* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Body in Action - Glasgow Gaelic School
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
High-altitude adaptation in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cord blood bank wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
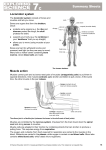
The Body in Action Standard Grade Biology The Skeleton • Supports our weight • Protects vital organs • Provides a point of attachment for muscles • Keeps our shape • The marrow is where red and white blood cells are made The Structure of Bone • Bones are made of living tissue • Made up of flexible fibres and hard minerals • Flexible fibres make bone bendy • Hard minerals give it strength Synovial Joints • The meeting point of 2 bones is called a joint • Some joints allow very little movement • Some allow a wide range of movement • Ball and socket joints (hip, shoulder) allow movement in 3 directions • Hinge joints (knee, elbow ) only allow movement in 1 plane • Ligaments hold 2 bones together The Structure of a Joint Cont. • The ends of the bones are covered with a layer of smooth cartilage • Cartilage acts as a shock absorber • The joint capsule contains synovial fluid which helps reduce friction between the bones Muscles and Movement Respiration and Breathing • The body needs oxygen in order to release energy from food (respiration) • Breathing supplies that oxygen and removes carbon dioxide, the waste product of respiration Lung Structure Gas Exchange in the Alveoli • • • • • • Alveoli increase the surface area for gas exchange They have a rich blood supply They have thin walls to allow easy diffusion They have moist surfaces Oxygen diffuses into the blood Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood into the air space • Blood carries oxygen to the cells and brings carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs Gas Exchange Breathing Breathing in • Intercostal muscles contract • Ribs move up and out • Diaphragm contracts and flattens • Chest volume increases, pressure decreases • Air is drawn into the lungs Breathing out • Intercostal muscles relax • Ribs move down and in • Diaphragm relaxes and moves up • Chest volume decreases, pressure increases • Air is forced out of the lungs Breathing in Breathing out Mucus and Cilia • Air passages are lined with ciliated cells and mucus producing cells • Mucus traps dust and germs • Cilia move the mucus out of the air passages to the nose The heart and circulation in mammals L.Os • Describe the flow of blood through the heart and its associated blood vessels • Describe the positions and functions of the heart valves • Explain the difference in thickness of the walls of the ventricles • State that the heart obtains its blood supplies from coronary arteries The Heart Blood Flow Blood Vessels • 3 main types • Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, have thick walls to withstand the high pressure • Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart, have thinner walls and valves to prevent backflow • Capillaries have walls 1 cell thick to allow diffusion to take place easily Gas Exchange at the Capillaries Valves and Blood Flow Blood • Blood is necessary for the transport of oxygen, nutrients and waste products round the body Part of the Blood Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Platelets Plasma Function Have no nucleus Contain haemoglobin Carry oxygen Fight disease and infection Involved in clotting Transports dissolved substances (food, carbon dioxide etc.) Co-ordination and the Nervous System 1. Every action we make is controlled by the nervous system 2. The sense organs detect information from the surroundings and send messages to the brain and spinal cord 3. The brain and spinal cord sort out these messages and send instructions to the body 4. The body responds Learning outcomes • Structure of the eye: • Cornea, iris, lens, retina, optic nerve • How we see The Eye The Pupil The lens • The lens focuses the light entering the eye onto the retina. • If the light is not focused, vision is blurry • Wearing glasses or contact lenses can help focus the light to make vision clear The retina • Made up of millions of light sensitive cells which convert light into nerve impulses which are carried to the brain via the optic nerve. • Rods are sensitive to dim light • Cones are sensitive to bright light and colour. The Ear and Hearing The Ear and Balance • The semi-circular canals are three tubes , each at right angles to each other • When the head moves, cells in the canals pick up the movement of fluid in the canals and sends a message to the brain The Nervous System • The central nervous system (CNS) comprises the brain, spinal cord and nerves • Sense organs contain receptors that detect stimuli (changes in the environment) • The receptors send messages, called nerve impulses, along the nerves to the brain and spinal cord • The CNS sends nerve impulses to muscles to bring about movement Nerves • Nerves are made up of nerve cells or neurones • There are 3 types of neurone • Nerve impulses travel in only 1 direction • The fatty sheath acts as insulation and speeds up the impulse • A relay neurone connects the sensory and motor neurones The Reflex Arc • The flame is the stimulus • The heat sensor in the skin sends an impulse along the sensory neurone to the spinal cord (red) • The impulse is passed to the relay neurone in the spinal cord (green) • The impulse passes to the motor neurone which carries a message to the muscle (blue) • The muscle contracts to move the hand away from the heat • NOW the brain feels the pain • Damage to body tissues is avoided The Brain Exercise and Fatigue • When we run fast the muscles use up a lot of glucose for energy • If enough oxygen cannot get to the muscles they respire anaerobically • Lactic acid is produced instead of carbon dioxide and water • Lactic acid builds up in the muscle and causes a sore, burning feeling • Aerobic respiration glucose + oxygen →carbon dioxide + water + energy • Anaerobic respiration glucose → lactic acid + energy • After exercise the lactic acid is broken down to carbon dioxide and water • The volume of oxygen needed to break down the lactic acidis called the oxygen debt The Effects of Training • During exercise the pulse rate and breathing rate increase • The heart beats faster to carry more oxygen and glucose to the muscles • After exercise they return to normal, this is the recovery time • The recovery time can be used as an indication of a person’s fitness • A fit person has a shorter recovery time than an unfit person