Review
... Limbic system: involved in emotion and learning. Motivational area. Higher brain functions are mostly associated with what part of the brain? What is the best way to study which part of the brain is most active during a particular action? What structures are included in the peripheral nervous system ...
... Limbic system: involved in emotion and learning. Motivational area. Higher brain functions are mostly associated with what part of the brain? What is the best way to study which part of the brain is most active during a particular action? What structures are included in the peripheral nervous system ...
BIOLOGY II: CHAPTER 9: Neuromuscular Junction
... 3. Sodium ions, Na+ ,diffuse from their higher concentration (in the synaptic cleft) to their lower concentration (inside the muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of ...
... 3. Sodium ions, Na+ ,diffuse from their higher concentration (in the synaptic cleft) to their lower concentration (inside the muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of ...
Brain Function and Organization via Imaging
... Micro Anatomy: The Neuron Components: 1. Cell body (gray matter) 2. Dendrites 3. Axon (white matter – from myelin sheathes) Axons may be very long e.g. front to back of brain or length of spinal chord ...
... Micro Anatomy: The Neuron Components: 1. Cell body (gray matter) 2. Dendrites 3. Axon (white matter – from myelin sheathes) Axons may be very long e.g. front to back of brain or length of spinal chord ...
Axon - Cloudfront.net
... Only cells with excitable membranes (like muscle cells and neurons) can generate APs. ...
... Only cells with excitable membranes (like muscle cells and neurons) can generate APs. ...
Biological Bases of Behavior, Barron`s Neuroanatomy, pages 78
... - neurotransmitters fit reception sites on the dendrites of the next neuron - next neuron cells membrane becomes permeable and positive ions rush in - Action Potential – if charge spreads across the neuron 12. What is the All Or Nothing Principle? - Neurons fire completely or not at all. ( If dendri ...
... - neurotransmitters fit reception sites on the dendrites of the next neuron - next neuron cells membrane becomes permeable and positive ions rush in - Action Potential – if charge spreads across the neuron 12. What is the All Or Nothing Principle? - Neurons fire completely or not at all. ( If dendri ...
A1982NV42600001
... localized populations of nerve ceilsi, apparently no one had tried it in the brain. “About this time, Anita Hendrickson3 of the University of Washington was exploring the usefuln~sof axonal transport for studying the central connections of the retina at the electron microscope level. She and I began ...
... localized populations of nerve ceilsi, apparently no one had tried it in the brain. “About this time, Anita Hendrickson3 of the University of Washington was exploring the usefuln~sof axonal transport for studying the central connections of the retina at the electron microscope level. She and I began ...
Nervous System
... An analogy is a relationship between two pairs of terms or phrases written as a : b :: c : d. The symbol : is read as “is to,” and the symbol :: is read as “as.” In the space provided, write the letter of the pair of terms or phrases that best completes the analogy shown. ...
... An analogy is a relationship between two pairs of terms or phrases written as a : b :: c : d. The symbol : is read as “is to,” and the symbol :: is read as “as.” In the space provided, write the letter of the pair of terms or phrases that best completes the analogy shown. ...
A1987K582900002
... in the rat visual cortex. His findings utilized a combined Golgi electron-microscopic method that revealed valuable new information about the synaptic relationships of the local circuit neurons of the cerebral cortex. The results of my study showed that the basket plexus that surrounds virtually eve ...
... in the rat visual cortex. His findings utilized a combined Golgi electron-microscopic method that revealed valuable new information about the synaptic relationships of the local circuit neurons of the cerebral cortex. The results of my study showed that the basket plexus that surrounds virtually eve ...
Snímek 1
... Schwann cell proliferation → bands of Büngner (guide for regenerating axon) neural cell body: swelling, peripheral displacement of nucleus, central chromatolysis Axonal regeneration 1 week after injury regenerating axon (axonal sprout) grows along bands of Büngner, grow rate 12mm per day scar tissue ...
... Schwann cell proliferation → bands of Büngner (guide for regenerating axon) neural cell body: swelling, peripheral displacement of nucleus, central chromatolysis Axonal regeneration 1 week after injury regenerating axon (axonal sprout) grows along bands of Büngner, grow rate 12mm per day scar tissue ...
Module 6
... One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates by using hormones that travel through the blood system ...
... One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates by using hormones that travel through the blood system ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM GENERALITY – INTRODUCTION
... 3. Myelin is made of special cells called Schwann Cells that forms an insulated sheath, or wrapping around the axon. 4. There are SMALL NODES or GAPS called the Nodes of Ranvier between adjacent myelin sheath cells along the axon. 5. As an impulse moves down a myelinated (covered with myelin) axon, ...
... 3. Myelin is made of special cells called Schwann Cells that forms an insulated sheath, or wrapping around the axon. 4. There are SMALL NODES or GAPS called the Nodes of Ranvier between adjacent myelin sheath cells along the axon. 5. As an impulse moves down a myelinated (covered with myelin) axon, ...
Neuroscience
... Sensory Neurons: transmit info from receptor cells in sensory organs (i.e. nose, ears, tongue, eyes, and skin) and internal organs to brain. Motor Neurons: Transmit info from the brain to muscles. Interneurons: Communicate between sensory and motor neurons. ...
... Sensory Neurons: transmit info from receptor cells in sensory organs (i.e. nose, ears, tongue, eyes, and skin) and internal organs to brain. Motor Neurons: Transmit info from the brain to muscles. Interneurons: Communicate between sensory and motor neurons. ...
Ions in Your Life
... Electrical impulse created by flow of ions in and out cell down the axon (Ca+) triggers the release of synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters into synaptic gap/cleft. Neurotransmitters bind with specific channels on next neuron to start electrical impulse (flow of ions) down next neuron’s a ...
... Electrical impulse created by flow of ions in and out cell down the axon (Ca+) triggers the release of synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters into synaptic gap/cleft. Neurotransmitters bind with specific channels on next neuron to start electrical impulse (flow of ions) down next neuron’s a ...
Year 9 Biology Part B Revision Excretory System Name the organs
... Weakened or dead virus causes antibodies to be produced. Antibodies remain in your Body (memory cells). Therefore if your body is invaded by this virus then the immune System is able to respond quickly. ...
... Weakened or dead virus causes antibodies to be produced. Antibodies remain in your Body (memory cells). Therefore if your body is invaded by this virus then the immune System is able to respond quickly. ...
Chapters 11: Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous
... 1. AP in presynaptic neuron triggers ________ion channels in axon terminal to open 2. ____________ of calcium ions causes synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft 3. Neurotransmitters bind to ____________ on postsynaptic neuron 4. Ion channels open, leading to a local potent ...
... 1. AP in presynaptic neuron triggers ________ion channels in axon terminal to open 2. ____________ of calcium ions causes synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft 3. Neurotransmitters bind to ____________ on postsynaptic neuron 4. Ion channels open, leading to a local potent ...
Document
... • Cerebrum= The largest part of the brain; it is responsible for learning and other conscious mental functions. • Thalamus= A midbrain structure that plays a major role in relaying information from the various sensory receptors to other ...
... • Cerebrum= The largest part of the brain; it is responsible for learning and other conscious mental functions. • Thalamus= A midbrain structure that plays a major role in relaying information from the various sensory receptors to other ...
Slide ()
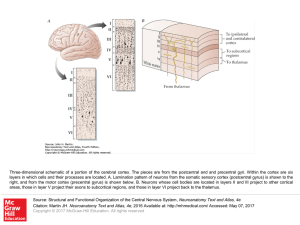
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
Communication and Control-The Nervous System chp 25-1
... • A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. • There are 3 parts to a neuron • Cell body • Dendrites: Information is received from other cells • Axon: Impulses are carried away from the cell body ...
... • A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. • There are 3 parts to a neuron • Cell body • Dendrites: Information is received from other cells • Axon: Impulses are carried away from the cell body ...
chapter the nervous system and the effects of drugs
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
Document
... • Myelin and Nodes of Ranvier speed the conduction • Pharmacology of voltage sensitive channels – Site of action of neurotoxic drugs (snake venom, scorpion toxins, plant alkaloids etc) – Site of action of local anesthetics (lidocaine) ...
... • Myelin and Nodes of Ranvier speed the conduction • Pharmacology of voltage sensitive channels – Site of action of neurotoxic drugs (snake venom, scorpion toxins, plant alkaloids etc) – Site of action of local anesthetics (lidocaine) ...
Neuro 16 Neurotransmitters Student
... GABAergic neurons of caudate nucleus and putamen project to substantia nigra and globus pallidus. Reduced concentrations in patients with Huntington’s chorea: ...
... GABAergic neurons of caudate nucleus and putamen project to substantia nigra and globus pallidus. Reduced concentrations in patients with Huntington’s chorea: ...
1 - optometrie.ch
... machinery (organelles) in the cell body, which produce axoplasm One of the important basic science concepts is understanding that axoplasmic flow is a dynamic process; and that when it stops, the axon dies. This is because the axon has little machinery (organelles) to make molecules that the axon re ...
... machinery (organelles) in the cell body, which produce axoplasm One of the important basic science concepts is understanding that axoplasmic flow is a dynamic process; and that when it stops, the axon dies. This is because the axon has little machinery (organelles) to make molecules that the axon re ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.