File
... Provides the diaphragm nutrients in order facilitate breathing • Half of the equation for respiration Glucose + Oxygen = water, carbon dioxide and energy ...
... Provides the diaphragm nutrients in order facilitate breathing • Half of the equation for respiration Glucose + Oxygen = water, carbon dioxide and energy ...
unit-4 task 1 - WordPress.com
... due to our muscle fibres being stretched further putting strain on our muscles causing them to slightly tear. 4) Exercise: Exercise has a big impact on the formation of your bones. E.G. the more amount of exercise you do the stronger your bones become which means they are less likely to break. Where ...
... due to our muscle fibres being stretched further putting strain on our muscles causing them to slightly tear. 4) Exercise: Exercise has a big impact on the formation of your bones. E.G. the more amount of exercise you do the stronger your bones become which means they are less likely to break. Where ...
6.6 Hormones & Reproduction
... Endocrine system • Produces and releases hormones • Hormones travel in the blood to target tissues • Long distance communication between cells ...
... Endocrine system • Produces and releases hormones • Hormones travel in the blood to target tissues • Long distance communication between cells ...
1 - VLE
... The amount of air breathed in or out of the lungs in one breath The maximum amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after breathing in as much as possible The amount of oxygen consumed during recovery above that which would have been ordinary been consumed in the same time at rest. 7. Which of th ...
... The amount of air breathed in or out of the lungs in one breath The maximum amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after breathing in as much as possible The amount of oxygen consumed during recovery above that which would have been ordinary been consumed in the same time at rest. 7. Which of th ...
File
... ENERGY SYSTEMS AVAILABLE DURING EXERCISE • There are three primary energy systems that supply the body with ATP during exercise. Phosphagen system (anaerobic) o Involves the breakdown of creatine phosphate (CP) and stored ATP to resynthesize ATP for immediate use ...
... ENERGY SYSTEMS AVAILABLE DURING EXERCISE • There are three primary energy systems that supply the body with ATP during exercise. Phosphagen system (anaerobic) o Involves the breakdown of creatine phosphate (CP) and stored ATP to resynthesize ATP for immediate use ...
Cardio Study Guide 10
... heartbeats per minute to pump blood through the body. The resting heart rate is taken when a person is at rest. The average resting heart rate is approximately 72 beats per minute for an adult. The resting rate for a person who is fit may be as low as 50 beats per minute. The more fit the person, th ...
... heartbeats per minute to pump blood through the body. The resting heart rate is taken when a person is at rest. The average resting heart rate is approximately 72 beats per minute for an adult. The resting rate for a person who is fit may be as low as 50 beats per minute. The more fit the person, th ...
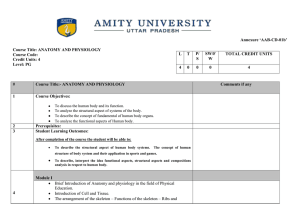
Annexure `AAB-CD-01b` Course Title: ANATOMY AND
... Blood and circulatory system: Constituents of blood and their function – Blood groups and blood transfusion, clotting of blood, the structure of the heart-properties of the heart muscle, Circulation of blood, cardiac cycle, blood pressure, Lymph and Lymphatic Circulation. Cardiac output. The Res ...
... Blood and circulatory system: Constituents of blood and their function – Blood groups and blood transfusion, clotting of blood, the structure of the heart-properties of the heart muscle, Circulation of blood, cardiac cycle, blood pressure, Lymph and Lymphatic Circulation. Cardiac output. The Res ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 4: “Cells, Tissues, Organs & Organ
... To support healthy organs and body systems, we all have the same basic needs. •Clean air and water •A nutritious and well-balanced diet •Exercise •Restful sleep ...
... To support healthy organs and body systems, we all have the same basic needs. •Clean air and water •A nutritious and well-balanced diet •Exercise •Restful sleep ...
Physical fitness
... • Muscles use fat, glucose, and amino acids for energy • Fat is the primary energy source during inactivity and low-to-moderate activity (aerobic) • Glucose is the primary source during high intensity, short duration activities (anaerobic) ...
... • Muscles use fat, glucose, and amino acids for energy • Fat is the primary energy source during inactivity and low-to-moderate activity (aerobic) • Glucose is the primary source during high intensity, short duration activities (anaerobic) ...
Grade 6: Lesson PLan 3 - Texas Heart Institute
... and release increased amounts of waste (such as carbon dioxide). This activity results in an increased demand for blood flow to the muscles. People who regularly participate in exercise benefit from that increased circulation. Active people have a healthier heart and lungs, stronger muscles and bone ...
... and release increased amounts of waste (such as carbon dioxide). This activity results in an increased demand for blood flow to the muscles. People who regularly participate in exercise benefit from that increased circulation. Active people have a healthier heart and lungs, stronger muscles and bone ...
Chapter 30.3
... From the circulatory system, glucose and oxygen molecules move from the capillaries into the cells of the body where cellular respiration occurs ...
... From the circulatory system, glucose and oxygen molecules move from the capillaries into the cells of the body where cellular respiration occurs ...
The Body in Action - Glasgow Gaelic School
... • Lactic acid is produced instead of carbon dioxide and water • Lactic acid builds up in the muscle and causes a sore, burning feeling • Aerobic respiration glucose + oxygen →carbon dioxide + water + energy • Anaerobic respiration glucose → lactic acid + energy • After exercise the lactic acid is br ...
... • Lactic acid is produced instead of carbon dioxide and water • Lactic acid builds up in the muscle and causes a sore, burning feeling • Aerobic respiration glucose + oxygen →carbon dioxide + water + energy • Anaerobic respiration glucose → lactic acid + energy • After exercise the lactic acid is br ...
Exercise Warming Up and Cooling Down
... A good cool-down should include five minutes of continued mild activity. Gradually, decrease the intensity to a slow walk. Also, spend a few minutes on slow stretching exercises to re-stretch the muscles. The cool-down will gradually slow down the heart’s pumping action and it will prevent blood fro ...
... A good cool-down should include five minutes of continued mild activity. Gradually, decrease the intensity to a slow walk. Also, spend a few minutes on slow stretching exercises to re-stretch the muscles. The cool-down will gradually slow down the heart’s pumping action and it will prevent blood fro ...
Oxygen Transport
... exchange of gases at the level of the tissues – extraction of O2 at the tissues in increased during exercise, skeletal muscle increases cellular respiration, and O2 is used to generate ATP an increase in the use of O2 results in a decline in PO2 within the skeletal muscle, and increase the gra ...
... exchange of gases at the level of the tissues – extraction of O2 at the tissues in increased during exercise, skeletal muscle increases cellular respiration, and O2 is used to generate ATP an increase in the use of O2 results in a decline in PO2 within the skeletal muscle, and increase the gra ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 4: “Cells, Tissues, Organs & Organ Systems”
... •Nervous system monitors environment conditions, through temperature-sensing cells in the skin. ...
... •Nervous system monitors environment conditions, through temperature-sensing cells in the skin. ...
Exercise and Blood Sugar
... Exercise keeps joints flexible and improves balance Exercise helps you to sleep better ...
... Exercise keeps joints flexible and improves balance Exercise helps you to sleep better ...
File
... Longer-term effects occur as the body adapts to regular exercise, including your heart getting larger, bones becoming denser and the vital capacity of your breath deepening ...
... Longer-term effects occur as the body adapts to regular exercise, including your heart getting larger, bones becoming denser and the vital capacity of your breath deepening ...
Respiration (Quick Questions) 1. In what part of cell does respiration
... 7. Building larger molecules (e.g. linking amino acids together to make protein molecules). To contract muscles. To maintain a steady body temperature. In plants to make amino acids from glucose. 8. Glycogen is a storage substance made up of many glucose molecules. It is stored in muscles tissues an ...
... 7. Building larger molecules (e.g. linking amino acids together to make protein molecules). To contract muscles. To maintain a steady body temperature. In plants to make amino acids from glucose. 8. Glycogen is a storage substance made up of many glucose molecules. It is stored in muscles tissues an ...
BODY SYSTEMS - rivervaleschools.com
... Why is there such a difference? What happens to these bones as you grow up? ...
... Why is there such a difference? What happens to these bones as you grow up? ...
Fitness Basics - University of Richmond
... Aerobic exercise increases the health and function of your heart, lungs, and circulatory system. For maximum effectiveness, aerobic exercise needs to be rhythmic, continuous and involve the large muscle groups, ...
... Aerobic exercise increases the health and function of your heart, lungs, and circulatory system. For maximum effectiveness, aerobic exercise needs to be rhythmic, continuous and involve the large muscle groups, ...
Lecture PowerPoint
... Understanding the Organization of the Body Cells: fundamental units of all living organisms. Cells are specialized to specific functions in the body. There is a division of labor. Some cells produce mineral for bone, some cells produce protein for muscle contraction, etc. Tissues: Tissues are group ...
... Understanding the Organization of the Body Cells: fundamental units of all living organisms. Cells are specialized to specific functions in the body. There is a division of labor. Some cells produce mineral for bone, some cells produce protein for muscle contraction, etc. Tissues: Tissues are group ...
Body in Action
... of training and recovery time. Recovery time is the time it takes for the heart rate, breathing rate and the lactic acid levels to return to normal resting values. A person who is in training will notice that the factors above will return to normal resting values quicker than a person who is not ...
... of training and recovery time. Recovery time is the time it takes for the heart rate, breathing rate and the lactic acid levels to return to normal resting values. A person who is in training will notice that the factors above will return to normal resting values quicker than a person who is not ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.