Aspects of mathematics and music in Ancient Greece
... coincides with the usual major type scale of western music and that two similar tetrachords (tone-tonelimma) are formed. Secondly, that the scale construction is based only on tone (~204 cents) and limma (~90 cents), which actually means that the difference between the ‘small’ step (~ semitone) and ...
... coincides with the usual major type scale of western music and that two similar tetrachords (tone-tonelimma) are formed. Secondly, that the scale construction is based only on tone (~204 cents) and limma (~90 cents), which actually means that the difference between the ‘small’ step (~ semitone) and ...
supplementaryMaterial_08Dec15
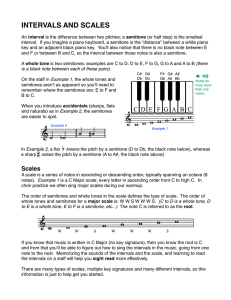
... piano, beginning on C, form a Major scale (C, D, E, F, G, A, B, C). The scale degrees form a hierarchy of stability (the tonal hierarchy), enabling notes to be used for different structural purposes throughout a musical piece (e.g., highly stable notes are more likely to occur at boundaries than uns ...
... piano, beginning on C, form a Major scale (C, D, E, F, G, A, B, C). The scale degrees form a hierarchy of stability (the tonal hierarchy), enabling notes to be used for different structural purposes throughout a musical piece (e.g., highly stable notes are more likely to occur at boundaries than uns ...
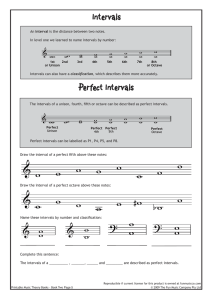
Intervals Perfect Intervals
... Intervals An Interval is the distance between two notes. In level one we learned to name intervals by number: ...
... Intervals An Interval is the distance between two notes. In level one we learned to name intervals by number: ...
Unit 3 – Scales, Keys & Modes
... Scale Degree Names In Minor scales – these terms may change slightly. (RAISED SUBMEDIANT and SUBTONIC) Certain pitches in the scale sound stronger or more stable than others. Scale degrees 4, 6, and 7 are ACTIVE TONES. Scale degrees 1 and 3 are considered RESOLUTION TONES because they are the notes ...
... Scale Degree Names In Minor scales – these terms may change slightly. (RAISED SUBMEDIANT and SUBTONIC) Certain pitches in the scale sound stronger or more stable than others. Scale degrees 4, 6, and 7 are ACTIVE TONES. Scale degrees 1 and 3 are considered RESOLUTION TONES because they are the notes ...
Diatonic Autoharps Explained
... The big advantage is that since there are no accidentals, you have strings ‘left over’. These extra strings are doubled with the notes in the seven-tone scale. Except for the bass and the very high notes, there are many notes which will have doubled strings. The sound of an acoustic diatonic autohar ...
... The big advantage is that since there are no accidentals, you have strings ‘left over’. These extra strings are doubled with the notes in the seven-tone scale. Except for the bass and the very high notes, there are many notes which will have doubled strings. The sound of an acoustic diatonic autohar ...
Artistic Song Leading (Lesson 7)
... The major scale consists of seven different pitches. There are half steps between the third and fourth and seventh and eighth scale degrees; whole steps exist between all other steps. Below is the C major scale. The pattern of whole and half steps is the same for all major scales. The Shape of the n ...
... The major scale consists of seven different pitches. There are half steps between the third and fourth and seventh and eighth scale degrees; whole steps exist between all other steps. Below is the C major scale. The pattern of whole and half steps is the same for all major scales. The Shape of the n ...
van tech music
... It is important to note that when written in text, we say the pitch name first, followed by the accidental (i.e. B-flat or F-sharp). However, when written on the staff, the accidental will always appear before the actual note. (i.e. ♭♩) C: Clefs - Each pitch has a place on the staff. A staff must in ...
... It is important to note that when written in text, we say the pitch name first, followed by the accidental (i.e. B-flat or F-sharp). However, when written on the staff, the accidental will always appear before the actual note. (i.e. ♭♩) C: Clefs - Each pitch has a place on the staff. A staff must in ...
History of Music Theory - Totally Ratted Limited
... device called the Monochord (which literally means “one string”) by his student Philolaus. This was a single stringed instrument with a moveable bridge and by positioning the bridge in different positions it was possible to play different notes on the string. His reported aim in his analysis of the ...
... device called the Monochord (which literally means “one string”) by his student Philolaus. This was a single stringed instrument with a moveable bridge and by positioning the bridge in different positions it was possible to play different notes on the string. His reported aim in his analysis of the ...
as a PDF
... Stabilizers (s) combine with foundation and active tones to produce complete triads. Most of the time they are inert, but sometimes they may also act like dissonances in terms of how they need to be resolved. Chordal dissonances (cd) are notes that clash mildly with the current harmonic function, ev ...
... Stabilizers (s) combine with foundation and active tones to produce complete triads. Most of the time they are inert, but sometimes they may also act like dissonances in terms of how they need to be resolved. Chordal dissonances (cd) are notes that clash mildly with the current harmonic function, ev ...
Tuning, Tonality, and 22
... fact that 12-equal is not the historical basis for the diatonic scale; in fact the converse is true, and 12equal was chosen over other meantone tunings only for convenience. Balzano focuses on certain grouptheoretical properties of 12-equal and of the diatonic scales within it. For example, his view ...
... fact that 12-equal is not the historical basis for the diatonic scale; in fact the converse is true, and 12equal was chosen over other meantone tunings only for convenience. Balzano focuses on certain grouptheoretical properties of 12-equal and of the diatonic scales within it. For example, his view ...
A Non-Pythagorean Musical Scale Based on Logarithms
... Difference tones and ideas for future compositions A beat frequency is a frequency defined as the absolute difference between two pitches sounded simultaneously; when this frequency is in the audible range and is perceived as a distinct pitch, it is called a difference tone. While audible beat frequ ...
... Difference tones and ideas for future compositions A beat frequency is a frequency defined as the absolute difference between two pitches sounded simultaneously; when this frequency is in the audible range and is perceived as a distinct pitch, it is called a difference tone. While audible beat frequ ...
Kamavardhini and the Blues scale – just one step and one note
... Since the ascend and descend notes are the same, we will examine just the ascend. ...
... Since the ascend and descend notes are the same, we will examine just the ascend. ...
A GUIDE TO THE TERMINOLOGY OF GERMAN HARMONY
... Riemann. The name of each secondary triad connects it with a primary triad, and so with one of Riemann’s three functional categories. The relationship supporting this connection, what the Germans call the “parallel” relation, is known in English as the “relative” relation: the association of major a ...
... Riemann. The name of each secondary triad connects it with a primary triad, and so with one of Riemann’s three functional categories. The relationship supporting this connection, what the Germans call the “parallel” relation, is known in English as the “relative” relation: the association of major a ...
class9#
... Consider the behavior of G# and Ab (same music-level pitch in C major. G# will be usually part of a transposition to A major (A) or A minor (Am), so it will function as a leading tone to A. Ab will probably be part of a modulation to Fm or Eb. it will go down to G. Ab and G# are not part of C, so th ...
... Consider the behavior of G# and Ab (same music-level pitch in C major. G# will be usually part of a transposition to A major (A) or A minor (Am), so it will function as a leading tone to A. Ab will probably be part of a modulation to Fm or Eb. it will go down to G. Ab and G# are not part of C, so th ...
SCALES and ORNAMENTS ~ Higher Level
... entirely on whole tones. Debussy used the whole-tone scale in some of his pieces which were influenced by Impressionism. ...
... entirely on whole tones. Debussy used the whole-tone scale in some of his pieces which were influenced by Impressionism. ...
w - Music at Hopkins
... MakeMusic grants permission to duplicate this worksheet for non-profit, educational use only, provided each copy includes this copyright notice. Copies may not be sold or included in any materials offered for sale to the general public. ...
... MakeMusic grants permission to duplicate this worksheet for non-profit, educational use only, provided each copy includes this copyright notice. Copies may not be sold or included in any materials offered for sale to the general public. ...
Chapter 1 summary
... a. note tied only to a note of equal or next-shorter value b. quarter rests not used c. eighth notes only occur on second half of beat and always in pairs (4/2 meter) d. pieces usually begin with a value of at least a dotted half note; more common is the whole note or breve e. final note is at least ...
... a. note tied only to a note of equal or next-shorter value b. quarter rests not used c. eighth notes only occur on second half of beat and always in pairs (4/2 meter) d. pieces usually begin with a value of at least a dotted half note; more common is the whole note or breve e. final note is at least ...
Minor Thirds
... feels happy or sad, depending on where you place the semitones. Pythagorean tuning is quite a clever method, and is indeed fundamental to modern music. ...
... feels happy or sad, depending on where you place the semitones. Pythagorean tuning is quite a clever method, and is indeed fundamental to modern music. ...
12_6_Deeper_Reading_Scales_and_Tuning
... In general, the 3/2 ratio of fundamental frequencies results in the best possible harmonic agreement between tones with different pitches. Therefore, tone pairs separated by musical intervals of perfect fifths will sound as harmonious as different pitches ever can sound. We can therefore identify a ...
... In general, the 3/2 ratio of fundamental frequencies results in the best possible harmonic agreement between tones with different pitches. Therefore, tone pairs separated by musical intervals of perfect fifths will sound as harmonious as different pitches ever can sound. We can therefore identify a ...
Musical Scales and Tuning
... In general, the 3/2 ratio of fundamental frequencies results in the best possible harmonic agreement between tones with different pitches. Therefore, tone pairs separated by musical intervals of perfect fifths will sound as harmonious as different pitches ever can sound. We can therefore identify a ...
... In general, the 3/2 ratio of fundamental frequencies results in the best possible harmonic agreement between tones with different pitches. Therefore, tone pairs separated by musical intervals of perfect fifths will sound as harmonious as different pitches ever can sound. We can therefore identify a ...
Music 181: Inversions of Intervals, Compound Intervals
... II. Compound intervals Any interval larger than an octave (8va) is a compound interval; intervals smaller than an octave are called simple intervals. Any compound interval can be reduced to a simple interval; in most musical contexts the compound interval and its simple counterpart are functionally ...
... II. Compound intervals Any interval larger than an octave (8va) is a compound interval; intervals smaller than an octave are called simple intervals. Any compound interval can be reduced to a simple interval; in most musical contexts the compound interval and its simple counterpart are functionally ...
Mode (music)

In the theory of Western music, mode (from Latin modus, ""measure, standard, manner, way, size, limit of quantity, method"") (Powers 2001, Introduction; OED) generally refers to a type of scale, coupled with a set of characteristic melodic behaviours. This use, still the most common in recent years, reflects a tradition dating to the Middle Ages, itself inspired by the theory of ancient Greek music.