12-2cut
... • Myelin sheaths speed impulse movement – like stadium with sections of empty seats. “Wave” jumps to next filled section – called saltatory conduction ...
... • Myelin sheaths speed impulse movement – like stadium with sections of empty seats. “Wave” jumps to next filled section – called saltatory conduction ...
Exam #2 Review Answers - Iowa State University
... a. Cornea, vitreous humor, lens, aqueous humor b. Lens, vitreous humor, cornea, aqueous humor c. Cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor d. Cornea, lens, aqueous humor, vitreous humor e. Lens, aqueous humor, cornea, vitreous humor ...
... a. Cornea, vitreous humor, lens, aqueous humor b. Lens, vitreous humor, cornea, aqueous humor c. Cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor d. Cornea, lens, aqueous humor, vitreous humor e. Lens, aqueous humor, cornea, vitreous humor ...
Biosychology_Intro Reading
... The somatic system is the part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for carrying sensory and motor information to and from the central nervous system. The somatic nervous system derives its name from the Greek word soma, which means "body." The somatic system is responsible for transmitting ...
... The somatic system is the part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for carrying sensory and motor information to and from the central nervous system. The somatic nervous system derives its name from the Greek word soma, which means "body." The somatic system is responsible for transmitting ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Myelin in the brain and spinal cord gets in the way of axon regeneration Interfering with myelin can aid axon repair and restore some function in rodents with spinal cord injuries. - a vaccine against myelin prompted axons regrowth and treated animals regained some movement in their hind legs ...
... Myelin in the brain and spinal cord gets in the way of axon regeneration Interfering with myelin can aid axon repair and restore some function in rodents with spinal cord injuries. - a vaccine against myelin prompted axons regrowth and treated animals regained some movement in their hind legs ...
Introduction to the Nervous System and Nerve Tissue
... Communication between neurons at a synaptic junction 1. Electrical Synapses: Communication via gap junctions between smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and some neurons of the CNS. Provide fast, synchronized, and two-way transmission of information. 2. Chemical Synapses: Communication via chemical neuro ...
... Communication between neurons at a synaptic junction 1. Electrical Synapses: Communication via gap junctions between smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and some neurons of the CNS. Provide fast, synchronized, and two-way transmission of information. 2. Chemical Synapses: Communication via chemical neuro ...
presentation
... n Vth=170mv, Refractory period =100ps n Constant PSP = 180mv n Gaussian PSP generates spikes with more timing reliable n Ion-channel variability is included (Gaussian) ...
... n Vth=170mv, Refractory period =100ps n Constant PSP = 180mv n Gaussian PSP generates spikes with more timing reliable n Ion-channel variability is included (Gaussian) ...
Ch03b
... shows the power of spreadsheets. • For example, suppose the cell B7 contains the value 8 and the cell C7 has the value 100. We can enter a value in another cell, say D8, to multiply cell B7 by C7. • The cell in D8 would then hold the formula: =B7*C7 which gives a value of 800. • If we change the val ...
... shows the power of spreadsheets. • For example, suppose the cell B7 contains the value 8 and the cell C7 has the value 100. We can enter a value in another cell, say D8, to multiply cell B7 by C7. • The cell in D8 would then hold the formula: =B7*C7 which gives a value of 800. • If we change the val ...
Is Neuronatin mRNA Dendritically localized in Hippocampal Neurons
... Synaptic plasticity is the capacity of neurons to alter the strength of their connections, and has been shown to occur in a synapse-specific fashion. Alterations in synaptic strength occur during late stages of brain development and in response to a variety of stimuli in the adult brain, including i ...
... Synaptic plasticity is the capacity of neurons to alter the strength of their connections, and has been shown to occur in a synapse-specific fashion. Alterations in synaptic strength occur during late stages of brain development and in response to a variety of stimuli in the adult brain, including i ...
steps in nerve impulse transmission
... II. Transmission Between Neurons Communication between neurons is accomplished by moving across a small gap called the synapse. ...
... II. Transmission Between Neurons Communication between neurons is accomplished by moving across a small gap called the synapse. ...
structure of the brain (cont.)
... PARTS OF THE NEURON (CONT.) • End bulbs or Terminal bulbs – located at extreme ends of the axon’s branches – miniature container that stores chemicals called neurotransmitters (used to communicate with neighboring cells) • Synapse – infinitely small space (20-30 billionths of a meter) – exists betw ...
... PARTS OF THE NEURON (CONT.) • End bulbs or Terminal bulbs – located at extreme ends of the axon’s branches – miniature container that stores chemicals called neurotransmitters (used to communicate with neighboring cells) • Synapse – infinitely small space (20-30 billionths of a meter) – exists betw ...
Introduction to the physiology of perception
... Transmission of Neural Impulses across the gap • An action potential is passed on to the next neuron through a synapse • A synapse is a process that releases neurotransmitters, chemicals stored in the synaptic vesicles (cavities) of the sending neuron • In a synapse, an action potential cause neurot ...
... Transmission of Neural Impulses across the gap • An action potential is passed on to the next neuron through a synapse • A synapse is a process that releases neurotransmitters, chemicals stored in the synaptic vesicles (cavities) of the sending neuron • In a synapse, an action potential cause neurot ...
Parts of the Neuron 45
... ferry outgoing messages to neighboring neurons across the synapse, a tiny gap that separates one neuron from another. Dendrites are treelike structures that project from the soma. Dendrites have receptor sites, or docking stations, that enable them to receive neurotransmitters released by neighborin ...
... ferry outgoing messages to neighboring neurons across the synapse, a tiny gap that separates one neuron from another. Dendrites are treelike structures that project from the soma. Dendrites have receptor sites, or docking stations, that enable them to receive neurotransmitters released by neighborin ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... c. The short section of nerve fiber between the axon hillock and the first glial cell is called the initial segment; the axon hillock plus initial segment constitute the trigger zone. Insight 12.2 Diseases of the Myelin Sheath D. Many nerve fibers in the CNS and PNS are unmyelinated, but in the PNS, ...
... c. The short section of nerve fiber between the axon hillock and the first glial cell is called the initial segment; the axon hillock plus initial segment constitute the trigger zone. Insight 12.2 Diseases of the Myelin Sheath D. Many nerve fibers in the CNS and PNS are unmyelinated, but in the PNS, ...
Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System
... Producing and sending electrochemical impulses. Releasing chemical messages Have a cell body, dendrites and axon. Cell body contains the nucleus Cell body is the ____________________ center and makes macromolecules Groups of cell bodies in CNS are called nuclei; in PNS are called ganglia Den ...
... Producing and sending electrochemical impulses. Releasing chemical messages Have a cell body, dendrites and axon. Cell body contains the nucleus Cell body is the ____________________ center and makes macromolecules Groups of cell bodies in CNS are called nuclei; in PNS are called ganglia Den ...
Nerve Impulse Transmission
... carry it toward the cell body, which contains the nucleus. • The axon carries the impulse from the cell body toward the synaptic knobs where it will be transferred to other neurons. ...
... carry it toward the cell body, which contains the nucleus. • The axon carries the impulse from the cell body toward the synaptic knobs where it will be transferred to other neurons. ...
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
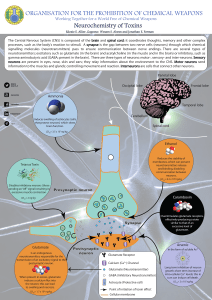
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... neurotransmitters are either Agonists or Antagonists. There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit ...
... neurotransmitters are either Agonists or Antagonists. There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit ...
lesson 6
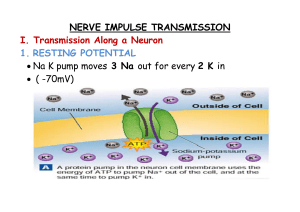
... ions “leak” down their concentration gradient - 3 Na+ ions are actively pumped out while 2 K+ ions are pumped in. ...
... ions “leak” down their concentration gradient - 3 Na+ ions are actively pumped out while 2 K+ ions are pumped in. ...
Nerve Tissue
... • a nerve signal can go no further when it reaches the end of the axon – triggers the release of a neurotransmitter – stimulates a new wave of electrical activity in the next cell across the ...
... • a nerve signal can go no further when it reaches the end of the axon – triggers the release of a neurotransmitter – stimulates a new wave of electrical activity in the next cell across the ...
Neurobiology of Consciousness Homework 1 Problem 1 Consider a
... The part of a neuron that transmits information over long distances is the: A) Soma B) Axon C) Dendrite D) Synapse Problem 11 Sensory neurons: A) Control muscles and produce movement B) Send messages away from the brain toward the periphery C) Gather information from the environment and convey it in ...
... The part of a neuron that transmits information over long distances is the: A) Soma B) Axon C) Dendrite D) Synapse Problem 11 Sensory neurons: A) Control muscles and produce movement B) Send messages away from the brain toward the periphery C) Gather information from the environment and convey it in ...
Take the 10-item multiple choice quiz to check
... (2) the muscle spindle is stretched (3) action potentials in sensory neurons of the muscle spindles increase (4) action potentials in alpha motor neurons of skeletal muscle fibers increase (5) skeletal muscle of the back contract a. b. c. d. e. ...
... (2) the muscle spindle is stretched (3) action potentials in sensory neurons of the muscle spindles increase (4) action potentials in alpha motor neurons of skeletal muscle fibers increase (5) skeletal muscle of the back contract a. b. c. d. e. ...
Simulation of myelinated neuron with focus on conduction speed
... Myelin sheath is a protective coat around the axon of a neuron and acts as an insulator to the electrical signal that is conducted down the axon as a neuron fires. This increases the conduction speed of action potential and thus is a critical factor in maintaining the proper communication within the ...
... Myelin sheath is a protective coat around the axon of a neuron and acts as an insulator to the electrical signal that is conducted down the axon as a neuron fires. This increases the conduction speed of action potential and thus is a critical factor in maintaining the proper communication within the ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.