Contribution of Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Neurons to
... cerebellar peduncle, and reached PPTN. PPTN was located 3–5 mm lateral from midline and 3–7 mm deeper than where auditory responses were observed. We recorded single units in that location and confirmed high-frequency tonic fiber activity (⬎20 Hz) within 3–5 mm from single units, since PPTN is close ...
... cerebellar peduncle, and reached PPTN. PPTN was located 3–5 mm lateral from midline and 3–7 mm deeper than where auditory responses were observed. We recorded single units in that location and confirmed high-frequency tonic fiber activity (⬎20 Hz) within 3–5 mm from single units, since PPTN is close ...
FREE Sample Here
... 6. In a neuron, the axon _______________________, and the dendrite ___________________________. a. synthesizes neurotransmitters; receives signals from other neurons b. conducts information to other neurons; generates action potentials c. generates action potentials; receives signals from other neur ...
... 6. In a neuron, the axon _______________________, and the dendrite ___________________________. a. synthesizes neurotransmitters; receives signals from other neurons b. conducts information to other neurons; generates action potentials c. generates action potentials; receives signals from other neur ...
the inferior colliculus of the rat: quantitative
... 0 and 255 correspond to white and black colors, respectively. The camera was connected to a Macintosh computer via a video digitizing card (Scion Corporation). Images were digitized and analyzed using Scion NIH Image software. In an attempt to preserve identical illumination conditions for different ...
... 0 and 255 correspond to white and black colors, respectively. The camera was connected to a Macintosh computer via a video digitizing card (Scion Corporation). Images were digitized and analyzed using Scion NIH Image software. In an attempt to preserve identical illumination conditions for different ...
Chapter 7
... Transmission of a Signal at Synapses Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve ...
... Transmission of a Signal at Synapses Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve ...
Neuronal Correlates for Preparatory Set Associated with Pro
... Electrophysiolog y. All experimental procedures were in accordance with the C anadian Council on Animal C are policy on the use and care of laboratory animals and approved by the Queen’s University Animal C are Committee. Surgical, electrophysiological, and data acquisition methods were described pr ...
... Electrophysiolog y. All experimental procedures were in accordance with the C anadian Council on Animal C are policy on the use and care of laboratory animals and approved by the Queen’s University Animal C are Committee. Surgical, electrophysiological, and data acquisition methods were described pr ...
Representation of Behavioral Tactics and Tactics
... cue onset, epoch 2 beginning 150 ms before Figure 4. A–C, Tactics-selective activity of a pmPFC neuron preferentially observed during the delay and response period of and ending 150 ms after the hold release, and tactics-only cued trials. Data plots and display formats are the same as in Figure 3. C ...
... cue onset, epoch 2 beginning 150 ms before Figure 4. A–C, Tactics-selective activity of a pmPFC neuron preferentially observed during the delay and response period of and ending 150 ms after the hold release, and tactics-only cued trials. Data plots and display formats are the same as in Figure 3. C ...
f729d19364fe6b8
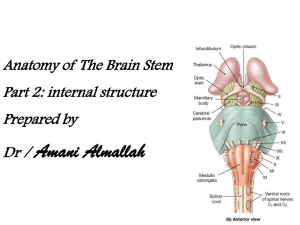
... it is large & composed of transverse fibers, longitudinal bundles & pontine nuclei. 1- The longituidinal bundles are: A- Corticospinal (pyramidal) tract: separated by transverse pontine fibers & collected inferiorly to form pyramid in medulla. B- Corticopontine fibers: end in pontine nuclei. II- Tra ...
... it is large & composed of transverse fibers, longitudinal bundles & pontine nuclei. 1- The longituidinal bundles are: A- Corticospinal (pyramidal) tract: separated by transverse pontine fibers & collected inferiorly to form pyramid in medulla. B- Corticopontine fibers: end in pontine nuclei. II- Tra ...
Short title: Thalamocortical computations during tactile sensation
... (from FS neurons) to L4 excitatory neurons is delayed by approximately 0.5 ms with respect to ...
... (from FS neurons) to L4 excitatory neurons is delayed by approximately 0.5 ms with respect to ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... dendrites of neurons in the nucleus laminaris of the chick brainstem were cut. This elimination of excitatory input by deafferentation causes retraction of the ventral dendrites whereas the dorsal dendrites, which retain innervation, remain unchanged (Benes et al., 1977; Deitch and Rubel, 1984). The ...
... dendrites of neurons in the nucleus laminaris of the chick brainstem were cut. This elimination of excitatory input by deafferentation causes retraction of the ventral dendrites whereas the dorsal dendrites, which retain innervation, remain unchanged (Benes et al., 1977; Deitch and Rubel, 1984). The ...
Discharge Rate of Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata Neurons Is
... injection, in 1-s bins, filtered with a 20-s Gaussian. The rate and SD in the first 30 s were used as a reference. First, the earliest time the rate deviated by ⬎3 SD from the reference was detected. Then the latest time there was a deviation of ⬎1 SD from the reference, occurring earlier than the 3 ...
... injection, in 1-s bins, filtered with a 20-s Gaussian. The rate and SD in the first 30 s were used as a reference. First, the earliest time the rate deviated by ⬎3 SD from the reference was detected. Then the latest time there was a deviation of ⬎1 SD from the reference, occurring earlier than the 3 ...
Potassium Currents Responsible for Inward and Outward
... in response to hyperpolarizing voltage ramps (Jiang and North, 1991). Thus, these data suggest that I,,, is responsible for inward rectification and contributes to the resting potential of spiny projection neurons. The outward rectification of neostriatal spiny neurons is postulated to depend upon s ...
... in response to hyperpolarizing voltage ramps (Jiang and North, 1991). Thus, these data suggest that I,,, is responsible for inward rectification and contributes to the resting potential of spiny projection neurons. The outward rectification of neostriatal spiny neurons is postulated to depend upon s ...
A Model of Surround Suppression Through Cortical Feedback
... All five V1 regions send feedforward projections to the V2 region. The feedforward projections originate from the V1 neurons and terminate on both excitatory and inhibitory neurons within the V2 region. The output weights extending from one V1 neuron take on a Gaussian pattern which is identical for ...
... All five V1 regions send feedforward projections to the V2 region. The feedforward projections originate from the V1 neurons and terminate on both excitatory and inhibitory neurons within the V2 region. The output weights extending from one V1 neuron take on a Gaussian pattern which is identical for ...
Simulating Populations of Neurons - Leeds VLE
... advances we have made over the last 100 years have allowed us to now consider processes on an individual level and use computational techniques to be able to simulate them. This project considers the paper Stable propagation of synchronous spiking in cortical neural networks (Diesmann, Gewaltig, & A ...
... advances we have made over the last 100 years have allowed us to now consider processes on an individual level and use computational techniques to be able to simulate them. This project considers the paper Stable propagation of synchronous spiking in cortical neural networks (Diesmann, Gewaltig, & A ...
Hybrid Scheme for Modeling Local Field Potentials from Point
... conservation, the sum of all transmembrane currents, including all ionic and capacitive currents, must be zero for each neuron. In a point-neuron model, all transmembrane currents are collapsed in a single point in space. The net transmembrane current, and hence the extracellular potential, therefor ...
... conservation, the sum of all transmembrane currents, including all ionic and capacitive currents, must be zero for each neuron. In a point-neuron model, all transmembrane currents are collapsed in a single point in space. The net transmembrane current, and hence the extracellular potential, therefor ...
166 - UCSF Physiology - University of California, San Francisco
... MgCl2, 26 NaHCO3, 1.25 KH2PO4, 10 glucose, and 2 ascorbic acid, pH 7.4. The perfusion rate was 15 ml/h. The field EPSPs (fEPSPs) were evoked in the CA1 stratum radiatum by stimulating the Schaffer– commissural field with twisted bipolar nichrome electrodes and were recorded with ACSF-filled glass pi ...
... MgCl2, 26 NaHCO3, 1.25 KH2PO4, 10 glucose, and 2 ascorbic acid, pH 7.4. The perfusion rate was 15 ml/h. The field EPSPs (fEPSPs) were evoked in the CA1 stratum radiatum by stimulating the Schaffer– commissural field with twisted bipolar nichrome electrodes and were recorded with ACSF-filled glass pi ...
propofol alters vesicular transport in rat cortical neuronal cultures
... Fig. 1. Propofol induces retrograde vesicle movement and increase vesicular velocity in neurons. (A) A neuron in Ca2+-containing medium (CCM) is shown 5 minutes (time -5) before exposure to propofol in a differential interference contrast image, with the cell body to the left and a branched neurite ...
... Fig. 1. Propofol induces retrograde vesicle movement and increase vesicular velocity in neurons. (A) A neuron in Ca2+-containing medium (CCM) is shown 5 minutes (time -5) before exposure to propofol in a differential interference contrast image, with the cell body to the left and a branched neurite ...
PDF Document
... Fig. 1. Challenges of optogenetically targeting cells outside of the brain. (A) Wide variations in ex- Strategies that use gene therapy viral vecpression of opsin proteins, tissue structure, and the mechanical environment of the peripheral nervous sys- tors to deliver DNA are more tractable tem may ...
... Fig. 1. Challenges of optogenetically targeting cells outside of the brain. (A) Wide variations in ex- Strategies that use gene therapy viral vecpression of opsin proteins, tissue structure, and the mechanical environment of the peripheral nervous sys- tors to deliver DNA are more tractable tem may ...
Rostral Fastigial Nucleus Activity in the Alert Monkey During Three
... different orientations 157 apart (including roll, pitch, vertical canal plane and intermediate planes). In addition, sinusoidal rotations around an earth-vertical axis (yaw stimulus) included different roll and pitch positions ( {107, {207 ). The latter positions were also used for static stimulatio ...
... different orientations 157 apart (including roll, pitch, vertical canal plane and intermediate planes). In addition, sinusoidal rotations around an earth-vertical axis (yaw stimulus) included different roll and pitch positions ( {107, {207 ). The latter positions were also used for static stimulatio ...
Glycolytic Enzymes Localize to Synapses under Energy Stress to
... 278 Neuron 90, 278–291, April 20, 2016 ª2016 Elsevier Inc. ...
... 278 Neuron 90, 278–291, April 20, 2016 ª2016 Elsevier Inc. ...
Changes in Intracellular pH Associated with Glutamate Excitotoxicity
... However, other experiments have questioned the sole involvement of calcium, sinceneuronal death can occur without large deviations in [Ca*+], and high potassium or cyanide induced increasesin [Ca*+], do not produce toxicity (Michaels and Rothman, 1990; Dubinsky and Rothman, 1991). Intracellular acid ...
... However, other experiments have questioned the sole involvement of calcium, sinceneuronal death can occur without large deviations in [Ca*+], and high potassium or cyanide induced increasesin [Ca*+], do not produce toxicity (Michaels and Rothman, 1990; Dubinsky and Rothman, 1991). Intracellular acid ...
Choice Coding in Frontal Cortex during Stimulus
... choices, the animal may learn to make a specific response when a specific pair of pictures is presented (a stimulus–response association). Reward-predictive neural activity could then reflect an AO association, indicating knowledge of the reward that is associated with that response. A second proble ...
... choices, the animal may learn to make a specific response when a specific pair of pictures is presented (a stimulus–response association). Reward-predictive neural activity could then reflect an AO association, indicating knowledge of the reward that is associated with that response. A second proble ...
THE REGULATION OF SLEEP AND WAKEFULNESS BY THE
... reduced and that orexin peptide levels are decreased to undetectable levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of narcoleptic patients4-6). Orexin/ataxin-3 mice are a well-studied model for narcolepsy; however, orexin neurons are absent from birth in orexin/ataxin-3 mice. Therefore, other neuronal mechanism ...
... reduced and that orexin peptide levels are decreased to undetectable levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of narcoleptic patients4-6). Orexin/ataxin-3 mice are a well-studied model for narcolepsy; however, orexin neurons are absent from birth in orexin/ataxin-3 mice. Therefore, other neuronal mechanism ...
Early Appearance of Inhibitory Input to the MNTB Supports Binaural
... immaturities that limit auditory processing in juvenile animals, they are able to lateralize sounds using binaural cues. This study explores a central mechanism that may compensate for these limitations during development. Interaural time and level difference processing by neurons in the superior ol ...
... immaturities that limit auditory processing in juvenile animals, they are able to lateralize sounds using binaural cues. This study explores a central mechanism that may compensate for these limitations during development. Interaural time and level difference processing by neurons in the superior ol ...
Rapid Taste Responses in the Gustatory Cortex during Licking
... were chosen to approximately match previous electrophysiological studies (Plata-Salaman et al., 1995; Katz et al., 2001, 2002). All chemicals were obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO) and were reagent grade. In addition to being used as a rinse, water was also considered to be a tastant (de Araujo et ...
... were chosen to approximately match previous electrophysiological studies (Plata-Salaman et al., 1995; Katz et al., 2001, 2002). All chemicals were obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO) and were reagent grade. In addition to being used as a rinse, water was also considered to be a tastant (de Araujo et ...
Cilia development, morphogenesis, and
... "'G?#(*8J iltrastructure of C. elegans cilia. 2a. Cilia in the amphid sensillum exhibit a variety of morphologies. The rod-like channel cilia are found in XS`, XSG, XSH, XSI, XSh, XSK, XDF, and XDL neurons. XDF and XDL possess two cilia each, while the other cells possess a single cilium. These cili ...
... "'G?#(*8J iltrastructure of C. elegans cilia. 2a. Cilia in the amphid sensillum exhibit a variety of morphologies. The rod-like channel cilia are found in XS`, XSG, XSH, XSI, XSh, XSK, XDF, and XDL neurons. XDF and XDL possess two cilia each, while the other cells possess a single cilium. These cili ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.