Module 3
... The All-or None Response • The idea that either the neuron fires or it does not- no part way firing. • Like a gun ...
... The All-or None Response • The idea that either the neuron fires or it does not- no part way firing. • Like a gun ...
Nueron - AP Psychology Community
... The All-or None Response • The idea that either the neuron fires or it does not- no part way firing. • Like a gun ...
... The All-or None Response • The idea that either the neuron fires or it does not- no part way firing. • Like a gun ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... simultaneously biological. The nervous system is complexity built from simplicity. The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... simultaneously biological. The nervous system is complexity built from simplicity. The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (Ach) transmitter plays a role in
... How a Neuron Fires… Action Potential – a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. Neurons fire these impulses in responses to senses or other neurons. A neurons reaction is an all-or-none response (neurons either fire or they don’t) *A strong stimulus can trigger more n ...
... How a Neuron Fires… Action Potential – a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. Neurons fire these impulses in responses to senses or other neurons. A neurons reaction is an all-or-none response (neurons either fire or they don’t) *A strong stimulus can trigger more n ...
July 1
... We have recently demonstrated that local activity in human cortex is represented in a broadband cortical spectral power law. Using a PCA based method on sub dural electrocorticographic recordings in humans, we were able to decouple this power law behavior from the classic alpha and beta rhythms, rev ...
... We have recently demonstrated that local activity in human cortex is represented in a broadband cortical spectral power law. Using a PCA based method on sub dural electrocorticographic recordings in humans, we were able to decouple this power law behavior from the classic alpha and beta rhythms, rev ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 9
... In order to trigger a neural impulse, excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must exceed a certain intensity, called a ________________________. Increasing a stimulus above this level will not increase the neural impulse's intensity. This phenomenon is called an ...
... In order to trigger a neural impulse, excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must exceed a certain intensity, called a ________________________. Increasing a stimulus above this level will not increase the neural impulse's intensity. This phenomenon is called an ...
Directed Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem
... heterogeneity in the degree of functional differentiation from plating to plating. Therefore we experimented with a recently published strategy for directed differentiation of iPSCs into medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) progenitors that had been shown to enrich cultures for GABAergic neurons. Three ...
... heterogeneity in the degree of functional differentiation from plating to plating. Therefore we experimented with a recently published strategy for directed differentiation of iPSCs into medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) progenitors that had been shown to enrich cultures for GABAergic neurons. Three ...
“Definitions” section of your binder Central nervous system
... -Messages from and to the brain travel in nerves (long strings of neurons) ->this is via electrical signals emitted as a signal once the neuron is stimulated past the minimum, or threshold level. -part of a Neuron ->Dendritess: thin fibres protruding from the cell body ->The cell body ...
... -Messages from and to the brain travel in nerves (long strings of neurons) ->this is via electrical signals emitted as a signal once the neuron is stimulated past the minimum, or threshold level. -part of a Neuron ->Dendritess: thin fibres protruding from the cell body ->The cell body ...
Slide ()
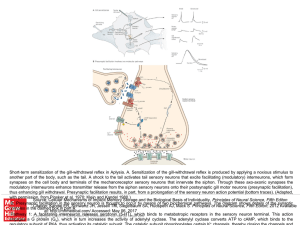
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Nervous System
... Gland to secrete a hormone e.g. S.A. node of the right atrium -bundles of nerves that detects blood ...
... Gland to secrete a hormone e.g. S.A. node of the right atrium -bundles of nerves that detects blood ...
Neural Decoding www.AssignmentPoint.com Neural decoding is a
... the back of our retina, these stimuli are converted from varying wavelengths to a series of neural spikes called action potentials. These pattern of action potentials are different for different objects and different colors; we therefore say that the neurons are encoding objects and colors by varyin ...
... the back of our retina, these stimuli are converted from varying wavelengths to a series of neural spikes called action potentials. These pattern of action potentials are different for different objects and different colors; we therefore say that the neurons are encoding objects and colors by varyin ...
Neurocognition Cognitive Neuroscience/neuropsychology
... All cognition is the result of neurological activity – most closely linked to cerebral cortex The study of the relationships between neuroscience and cognitive psychology, especially those theories of the mind dealing with memory, sensation and perception, problem solving, language processing, motor ...
... All cognition is the result of neurological activity – most closely linked to cerebral cortex The study of the relationships between neuroscience and cognitive psychology, especially those theories of the mind dealing with memory, sensation and perception, problem solving, language processing, motor ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The City College of New York
... Dr. Maria Uriarte, Columbia University Tropical Forest responses to climate variability and human land use: From stand dynamics to ecosystem services ...
... Dr. Maria Uriarte, Columbia University Tropical Forest responses to climate variability and human land use: From stand dynamics to ecosystem services ...
Toward STDP-based population action in large networks of spiking
... simple binary units [1], to integrate and fire [2] or more elaborate conductancebased models [3, 4]. The functional role of this synchronous activity is not fully clarified yet. Spontaneous brain activity is characterized by a high degree of irregularity [5]. Some synchrony can however be observed d ...
... simple binary units [1], to integrate and fire [2] or more elaborate conductancebased models [3, 4]. The functional role of this synchronous activity is not fully clarified yet. Spontaneous brain activity is characterized by a high degree of irregularity [5]. Some synchrony can however be observed d ...
CaV3.1 is tremor rhythm pacemaker
... rhythmic burst discharges in response to harmaline-induced hyperpolarization. In addition, selective knock-down of this gene in the inferior olive efficiently suppressed harmaline-induced tremor in wild-type mice; Thus, CaV3.1 is a molecular pacemaker substrate for the intrinsic neuronal oscillation ...
... rhythmic burst discharges in response to harmaline-induced hyperpolarization. In addition, selective knock-down of this gene in the inferior olive efficiently suppressed harmaline-induced tremor in wild-type mice; Thus, CaV3.1 is a molecular pacemaker substrate for the intrinsic neuronal oscillation ...
Os textos são da exclusiva responsabilidade dos autores
... about the rejection/exclusion experience were also evident for slow wave neural activity. Greater distress was associated with a more negative frontal slow wave and a larger late positive potential (LPP), with children of high and low levels of distress showing markedly different patterns of cortica ...
... about the rejection/exclusion experience were also evident for slow wave neural activity. Greater distress was associated with a more negative frontal slow wave and a larger late positive potential (LPP), with children of high and low levels of distress showing markedly different patterns of cortica ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... 1. Electrical current travels down the axon 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to pass to the next cell - what type ...
... 1. Electrical current travels down the axon 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to pass to the next cell - what type ...
Nervous System Notes
... nerve pathway that consists of a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron ...
... nerve pathway that consists of a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron ...
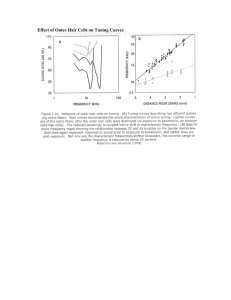
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
... The basilar membrane divides the cochlea along its length and responds to oscillations in the cochlear fluids in a frequency-specific way because of its graded mechanical properties. High-frequency sound waves elicit maximal responses at the basal end of the membrane, near the stapes, whereas lowfre ...
... The basilar membrane divides the cochlea along its length and responds to oscillations in the cochlear fluids in a frequency-specific way because of its graded mechanical properties. High-frequency sound waves elicit maximal responses at the basal end of the membrane, near the stapes, whereas lowfre ...
Development
... Parkinson’s Disease • Due to loss of substantia nigra dopamine neurons. • Common in people over 80. • Treated with L-dopa, DA transplants, or DA receptor agonists. • 5-10% early-onset familial: several genes identified (alpha-synuclein, parkin) • 90% sporadic: pesticides and MPTP. • Mitochondria an ...
... Parkinson’s Disease • Due to loss of substantia nigra dopamine neurons. • Common in people over 80. • Treated with L-dopa, DA transplants, or DA receptor agonists. • 5-10% early-onset familial: several genes identified (alpha-synuclein, parkin) • 90% sporadic: pesticides and MPTP. • Mitochondria an ...
The Nervous System
... 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.