of the brain and the spinal cord Shielded by bones Skull protects the brain Spine protects the spinal cord ...
... Consists of the brain and the spinal cord Shielded by bones Skull protects the brain Spine protects the spinal cord ...
Unit 3A–Neural Processing and the Endocrine System
... neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs neurotransmitter that influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord ...
... neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs neurotransmitter that influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Quiz Answers
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
The Nervous System
... •These are the suport cells in the peripheral nervous system. •Schwann cells provide the myelin sheath for peripheral axons. •Satellite cells serve a slightly similar function to astrocytes, supporting the cell bodies of peripheral neurons. ...
... •These are the suport cells in the peripheral nervous system. •Schwann cells provide the myelin sheath for peripheral axons. •Satellite cells serve a slightly similar function to astrocytes, supporting the cell bodies of peripheral neurons. ...
PPT
... Decades ago, a common treatment of epilepsy was to cut the corpus callosum, which is the main connection between the hemispheres, in order to limit the spreading of epileptic activity. These split-brain patients typically behaved and felt like healthy people in everyday life situations. In laborator ...
... Decades ago, a common treatment of epilepsy was to cut the corpus callosum, which is the main connection between the hemispheres, in order to limit the spreading of epileptic activity. These split-brain patients typically behaved and felt like healthy people in everyday life situations. In laborator ...
Directed Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem
... from three siblings, two with the GEFS+ K1270T mutation and one without (Control). In our initial studies Control iPSCs were used to derive expandable lines of neural stem cells (NSCs). However, when the NSCs were differentiated into neurons using standard procedures, only 10% of the cells examined ...
... from three siblings, two with the GEFS+ K1270T mutation and one without (Control). In our initial studies Control iPSCs were used to derive expandable lines of neural stem cells (NSCs). However, when the NSCs were differentiated into neurons using standard procedures, only 10% of the cells examined ...
Nervous System II – Neurons
... Nervous System II – Neurons Neurons Information is transmitted through ...
... Nervous System II – Neurons Neurons Information is transmitted through ...
Nervous System Cells
... • Many vertebrate peripheral neurons have an insulating sheath around the axon called myelin which is formed by Schwann cells. • Myelin sheathing allows these neurons to conduct nerve impulses faster than in non-myelinated neurons. ...
... • Many vertebrate peripheral neurons have an insulating sheath around the axon called myelin which is formed by Schwann cells. • Myelin sheathing allows these neurons to conduct nerve impulses faster than in non-myelinated neurons. ...
Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now
... Axon – carry impulses away from the cell body Axon Terminals – the end of the axons, sends impulse to other neurons ...
... Axon – carry impulses away from the cell body Axon Terminals – the end of the axons, sends impulse to other neurons ...
Nervous System
... B) Motor neurons convey signals from the CNS to effector cells. C) Interneurons integrate data and relay appropriate signals to other interneurons or to motor neurons. D) The PNS includes nerves and ganglia. E) The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. ...
... B) Motor neurons convey signals from the CNS to effector cells. C) Interneurons integrate data and relay appropriate signals to other interneurons or to motor neurons. D) The PNS includes nerves and ganglia. E) The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. ...
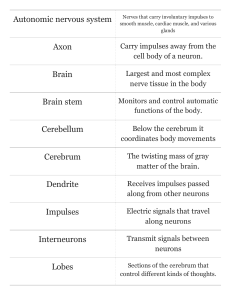
“Definitions” section of your binder Central nervous system
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
Structure of a Neuron
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
1-The cell body
... called synapses. 3-The axon (Gr. axon, axis), which is a single long process ending at synapses specialized to generate and conduct nerve impulses to other cells (nerve, muscle, and gland cells). Axons may also receive information from other neurons, information that mainly modifies the transmission ...
... called synapses. 3-The axon (Gr. axon, axis), which is a single long process ending at synapses specialized to generate and conduct nerve impulses to other cells (nerve, muscle, and gland cells). Axons may also receive information from other neurons, information that mainly modifies the transmission ...
An ultra small array of electrodes for stimulating multiple
... After cleaning, replatinization was performed if visual inspection revealed the loss of the platinum black layer from any of the electrodes. ...
... After cleaning, replatinization was performed if visual inspection revealed the loss of the platinum black layer from any of the electrodes. ...
File
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
Development
... Parkinson’s Disease • Due to loss of substantia nigra dopamine neurons. • Common in people over 80. • Treated with L-dopa, DA transplants, or DA receptor agonists. • 5-10% early-onset familial: several genes identified (alpha-synuclein, parkin) • 90% sporadic: pesticides and MPTP. • Mitochondria an ...
... Parkinson’s Disease • Due to loss of substantia nigra dopamine neurons. • Common in people over 80. • Treated with L-dopa, DA transplants, or DA receptor agonists. • 5-10% early-onset familial: several genes identified (alpha-synuclein, parkin) • 90% sporadic: pesticides and MPTP. • Mitochondria an ...
Peripheral Nerve Repair
... •crucial for human movement and function • Highway for information processing and response •Sensory Neurons- send stimulation information from senses to the brain. • Motor Neurons- send commands from the brain to muscles or other organs ...
... •crucial for human movement and function • Highway for information processing and response •Sensory Neurons- send stimulation information from senses to the brain. • Motor Neurons- send commands from the brain to muscles or other organs ...
Print › Nervous System | Quizlet
... Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain ...
... Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain ...
Ocular Dominance Columns
... Early experience and neural development Overview of neuronal development Neuronal survival vs. apoptosis Competition for cortical space The critical period Cortical plasticity in the adult ...
... Early experience and neural development Overview of neuronal development Neuronal survival vs. apoptosis Competition for cortical space The critical period Cortical plasticity in the adult ...