common arrhythmias - Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana
... ECG Heart Monitors These devices record your heartbeat for a longer time than an office-based ECG. They help find arrhythmias that occur less often. A Holter monitor can be worn for up to 2 days. It provides a constant recording of heart activity. • An event monitor can be worn for several weeks. On ...
... ECG Heart Monitors These devices record your heartbeat for a longer time than an office-based ECG. They help find arrhythmias that occur less often. A Holter monitor can be worn for up to 2 days. It provides a constant recording of heart activity. • An event monitor can be worn for several weeks. On ...
sinus node dysfunction - Continuing Medical Education
... of up to 3 seconds are seen in 11% of normal patients during holter monitoring, and even more commonly in athletes (36%). In contrast pauses of > 3 seconds are rare in normal individuals and are generally regarded as pathological. They represent a failure of impulse generation within the SA node, an ...
... of up to 3 seconds are seen in 11% of normal patients during holter monitoring, and even more commonly in athletes (36%). In contrast pauses of > 3 seconds are rare in normal individuals and are generally regarded as pathological. They represent a failure of impulse generation within the SA node, an ...
Atrial fibrillation in pure rheumatic mitral valvular disease is
... • the lazy and progressive blood’s stagnation in the atrial chamber and its remoulding, • the progressive thickening, fibrosis and calcification of the valvular system, could be the physiopathological link between the diseases. From this point of view, it is not already clear if left atrium dilatati ...
... • the lazy and progressive blood’s stagnation in the atrial chamber and its remoulding, • the progressive thickening, fibrosis and calcification of the valvular system, could be the physiopathological link between the diseases. From this point of view, it is not already clear if left atrium dilatati ...
Lead wires and electrodes - O6U E
... Single and dual chamber: • The word chamber in dual or single chamber pacing refers to a chamber of the heart in which a lead is placed. • A single chamber pacemaker usually has a pacing lead in either the right atrium, or the right ventricle. These would be called, respectively, an atrial single c ...
... Single and dual chamber: • The word chamber in dual or single chamber pacing refers to a chamber of the heart in which a lead is placed. • A single chamber pacemaker usually has a pacing lead in either the right atrium, or the right ventricle. These would be called, respectively, an atrial single c ...
narrow-qrs tachycardias
... demand for oxygen increases as the heart rate increases. As the heart rate increases, there is less time for the ventricles to fill and less blood for the ventricles to pump out with each contraction. This can lead to decreased cardiac output. Because the coronary arteries fill when the ventricles a ...
... demand for oxygen increases as the heart rate increases. As the heart rate increases, there is less time for the ventricles to fill and less blood for the ventricles to pump out with each contraction. This can lead to decreased cardiac output. Because the coronary arteries fill when the ventricles a ...
Outpatient Approach to Palpitations
... followed by targeted diagnostic testing are necessary to distinguish a cardiac cause from other causes of palpitations. Standard 12-lead electrocardiography is an essential initial diagnostic test. Cardiac imaging is recommended if history, physical examination, or electrocardiography suggests struc ...
... followed by targeted diagnostic testing are necessary to distinguish a cardiac cause from other causes of palpitations. Standard 12-lead electrocardiography is an essential initial diagnostic test. Cardiac imaging is recommended if history, physical examination, or electrocardiography suggests struc ...
Download(302)
... • Etiology: There are several types of PSVT but all originate above the ventricles (therefore the QRS is narrow). • Most common: abnormal conduction in the AV node (reentrant circuit looping in the AV node). For more presentations www.medicalppt.blogspot.com ...
... • Etiology: There are several types of PSVT but all originate above the ventricles (therefore the QRS is narrow). • Most common: abnormal conduction in the AV node (reentrant circuit looping in the AV node). For more presentations www.medicalppt.blogspot.com ...
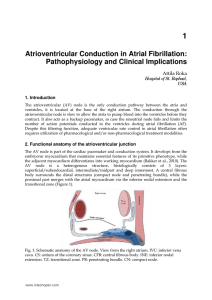
Atrioventricular Conduction in Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiology
... significant difference in the primary composite endpoint of mortality, cardiovascular hospitalization and myocardial infarction. However, patients with mean heart rates during AF within the AFFIRM (≤80/minute) or RACE (<100/minute) criteria had a better outcome than patients with heart rates ≥100/mi ...
... significant difference in the primary composite endpoint of mortality, cardiovascular hospitalization and myocardial infarction. However, patients with mean heart rates during AF within the AFFIRM (≤80/minute) or RACE (<100/minute) criteria had a better outcome than patients with heart rates ≥100/mi ...
Cardiac Arrhythmias: What to Treat, When and How
... Sinus tachycardia is almost always the result of clinical derangements not related to primary cardiac disease. The underlying situation commonly involved hypotension, but pain may also contribute. The underlying disease should be treated; sinus tachycardia is not a fatal arrhythmia and usually resol ...
... Sinus tachycardia is almost always the result of clinical derangements not related to primary cardiac disease. The underlying situation commonly involved hypotension, but pain may also contribute. The underlying disease should be treated; sinus tachycardia is not a fatal arrhythmia and usually resol ...
Risk of Arrhythmia Recurrence After Successful Ablation of
... Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and is difficult to treat.1 It may present with a variety of symptoms ranging in severity from mild to disabling.2 While some patients get diagnosed at the time of a routine visit and are not aware of their arrhythmia, others m ...
... Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and is difficult to treat.1 It may present with a variety of symptoms ranging in severity from mild to disabling.2 While some patients get diagnosed at the time of a routine visit and are not aware of their arrhythmia, others m ...
Manuscript
... rate, including emotion/mood, body position, fitness, activity, temperature/weather, medication, and even genes. There are nine main types of heart rates. The first and most common is a Normal Sinus Rhythm, which ranges from 60-100 beats per minute. Another common heart rate is Premature Ventricula ...
... rate, including emotion/mood, body position, fitness, activity, temperature/weather, medication, and even genes. There are nine main types of heart rates. The first and most common is a Normal Sinus Rhythm, which ranges from 60-100 beats per minute. Another common heart rate is Premature Ventricula ...
RT30 EKG Strips - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... Rate: Since some beats are not conducted, the ventricular rate is usually slightly slower than normal (< 100 bpm). Atrial rate (60-100 bpm). P wave: Upright & uniform. Some P waves are not followed by QRS complexes. PRI: The PRI will get progressively longer, until one P wave is not followed by a QR ...
... Rate: Since some beats are not conducted, the ventricular rate is usually slightly slower than normal (< 100 bpm). Atrial rate (60-100 bpm). P wave: Upright & uniform. Some P waves are not followed by QRS complexes. PRI: The PRI will get progressively longer, until one P wave is not followed by a QR ...
The Rate Dependent Bundle Branch Block
... reverted to normal sinus rhythm intermittently during peri-operative period. This intermittent ratedependent LBBB is a rare entity. Though hypertension is one significant co-morbid condition, the risk evalution of LBBB during anesthesia only on an ECG finding, is not justifiable. Rather patient shou ...
... reverted to normal sinus rhythm intermittently during peri-operative period. This intermittent ratedependent LBBB is a rare entity. Though hypertension is one significant co-morbid condition, the risk evalution of LBBB during anesthesia only on an ECG finding, is not justifiable. Rather patient shou ...
diseases of the cardiovascular system
... most commonly diagnosed heart diseases. It was discovered that this was caused by a deficiency of TAURINE, an amino acid. Since that time commercial foods have added taurine to feline diets, which has significantly decreased the number of cases of feline DCM ...
... most commonly diagnosed heart diseases. It was discovered that this was caused by a deficiency of TAURINE, an amino acid. Since that time commercial foods have added taurine to feline diets, which has significantly decreased the number of cases of feline DCM ...
Drugs for Dysrhythmias Expanded Key Concepts
... Some dysrhythmias produce no symptoms and are harmless, while others are life threatening. The frequency of dysrhythmias is difficult to predict, although it is thought to be quite common, particularly in the geriatric population. 23.2 Dysrhythmias are classified by the location (atrial or ventricul ...
... Some dysrhythmias produce no symptoms and are harmless, while others are life threatening. The frequency of dysrhythmias is difficult to predict, although it is thought to be quite common, particularly in the geriatric population. 23.2 Dysrhythmias are classified by the location (atrial or ventricul ...
CASE 9
... after atrial contraction can fill the ventricles. Second, action potential conduction in the AV node is blocked easily because of the long refractory periods and other features of the action potential. This protects the ventricles from excessive frequencies of contraction, which can prevent effectiv ...
... after atrial contraction can fill the ventricles. Second, action potential conduction in the AV node is blocked easily because of the long refractory periods and other features of the action potential. This protects the ventricles from excessive frequencies of contraction, which can prevent effectiv ...
Simultaneous conduction over the fast and slow
... block is present on the SP impeding its activation by the impulse coming down from the FP. The second is that the critical slowing of conduction in the SP allows the recovery of excitability of the FP retrogradely and thus initiates nodal reentrant arrhythmia. To date, a few case reports have been p ...
... block is present on the SP impeding its activation by the impulse coming down from the FP. The second is that the critical slowing of conduction in the SP allows the recovery of excitability of the FP retrogradely and thus initiates nodal reentrant arrhythmia. To date, a few case reports have been p ...
2nd Announcement - Istituto di Medicina e Scienza dello Sport
... recognize the «Cardiostim style» by the principles that made it a success: a strong presence outside the EU, especially North Americans, a large emphasis placed on innovation and education, a forum for industry. You will find just as much of the scientific and academic EHRA hand, and all activities ...
... recognize the «Cardiostim style» by the principles that made it a success: a strong presence outside the EU, especially North Americans, a large emphasis placed on innovation and education, a forum for industry. You will find just as much of the scientific and academic EHRA hand, and all activities ...
Safe Technique of Removal of Left Atrial Thrombus during Mitral
... Removal of an organized thrombus from left atrium can be challenging especially when it is huge in size and the presence of dense adhesion and absence of cleavage plane makes its removal difficult 14. and under such circumstances residual organized material can be left 14. Gallo and colleagues 8 pra ...
... Removal of an organized thrombus from left atrium can be challenging especially when it is huge in size and the presence of dense adhesion and absence of cleavage plane makes its removal difficult 14. and under such circumstances residual organized material can be left 14. Gallo and colleagues 8 pra ...
Ratio of Peak Early to Late Diastolic Filling Velocity of the Left
... probe was used for TEE. The following parameters were measured using standard views and techniques : left ventricular end-diastolic dimension ; left ventricular percentage fractional shortening ; left ventricular mass index ; presence of atrial septal aneurysm and patent foramen ovale ; and spontane ...
... probe was used for TEE. The following parameters were measured using standard views and techniques : left ventricular end-diastolic dimension ; left ventricular percentage fractional shortening ; left ventricular mass index ; presence of atrial septal aneurysm and patent foramen ovale ; and spontane ...
Welcome to Vibrationdata Ni hao
... electrical currents. Any two points on the body may be connected by electrical leads to monitor the rhythm of the heart. Specifically, the EKG monitors the potential changes due to excitation (depolarization) and recovery (repolarization) of the heart muscle. ...
... electrical currents. Any two points on the body may be connected by electrical leads to monitor the rhythm of the heart. Specifically, the EKG monitors the potential changes due to excitation (depolarization) and recovery (repolarization) of the heart muscle. ...
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF or A-fib) is an abnormal heart rhythm characterized by rapid and irregular beating. Often it starts as brief periods of abnormal beating which become longer and possibly constant over time. Most episodes have no symptoms. Occasionally there may be heart palpitations, fainting, shortness of breath, or chest pain. The disease increases the risk of heart failure, dementia, and stroke.Hypertension and valvular heart disease are the most common alterable risk factors for AF. Other heart-related risk factors include heart failure, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, and congenital heart disease. In the developing world valvular heart disease often occurs as a result of rheumatic fever. Lung-related risk factors include COPD, obesity, and sleep apnea. Other factors include excess alcohol intake, diabetes mellitus, and thyrotoxicosis. However, half of cases are not associated with one of these risks. A diagnosis is made by feeling the pulse and may be confirmed using an electrocardiogram (ECG). The typical ECG shows no P waves and an irregular ventricular rate.AF is often treated with medications to slow the heart rate to a near normal range (known as rate control) or to convert the rhythm to normal sinus rhythm (known as rhythm control). Electrical cardioversion can also be used to convert AF to a normal sinus rhythm and is often used emergently if the person is unstable. Ablation may prevent recurrence in some people. Depending on the risk of stroke either aspirin or anti-clotting medications such as warfarin or a novel oral anticoagulant may be recommended. While these medications reduce this risk, they increase rates of major bleeding.Atrial fibrillation is the most common serious abnormal heart rhythm. In Europe and North America, as of 2014, it affects about 2% to 3% of the population. This is an increase from 0.4 to 1% of the population around 2005. In the developing world about 0.6% of males and 0.4% of females are affected. The percentage of people with AF increases with age with 0.14% under 50 years old, 4% between 60 and 70 years old, and 14% over 80 years old being affected. A-fib and atrial flutter resulted in 112,000 deaths in 2013, up from 29,000 in 1990. The first known report of an irregular pulse was by John Baptist Senac in 1749. This was first documented by ECG in 1909 by Thomas Lewis.