Neuron Anatomy Activity - Ask a Biologist
... 1. Synapses: Send electrical impulses to neighboring neurons. 2. Myelin sheaths: Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly. 3. Axon: Transfers electrical impulse signals from the cell body to the synapse. 4. Soma: ...
... 1. Synapses: Send electrical impulses to neighboring neurons. 2. Myelin sheaths: Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly. 3. Axon: Transfers electrical impulse signals from the cell body to the synapse. 4. Soma: ...
Brumberg - QC Queens College
... individual elements of a cortical circuit and how they interact brings us a step closer to understanding the function of the circuit as a whole and ultimately its behavior in response to environmental stimuli. While the analogy applies to the neocortex, deciphering the cortical microcircuit is much ...
... individual elements of a cortical circuit and how they interact brings us a step closer to understanding the function of the circuit as a whole and ultimately its behavior in response to environmental stimuli. While the analogy applies to the neocortex, deciphering the cortical microcircuit is much ...
White blood cells play important roles in protecting us from infections
... 4. Anticipated effects and future applications of research ...
... 4. Anticipated effects and future applications of research ...
3-8_NeuronDiversity_SalmaA
... Glutamatergic neurons: Glutamate is one of two primary excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter, the other being Aspartate. Glutamate receptors are one of four categories, three of which are ligand-gated ion channels and one of which is a G-protein coupled receptor (often referred to as GPCR).Glutamat ...
... Glutamatergic neurons: Glutamate is one of two primary excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter, the other being Aspartate. Glutamate receptors are one of four categories, three of which are ligand-gated ion channels and one of which is a G-protein coupled receptor (often referred to as GPCR).Glutamat ...
A2.2.2.SecretSignals - jj-sct
... Activity 2.2.2: The Secret to Signals Introduction The secrets of neuron communication have been studied by scientists for centuries. We have learned that chemical and electrical factors work together to send signals. We know that the brain and spinal cord team up to deal with all the messages that ...
... Activity 2.2.2: The Secret to Signals Introduction The secrets of neuron communication have been studied by scientists for centuries. We have learned that chemical and electrical factors work together to send signals. We know that the brain and spinal cord team up to deal with all the messages that ...
Chapter 3: The nerve cell Multiple Choice Questions (1
... b. a model of a brain function that utilizes idealized neurons c. the circuitry that is found in artificial intelligence devices d. a tangle of neuronal axons that no longer function properly 4. The reentrant, or ” two-way”, connections between neuronal arrays are a. by far the most common connectio ...
... b. a model of a brain function that utilizes idealized neurons c. the circuitry that is found in artificial intelligence devices d. a tangle of neuronal axons that no longer function properly 4. The reentrant, or ” two-way”, connections between neuronal arrays are a. by far the most common connectio ...
PowerPoint for 9/29
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
BOX 2.1 THE NEURON DOCTRINE The cell theory, which states
... known as the neurondoctrine. This great concept in essence states that the cell theory applies to the nervous system: each neuron is an individual entity, the basic unit of neural circuitry (Fig. 2.2B). The acrimonious debate between reticularists and proponents of the neuron doctrine raged for deca ...
... known as the neurondoctrine. This great concept in essence states that the cell theory applies to the nervous system: each neuron is an individual entity, the basic unit of neural circuitry (Fig. 2.2B). The acrimonious debate between reticularists and proponents of the neuron doctrine raged for deca ...
Document
... • A neuron which carries signals from tissue to brain is a sensory neuron or afferent neuron. • A neuron which carries signals from the brain to tissue is a motor neuron or efferent neuron. ...
... • A neuron which carries signals from tissue to brain is a sensory neuron or afferent neuron. • A neuron which carries signals from the brain to tissue is a motor neuron or efferent neuron. ...
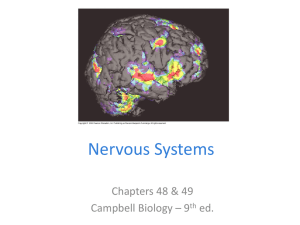
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... dendrites: receive incoming messages axons: transmit messages away to other cells myelin sheath: fatty insulation covering axon, speeds up nerve impulses • synapse: junction between 2 neurons • neurotransmitter: chemical messengers sent across synapse • Glia: cells that support neurons – Eg. Schwann ...
... dendrites: receive incoming messages axons: transmit messages away to other cells myelin sheath: fatty insulation covering axon, speeds up nerve impulses • synapse: junction between 2 neurons • neurotransmitter: chemical messengers sent across synapse • Glia: cells that support neurons – Eg. Schwann ...
Activity of Spiking Neurons Stimulated by External Signals of
... Spiking neuron systems gained increasing interest in recent years because they represent spatio-temporal relations within simulated systems, unlike the spatial simple neuron models found in artificial neural systems. They are also closer to biophysical models of neurons, synapses, and related elemen ...
... Spiking neuron systems gained increasing interest in recent years because they represent spatio-temporal relations within simulated systems, unlike the spatial simple neuron models found in artificial neural systems. They are also closer to biophysical models of neurons, synapses, and related elemen ...
The Nervous System
... • Dendrites: extend from cell body, receive information from other cells. ...
... • Dendrites: extend from cell body, receive information from other cells. ...
How Does the Brain Work?
... The primitive brainstem regulates balance, coordination and life-sustaining processes such as breathing and heartbeat. Throughout the brain, neurons communicate with one another through interlocking circuits. When a neuron is stimulated, it generates a tiny electrical current, which passes down a fi ...
... The primitive brainstem regulates balance, coordination and life-sustaining processes such as breathing and heartbeat. Throughout the brain, neurons communicate with one another through interlocking circuits. When a neuron is stimulated, it generates a tiny electrical current, which passes down a fi ...
Slide 1
... various periodic signals from grid cells to identify the rats location. Hippocampus cell fires only when rat is in specific location ...
... various periodic signals from grid cells to identify the rats location. Hippocampus cell fires only when rat is in specific location ...
Nerve Tissue Notes
... “The secret of action is to begin.” 1. What does this mean to you? 2. How can you apply this to Biology II? ...
... “The secret of action is to begin.” 1. What does this mean to you? 2. How can you apply this to Biology II? ...
Brain Questions
... 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripheral nervous system is composed of what? 4- What is the axon of a neuron wrapped in? What is its function? 5- How do signals travel down the axon? 6- What role do dendrites have in cell to cell communication? 7- What is the difference betw ...
... 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripheral nervous system is composed of what? 4- What is the axon of a neuron wrapped in? What is its function? 5- How do signals travel down the axon? 6- What role do dendrites have in cell to cell communication? 7- What is the difference betw ...
3-2_UniqueFt_of_Neurons
... dendrites: neurons have multiple dendrites (which also can branch multiple times) that connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the de ...
... dendrites: neurons have multiple dendrites (which also can branch multiple times) that connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the de ...
Slide 1
... perform particular tasks. Under proper conditions, stem cells begin to develop or ‘differentiate’ into specialized cells that carry out a specific function, such as in the skin, muscle or brain. Additionally, stem cells can ‘self-renew,’ that is they can divide and give rise to more stem cells. ...
... perform particular tasks. Under proper conditions, stem cells begin to develop or ‘differentiate’ into specialized cells that carry out a specific function, such as in the skin, muscle or brain. Additionally, stem cells can ‘self-renew,’ that is they can divide and give rise to more stem cells. ...
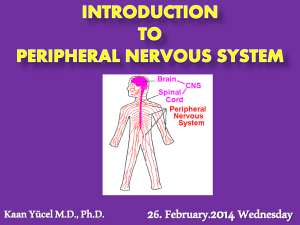
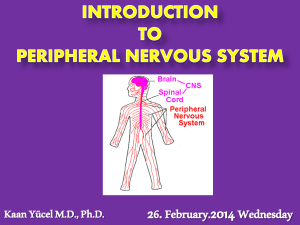
Nervous System Outline 1
... C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands or muscles to “create” a response. 1. The response is carried out by Effector Cells. a. Effectors are Muscles or Glands. These structures can have an effect on your body. D. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 1. This incl ...
... C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands or muscles to “create” a response. 1. The response is carried out by Effector Cells. a. Effectors are Muscles or Glands. These structures can have an effect on your body. D. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 1. This incl ...