Neuroscience
... Hippocampus: Involved in forming new memories. Neurogenesis takes place. Thalamus: Processes and distributes sensory and motor info to and from cerebral cortex. Regulates awareness, attention, and motivation Hypothalamus: Regulates both divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System. Amygdala: involved i ...
... Hippocampus: Involved in forming new memories. Neurogenesis takes place. Thalamus: Processes and distributes sensory and motor info to and from cerebral cortex. Regulates awareness, attention, and motivation Hypothalamus: Regulates both divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System. Amygdala: involved i ...
The Nervous System- Nervous Tissue
... Functional classification based on type of information & direction of information transmission: • Sensory (afferent) neurons – • transmit sensory information from receptors of PNS towards ...
... Functional classification based on type of information & direction of information transmission: • Sensory (afferent) neurons – • transmit sensory information from receptors of PNS towards ...
Biopsychology and the Foundations of Neuroscience Chapter 3
... Since the early 1800s we have come a long ways when a German physician developed the theory of phrenology. ◦ Phrenology claimed that bumps on the skull could reveal our mental abilities and character traits. ...
... Since the early 1800s we have come a long ways when a German physician developed the theory of phrenology. ◦ Phrenology claimed that bumps on the skull could reveal our mental abilities and character traits. ...
Test.
... • Also some neurons respond to specific stimuli – e.g. to faces but not to dogs. • There might even be a Clinton cell… ...
... • Also some neurons respond to specific stimuli – e.g. to faces but not to dogs. • There might even be a Clinton cell… ...
Nervous Systems (ch. 48 & 49) Sum13
... • All neurons use same basic signal • Wiring pattern in brain distinguishes stimuli 2) Signal intensity of stimulus • All signals similar in size (all-or-none response) ...
... • All neurons use same basic signal • Wiring pattern in brain distinguishes stimuli 2) Signal intensity of stimulus • All signals similar in size (all-or-none response) ...
Motor
... neuron. From Fetz and Cheney (1980). (C) These anatomic and physiologic findings indicate that the output of single corticospinal neurons often diverges to influence multiple muscles. From Cheney et al. (1985). ...
... neuron. From Fetz and Cheney (1980). (C) These anatomic and physiologic findings indicate that the output of single corticospinal neurons often diverges to influence multiple muscles. From Cheney et al. (1985). ...
The Neuron
... - Cell membrane open and the positive ions rush in when enough has entered to make the inside more positive than the outside. The cell membrane closes again. This opens/close of cell membrane occurs along the length of the neural membrane creating the neural impulse that travels down the axon = like ...
... - Cell membrane open and the positive ions rush in when enough has entered to make the inside more positive than the outside. The cell membrane closes again. This opens/close of cell membrane occurs along the length of the neural membrane creating the neural impulse that travels down the axon = like ...
Chapter 33 Nervous System
... i. Many types of sense receptors which respond to temperature, pressure and pain are found in epidermis and dermis of skin ii. Fingertips detect light touch iii. Sole of feet respond to heavy pressure iv. Pain receptors are simple (consist of free nerve endings) and found in all tissues except for b ...
... i. Many types of sense receptors which respond to temperature, pressure and pain are found in epidermis and dermis of skin ii. Fingertips detect light touch iii. Sole of feet respond to heavy pressure iv. Pain receptors are simple (consist of free nerve endings) and found in all tissues except for b ...
Nervous System
... questionnaire to identify past medical problems, difficulties in daily activities, etc. Physical examination, including hearing & sight ...
... questionnaire to identify past medical problems, difficulties in daily activities, etc. Physical examination, including hearing & sight ...
Chemistry of Psychology - Point Loma High School
... Used by more neurons than any other Lots in Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus Too much Glutamate = causes neurons to die Plays a role in allowing and supporting synaptic connections allows messages to cross synapse efficiently Important for learning & memory (p98) Peptides= Endorphins Hund ...
... Used by more neurons than any other Lots in Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus Too much Glutamate = causes neurons to die Plays a role in allowing and supporting synaptic connections allows messages to cross synapse efficiently Important for learning & memory (p98) Peptides= Endorphins Hund ...
The Nervous System
... • Nervous systems function in sensory input, integration, and motor output. • The nervous system is composed of neurons and supporting cells. • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-n ...
... • Nervous systems function in sensory input, integration, and motor output. • The nervous system is composed of neurons and supporting cells. • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-n ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... 3. Axon: extension of a neuron which sends messages from the soma to other neuron. Longest part of the neuron. (Think “axis” … a ...
... 3. Axon: extension of a neuron which sends messages from the soma to other neuron. Longest part of the neuron. (Think “axis” … a ...
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
A Biologically Inspired Visuo-Motor Control Model based on a Deflationary
... account for the following biological data: – mirror neuron are active in the same way during both executed-GO actions and observed-GO actions. (This is accounted for by the OA model too.) – an inactivation of mirror neurons causes a motor slowing, but the correct action is still performed. This mean ...
... account for the following biological data: – mirror neuron are active in the same way during both executed-GO actions and observed-GO actions. (This is accounted for by the OA model too.) – an inactivation of mirror neurons causes a motor slowing, but the correct action is still performed. This mean ...
Neurophysiology Complete
... to Na ions when a neuron is activated by a stimulus of adequate intensity Depolarization: the interior becomes less negative, exterior becomes less positive Action potential: when depolarization reaches a certain point so that the membrane polarity changes Repolarization: within a millisecond Na and ...
... to Na ions when a neuron is activated by a stimulus of adequate intensity Depolarization: the interior becomes less negative, exterior becomes less positive Action potential: when depolarization reaches a certain point so that the membrane polarity changes Repolarization: within a millisecond Na and ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... VI. Effects of Aging A. Natural decline in functioning neurons, including sensory neurons. (balance loss, coordination, blood pressure, bladder) B. By the age of 60 up to 50% loss of lower motor neurons in lumbar region. (loss of muscle mass & increase fatigue) C. Size and weight of the brain decre ...
... VI. Effects of Aging A. Natural decline in functioning neurons, including sensory neurons. (balance loss, coordination, blood pressure, bladder) B. By the age of 60 up to 50% loss of lower motor neurons in lumbar region. (loss of muscle mass & increase fatigue) C. Size and weight of the brain decre ...
Chapter 14
... body), bipolar (two processes extend from the cell body), and multipolar (three or more processes extend from the cell body). The three functional types of neurons are sensory neurons (afferent, unipolar, and bipolar neurons), interneurons (multipolar neurons that lie entirely within the CNS and car ...
... body), bipolar (two processes extend from the cell body), and multipolar (three or more processes extend from the cell body). The three functional types of neurons are sensory neurons (afferent, unipolar, and bipolar neurons), interneurons (multipolar neurons that lie entirely within the CNS and car ...
Lecture notes - University of Sussex
... composite message in many nerve fibres.” Lord Adrian, Nobel Acceptance Speech, 1932. ...
... composite message in many nerve fibres.” Lord Adrian, Nobel Acceptance Speech, 1932. ...
CH005a NERVOUS SYS - INTRO 10-22
... Neurons Functional unit of nervous system Have capacity to produce action ...
... Neurons Functional unit of nervous system Have capacity to produce action ...
Pt2Localization - MemoryAndCognition
... Hypothesis 1: specificity tuning – a particular neuron could selectively fire when you see that person ...
... Hypothesis 1: specificity tuning – a particular neuron could selectively fire when you see that person ...
The Nervous System
... communicate electrically down the axon Happens via movement of ions (Na and K) across the axon membrane ...
... communicate electrically down the axon Happens via movement of ions (Na and K) across the axon membrane ...
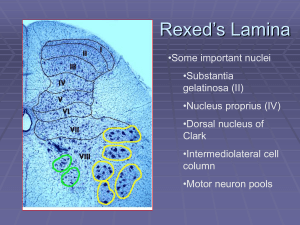
Rexed`s Lamina
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...