rudiments of music
... 41. Scales may start from any note, but the use of sharps Dr fiats will be necessary in all Scales except C major, so. as to. obtain the correct order of Tones and Semitones. Majo.r and Mino.r Scales are called Diatonic because each successive note is different in name. The Chromatic Scale is so. ca ...
... 41. Scales may start from any note, but the use of sharps Dr fiats will be necessary in all Scales except C major, so. as to. obtain the correct order of Tones and Semitones. Majo.r and Mino.r Scales are called Diatonic because each successive note is different in name. The Chromatic Scale is so. ca ...
Music K-8 - Aspen Academy
... Peter and the Wolf- Prokofiev Hansel and Gretel – Humperdinck The Sorcerer’s Apprentice- Dukas The Nutcracker- Tchaikovsky ...
... Peter and the Wolf- Prokofiev Hansel and Gretel – Humperdinck The Sorcerer’s Apprentice- Dukas The Nutcracker- Tchaikovsky ...
Read More About Melody - Seycove Music Composition
... A melody is a sequence of notes or pitches, one after the other, which create the “tune” of a piece. Most times, when you sing a song, you are singing its melody. ...
... A melody is a sequence of notes or pitches, one after the other, which create the “tune” of a piece. Most times, when you sing a song, you are singing its melody. ...
file here.
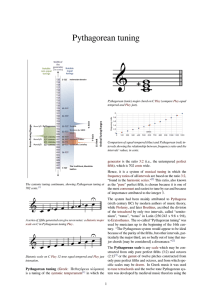
... (3:2)4 give us the next ascending perfect fifth (in our example, from “A” up to “E”), which works out to 81:16. But to find this pitch within our original “C” to “C” octave we must reduce it. When we reduced (3:2)2 to find our major second we reduced it by one octave, or 2:1. But here we must bring ...
... (3:2)4 give us the next ascending perfect fifth (in our example, from “A” up to “E”), which works out to 81:16. But to find this pitch within our original “C” to “C” octave we must reduce it. When we reduced (3:2)2 to find our major second we reduced it by one octave, or 2:1. But here we must bring ...
Quia Tier 4 powerpoint from class
... What solfege syllable is a second above DO? What solfege syllable is a third above DO? What solfege syllable is a fourth above DO? ...
... What solfege syllable is a second above DO? What solfege syllable is a third above DO? What solfege syllable is a fourth above DO? ...
Beethoven Septet in Eb, mvt
... The harmony is largely diatonic and triadic, and there are clear perfect cadences, e.g. b.4 But: This is 20th century music, and Poulenc has a distinctive take on traditional harmony, derived in part from Stravinsky’s Neo-Classical scores such as Pulcinella (Anthology p.139) in which standard chords ...
... The harmony is largely diatonic and triadic, and there are clear perfect cadences, e.g. b.4 But: This is 20th century music, and Poulenc has a distinctive take on traditional harmony, derived in part from Stravinsky’s Neo-Classical scores such as Pulcinella (Anthology p.139) in which standard chords ...
Write like Mozart – lecture notes Table of Contents
... Analysis: Beethoven's bagatelle, op. 119 #1......................................................................................53 Harmonic analysis of the first and third phrases............................................................................54 Harmonic analysis of the second phrase... ...
... Analysis: Beethoven's bagatelle, op. 119 #1......................................................................................53 Harmonic analysis of the first and third phrases............................................................................54 Harmonic analysis of the second phrase... ...
Musical_language
... All sound can be described using a few basic adjectives: • Pitch: high or low • Volume: loud or soft • Texture: thick or thin • Speed: fast or slow ...
... All sound can be described using a few basic adjectives: • Pitch: high or low • Volume: loud or soft • Texture: thick or thin • Speed: fast or slow ...
投影片 1
... Whether the piece employs articulation/ bowing markings (i.e. slurs), and performing techniques (e.g., pizz.) As string instruments cover wide pitch ranges, a piece shall avoid focusing only on a narrow tessitura of the instrument ...
... Whether the piece employs articulation/ bowing markings (i.e. slurs), and performing techniques (e.g., pizz.) As string instruments cover wide pitch ranges, a piece shall avoid focusing only on a narrow tessitura of the instrument ...
0410 music - PastPapers.Co
... between string instruments/violins [1] and the arpeggios are played by flutes [1]. The melody is also accompanied homophonically [1]. There is a pizzicato bass line/walking/scalic bass line [1]; bassoon [1]. Cymbal crash on the last beat [1] ...
... between string instruments/violins [1] and the arpeggios are played by flutes [1]. The melody is also accompanied homophonically [1]. There is a pizzicato bass line/walking/scalic bass line [1]; bassoon [1]. Cymbal crash on the last beat [1] ...
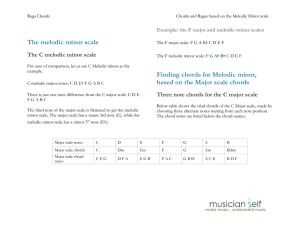
Chords and Ragas based on the Melodic minor scale
... interval. This mode, the 3rd mode of the Melodic minor scale can be called the Lydian augmented scale because it has the notes of the Lydian scale, with the 5th note sharpened or augmented. (Remember the augmented chord: the 5th note sharpened from the major chord.) Since a Pa note is absent and two ...
... interval. This mode, the 3rd mode of the Melodic minor scale can be called the Lydian augmented scale because it has the notes of the Lydian scale, with the 5th note sharpened or augmented. (Remember the augmented chord: the 5th note sharpened from the major chord.) Since a Pa note is absent and two ...
Chinese theories of music
... Greek philosopher Pythagoras who lived during the same period. The first frequency of the system was called Huangzhong “Yellow Bell” which served as the primal generator of the whole series of twelve. Various methods were employed to determine this all important first pitch, from listening to birds, ...
... Greek philosopher Pythagoras who lived during the same period. The first frequency of the system was called Huangzhong “Yellow Bell” which served as the primal generator of the whole series of twelve. Various methods were employed to determine this all important first pitch, from listening to birds, ...
VAN TECH MUSIC THEORY Package – IA
... A triad is a collection of three pitches played simultaneously (harmonic triad) or in sequence (melodic triad). A Major triad is comprised of the first, third and fifth scale degrees. We call this “spelling a chord”. Triads can also be called chords and are used by composers to add musical interest ...
... A triad is a collection of three pitches played simultaneously (harmonic triad) or in sequence (melodic triad). A Major triad is comprised of the first, third and fifth scale degrees. We call this “spelling a chord”. Triads can also be called chords and are used by composers to add musical interest ...
File - Melissa Hayes
... (about 1600) until the breakdown of tonal harmony at the end of the Romantic period (1900). It continued to be used by some composers after this period. The major scale is made up of eight notes. These are each given a scale degree number. Below is an example of a C major scale. Below each note is i ...
... (about 1600) until the breakdown of tonal harmony at the end of the Romantic period (1900). It continued to be used by some composers after this period. The major scale is made up of eight notes. These are each given a scale degree number. Below is an example of a C major scale. Below each note is i ...
Music Theory 101
... consistently played one 1/2 step higher or lower than the equivalent natural notes. Key signatures are generally written immediately after the clef at the beginning of a line A key signature will have either sharps or flats, but there will not be any key signatures with both. To determine the key ba ...
... consistently played one 1/2 step higher or lower than the equivalent natural notes. Key signatures are generally written immediately after the clef at the beginning of a line A key signature will have either sharps or flats, but there will not be any key signatures with both. To determine the key ba ...
Impressionism
... •Use of whole-tone scale 1. Six (6) notes per octave 2. Symmetrical Scale 3. Lack of Leading-Tone Effect 4. Lack of strong dissonance ...
... •Use of whole-tone scale 1. Six (6) notes per octave 2. Symmetrical Scale 3. Lack of Leading-Tone Effect 4. Lack of strong dissonance ...
TALKING TO YOUR RHYTHM SECTION Chris Sharp, Ph.D. FMEA
... established ones) do not provide enough information for your drummer, particularly if they are not versed in a variety of styles! However, there are some general guidelines to which the majority do adhere. For notes on the snare, toms, and bass drum, standard note heads are usually used; cymbals ...
... established ones) do not provide enough information for your drummer, particularly if they are not versed in a variety of styles! However, there are some general guidelines to which the majority do adhere. For notes on the snare, toms, and bass drum, standard note heads are usually used; cymbals ...
Melody - Some Basics
... usually defines itself by resting or holding or coming to some point of resolution (rhythmically and/or tonally) and, especially in vocal music, is directly related to the natural areas to breathe. Short phrases usually group together to form a longer phrase. In the following example, phrase 1 and p ...
... usually defines itself by resting or holding or coming to some point of resolution (rhythmically and/or tonally) and, especially in vocal music, is directly related to the natural areas to breathe. Short phrases usually group together to form a longer phrase. In the following example, phrase 1 and p ...
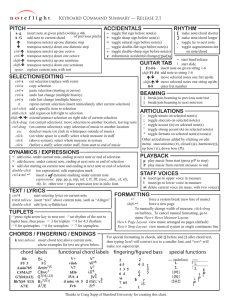
Keyboard Command Summary
... p play music from start (press p/P to stop) P play music from current measure to end ...
... p play music from start (press p/P to stop) P play music from current measure to end ...
Scales and Temperament - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... 12-tone equal temperament is special in that it is the smallest division of the octave that does a reasonable job of approximating the just intervals we like to hear ...
... 12-tone equal temperament is special in that it is the smallest division of the octave that does a reasonable job of approximating the just intervals we like to hear ...
ATTAINMENT TARGET
... b) play a steady G major scale & arpeggio a) understand repeat signs b) understand 3/4 time c) understand slurs d) read notes learned so far ...
... b) play a steady G major scale & arpeggio a) understand repeat signs b) understand 3/4 time c) understand slurs d) read notes learned so far ...
Jeffrey Perry
... the same register. In the latter passage, however, F# and Fq are not major and minor chordal thirds of the local "tonic," but rather an accented passing tone (part of the cadential six-four that adumbrates D major) and the third of a dissonant seventh chord, respectively. This use of register and te ...
... the same register. In the latter passage, however, F# and Fq are not major and minor chordal thirds of the local "tonic," but rather an accented passing tone (part of the cadential six-four that adumbrates D major) and the third of a dissonant seventh chord, respectively. This use of register and te ...
Notation
... They are used when a sharped or flatted note is followed by a “normal” version of the same note (Bar lines automatically cancel added sharps or flats) ...
... They are used when a sharped or flatted note is followed by a “normal” version of the same note (Bar lines automatically cancel added sharps or flats) ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.