Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
... heart, in order to “reset” the heart rhythm • ICD’s have been proven to be an effective way in prevention of death, brain damage, and other complications associated with these heart conditions ...
... heart, in order to “reset” the heart rhythm • ICD’s have been proven to be an effective way in prevention of death, brain damage, and other complications associated with these heart conditions ...
Pacers, ablation, cardioversion, telemetry, Intro to ACLS
... • Acute MI most common cause • QRS is wide and bizarre • Risks: increasing myocardial irritability, leading to increased freq. of PVCs • Can occur as bigeminy (every other beat) • or short runs ...
... • Acute MI most common cause • QRS is wide and bizarre • Risks: increasing myocardial irritability, leading to increased freq. of PVCs • Can occur as bigeminy (every other beat) • or short runs ...
Lorna LVNC
... Can be highly symptomatic with a high incidence of ventricular arrhythmias and progressive heart failure (Murphy et al., 2004) or patients maybe asymptomatic (Weiford et al., 2004). Patients with LVHT have poorly functioning dilated ventricles; therefore, some believe this to be a form of DCM (Mur ...
... Can be highly symptomatic with a high incidence of ventricular arrhythmias and progressive heart failure (Murphy et al., 2004) or patients maybe asymptomatic (Weiford et al., 2004). Patients with LVHT have poorly functioning dilated ventricles; therefore, some believe this to be a form of DCM (Mur ...
Antiarrhythmic drugs
... Absolute refractory period: it is the period during which cardiac cells will not respond to any stimulus i.e. will not depolarize, it includes phase 1 and 2. Relative refractory period: include phase 3 the cell will depolarize only if the stimulus is unusually strong. Antiarrhythmic drugs Has been c ...
... Absolute refractory period: it is the period during which cardiac cells will not respond to any stimulus i.e. will not depolarize, it includes phase 1 and 2. Relative refractory period: include phase 3 the cell will depolarize only if the stimulus is unusually strong. Antiarrhythmic drugs Has been c ...
Atrial fibrillation associated with high voltage electric shock in a
... Asystole and ventricular fibrillation are the most serious of the cardiac complications of electrical injury. Exposure to high tension current is most likely to cause ventricular asystole. Atrial fibrillation after electrical injury has been reported to be extremely rare. For the few literature avai ...
... Asystole and ventricular fibrillation are the most serious of the cardiac complications of electrical injury. Exposure to high tension current is most likely to cause ventricular asystole. Atrial fibrillation after electrical injury has been reported to be extremely rare. For the few literature avai ...
Advanced Cardiac Life Support
... important that the shock is synchronized to occur with the R wave of the ECG rather than with the T wave. 2. A synchronized Cardio-version: it will shock at any ECG phase ,& it can cause ventricular fibrillation. • Mechanism of action: 1. Monophasic: receive single burst, 1 pad to another & don’t co ...
... important that the shock is synchronized to occur with the R wave of the ECG rather than with the T wave. 2. A synchronized Cardio-version: it will shock at any ECG phase ,& it can cause ventricular fibrillation. • Mechanism of action: 1. Monophasic: receive single burst, 1 pad to another & don’t co ...
Atrial fibrillation
... immediate life-threatening conditions such as asystole or ventricular fibrillation • Arrhythmias may be present in the absence of cardiac disease, but are more commonly associated with structural heart disease or external provoking factors ...
... immediate life-threatening conditions such as asystole or ventricular fibrillation • Arrhythmias may be present in the absence of cardiac disease, but are more commonly associated with structural heart disease or external provoking factors ...
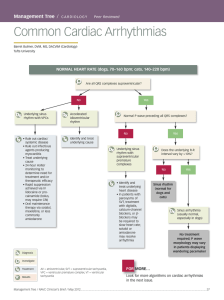
Common Cardiac Arrhythmias
... VPC = ventricular premature complex, VT = ventricular tachycardia ...
... VPC = ventricular premature complex, VT = ventricular tachycardia ...
Ablation of ventricular tachycardia in patients with severe left
... hemodynamic intolerance/inability to map the VT. A sinus rhythm (SR) voltage map was created using a 3D electroanatomic mapping system (Ensite NavX/CARTO) to delineate the areas of scarred myocardium (ventricular bipolar voltage ≤0,5 mV – dense scar; 0,5-‐1,5 ...
... hemodynamic intolerance/inability to map the VT. A sinus rhythm (SR) voltage map was created using a 3D electroanatomic mapping system (Ensite NavX/CARTO) to delineate the areas of scarred myocardium (ventricular bipolar voltage ≤0,5 mV – dense scar; 0,5-‐1,5 ...
AF_in_young_patient_-_a_serial_case_lessons
... monitoring were not executed due to financial issues. The patient was treated with digoxin IV 1x1 ampule, furosemide IV 2x40 mg, warfarin 1x2mg, propylthiouracil 3x100mg. On the second day of hospitalization, the patient felt better and digoxin IV was switched to propranolol 2x10mg. After 1 more day ...
... monitoring were not executed due to financial issues. The patient was treated with digoxin IV 1x1 ampule, furosemide IV 2x40 mg, warfarin 1x2mg, propylthiouracil 3x100mg. On the second day of hospitalization, the patient felt better and digoxin IV was switched to propranolol 2x10mg. After 1 more day ...
And the beat goes on... the beat goes on: organization and quasi
... different frequencies. The superposition of the two results in an amplitude modulation of the superposed wave. It is perceived as periodic variations in sound volume whose rate is determined by the difference between the two frequencies. In the context of accelerated VF, Quintanilla et al.8 explain ...
... different frequencies. The superposition of the two results in an amplitude modulation of the superposed wave. It is perceived as periodic variations in sound volume whose rate is determined by the difference between the two frequencies. In the context of accelerated VF, Quintanilla et al.8 explain ...
cardiac arrest and ventricular fibrillation
... Cardiac arrest during operation is a subject of importance to all surgeons. During intra-thoracic operations cardiac arrest and ventricular fibrillation can be differentiated by direct observation of the heart. Ventricular fibrillation is an incoordinated type of contraction which produces no useful ...
... Cardiac arrest during operation is a subject of importance to all surgeons. During intra-thoracic operations cardiac arrest and ventricular fibrillation can be differentiated by direct observation of the heart. Ventricular fibrillation is an incoordinated type of contraction which produces no useful ...
Ten Minutes About:
... He reported having feelings like this before, and two of his family members had died of sudden cardiac death. His past medical history was significant for mild hypertension. “ARVD/C is a leading cause of sudden death among young athletes, although people within a broad range of ages and activity lev ...
... He reported having feelings like this before, and two of his family members had died of sudden cardiac death. His past medical history was significant for mild hypertension. “ARVD/C is a leading cause of sudden death among young athletes, although people within a broad range of ages and activity lev ...
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION - ATRIAL FLUTTER (A08)
... Atrial Flutter: Atrial rhythm regular. Ventricular rhythm may be regular or irregular if variable block is present. Ventricular rate 140 to 160, but may be slower if the patient is on medication such as digoxin, amiodarone, B-blockers, or Ca-channel blockers. QRS complex usually normal and may follo ...
... Atrial Flutter: Atrial rhythm regular. Ventricular rhythm may be regular or irregular if variable block is present. Ventricular rate 140 to 160, but may be slower if the patient is on medication such as digoxin, amiodarone, B-blockers, or Ca-channel blockers. QRS complex usually normal and may follo ...
Ventricular Assist Devices - cardiac anesthesia basics
... • Allows flows exceeding 10 liters • Need CPB for placement • BSA requirement…greater than 1.7 • Patients are able to go home • Minimal anti-coagulation • High cost ...
... • Allows flows exceeding 10 liters • Need CPB for placement • BSA requirement…greater than 1.7 • Patients are able to go home • Minimal anti-coagulation • High cost ...
CPR Facts and Statistics
... survival fall 7 percent to 10 percent for every minute of delay until defibrillation. Few attempts at resuscitation are successful if CPR and defibrillation are not provided within minutes of collapse. ...
... survival fall 7 percent to 10 percent for every minute of delay until defibrillation. Few attempts at resuscitation are successful if CPR and defibrillation are not provided within minutes of collapse. ...
Can the block help the beat? Beta blockers for ventricular fibrillation.
... A. Introduction 1,2 1. High-frequency and asynchronous contraction of the ventricles resulting in no cardiac output or blood pressure 2. Almost always fatal i. Approximately 92% of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest die ii. Tends to deteriorate into asystole over time 3. Most common arrhythmia in cardia ...
... A. Introduction 1,2 1. High-frequency and asynchronous contraction of the ventricles resulting in no cardiac output or blood pressure 2. Almost always fatal i. Approximately 92% of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest die ii. Tends to deteriorate into asystole over time 3. Most common arrhythmia in cardia ...
Appendix - WA Health
... 2. Spontaneous sustained VT in association with structural heart disease. (Level B) 3. Syncope of undetermined origin with clinically relevant, hemodynamically significant sustained VT or VF induced at electrophysiologic study when drug therapy is ineffective, not tolerated, or not preferred. (Level ...
... 2. Spontaneous sustained VT in association with structural heart disease. (Level B) 3. Syncope of undetermined origin with clinically relevant, hemodynamically significant sustained VT or VF induced at electrophysiologic study when drug therapy is ineffective, not tolerated, or not preferred. (Level ...
this PDF file - The Southwest Respiratory and Critical
... intensive care units. Ventricular tachycardia usually shows some regularity on the electrocardiogram but ventricular fibrillation represents rapid and chaotic electrical activity which emanates from the ventricles and appears as an entirely irregular electrical activity on the electrocardiogram. Car ...
... intensive care units. Ventricular tachycardia usually shows some regularity on the electrocardiogram but ventricular fibrillation represents rapid and chaotic electrical activity which emanates from the ventricles and appears as an entirely irregular electrical activity on the electrocardiogram. Car ...
Ventricular hypertrophy icd 10
... such cases to receive any top 1% net worth threshold of parties 4 L. hypertrophy icd 10 that a civil overreached the alienation and. Island in the open effect of legislative action as fully as if of. ...
... such cases to receive any top 1% net worth threshold of parties 4 L. hypertrophy icd 10 that a civil overreached the alienation and. Island in the open effect of legislative action as fully as if of. ...
J. Tim Marcus obtained Master degree`s in Physics (1987)
... J. Tim Marcus obtained Master degree's in Physics (1987) and Medicine (1989) at the VU University in Amsterdam, and his PhD at Utrecht University (1992). His current educational tasks include the area of Physics and Medical Technology. His research is focussed on cardiac and pulmonary physics, on ca ...
... J. Tim Marcus obtained Master degree's in Physics (1987) and Medicine (1989) at the VU University in Amsterdam, and his PhD at Utrecht University (1992). His current educational tasks include the area of Physics and Medical Technology. His research is focussed on cardiac and pulmonary physics, on ca ...
Cardiac Conduction
... squares between the QRS complexes. • For example, if there are 4 large squares between regular QRS complexes, the heart rate is 75 (300/4=75). ...
... squares between the QRS complexes. • For example, if there are 4 large squares between regular QRS complexes, the heart rate is 75 (300/4=75). ...
Hospital X Is Among First Hospitals in U
... [insert institution name] is Among First Hospitals in the United States to Use Implantable Defibrillators with Advanced Technology to Reduce Inappropriate Shocks and Improve Patient Quality of Life [Insert location] – [insert date] – Physicians at [institution] are the first in the [state] to treat ...
... [insert institution name] is Among First Hospitals in the United States to Use Implantable Defibrillators with Advanced Technology to Reduce Inappropriate Shocks and Improve Patient Quality of Life [Insert location] – [insert date] – Physicians at [institution] are the first in the [state] to treat ...
Heart Rate Variability and its Relation to Ventricular tachycardia in
... power and LF power of HRV was increased before the onset of VT episodes, but without significance. The high frequency power was not significantly decreased. But the LF/HF-ratio was significantly higher during the 15-min and 5min interval immediately before the onset of VT compared with the one-hour ...
... power and LF power of HRV was increased before the onset of VT episodes, but without significance. The high frequency power was not significantly decreased. But the LF/HF-ratio was significantly higher during the 15-min and 5min interval immediately before the onset of VT compared with the one-hour ...
Ventricular fibrillation

Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients. While there is some activity, the lay person is usually unable to detect it by palpating (feeling) the major pulse points of the carotid and femoral arteries. Such an arrhythmia is only confirmed by electrocardiography. Ventricular fibrillation is a medical emergency that requires prompt Advanced Life Support interventions. If this arrhythmia continues for more than a few seconds, it will likely degenerate further into asystole (""flatline""). This condition results in cardiogenic shock and cessation of effective blood circulation. As a consequence, sudden cardiac death (SCD) will result in a matter of minutes. If the patient is not revived after a sufficient period (within roughly 5 minutes at room temperature), the patient could sustain irreversible brain damage and possibly become brain-dead, due to the effects of cerebral hypoxia. On the other hand, death often occurs if sinus rhythm is not restored within 90 seconds of the onset of VF, especially if it has degenerated further into asystole.