Molecular prosthetics for vision restoration based on freely
... molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity for fundamental and therapeutic purposes. In the first case, simultaneous photocontrol of synaptic receptors and fluorescence imaging of neuronal activity in vivo will allow studying synaptic plasticity from the single dendrit ...
... molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity for fundamental and therapeutic purposes. In the first case, simultaneous photocontrol of synaptic receptors and fluorescence imaging of neuronal activity in vivo will allow studying synaptic plasticity from the single dendrit ...
Document
... Networks in the brain stem of vertebrates responsible for maintaining eye position appear to act as integrators. Eye position changes in response to bursts of ocular motor neurons in brain stem. Neurons in the brainstem integrate these signals. Their activity is approximately proportional to horizon ...
... Networks in the brain stem of vertebrates responsible for maintaining eye position appear to act as integrators. Eye position changes in response to bursts of ocular motor neurons in brain stem. Neurons in the brainstem integrate these signals. Their activity is approximately proportional to horizon ...
Test Question 1 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive
... c) Why do researchers not always use more direct representations of the neural activity from EEG or MEG? AW: Less good spatial resolution. Does not see the deeper sources very well Test Question 3 Why is the term “EMG investigation” strictly speaking not correct for a routine electro-diagnostic inve ...
... c) Why do researchers not always use more direct representations of the neural activity from EEG or MEG? AW: Less good spatial resolution. Does not see the deeper sources very well Test Question 3 Why is the term “EMG investigation” strictly speaking not correct for a routine electro-diagnostic inve ...
sheets DA 7
... Networks in the brain stem of vertebrates responsible for maintaining eye position appear to act as integrators. Eye position changes in response to bursts of ocular motor neurons in brain stem. Neurons in the brainstem integrate these signals. Their activity is approximately proportional to horizon ...
... Networks in the brain stem of vertebrates responsible for maintaining eye position appear to act as integrators. Eye position changes in response to bursts of ocular motor neurons in brain stem. Neurons in the brainstem integrate these signals. Their activity is approximately proportional to horizon ...
Slide ()
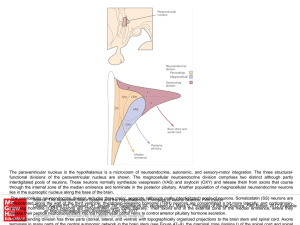
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Slide ()
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Document
... - Neural network is a computational model that simulate some properties of the human brain. - The connections and nature of units determine the behavior of a neural network. - Perceptrons are feed-forward networks that can only ...
... - Neural network is a computational model that simulate some properties of the human brain. - The connections and nature of units determine the behavior of a neural network. - Perceptrons are feed-forward networks that can only ...
A.1 Neural Development
... An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other parts of the body A developing neuron forms multiple synapses Synapses that are nut used do not persist Neural pruning involves the loss of unused neurons The plasticity of ...
... An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other parts of the body A developing neuron forms multiple synapses Synapses that are nut used do not persist Neural pruning involves the loss of unused neurons The plasticity of ...
Single Unit Recording
... electrode introduced into the brain of a living animal will detect electrical activity that is generated by the neurons adjacent to the electrode tip. If the electrode is a microelectrode, with a tip size of 3 to 10 micrometers, the electrode will often isolate the activity of a single neuron. The a ...
... electrode introduced into the brain of a living animal will detect electrical activity that is generated by the neurons adjacent to the electrode tip. If the electrode is a microelectrode, with a tip size of 3 to 10 micrometers, the electrode will often isolate the activity of a single neuron. The a ...
Slide ()
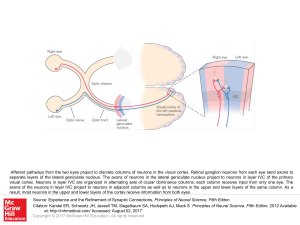
... separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the primary visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. Th ...
... separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the primary visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. Th ...
Option A Neural Development Study Guide A1 A2
... How the neural tube of embryonic chordates forms How differentiation of the neural tube produces neurons That immature neurons migrate to a final location That chemical stimuli influence the growth of axons to other parts of the body Multiple synapses form with developing neurons Unused synapses are ...
... How the neural tube of embryonic chordates forms How differentiation of the neural tube produces neurons That immature neurons migrate to a final location That chemical stimuli influence the growth of axons to other parts of the body Multiple synapses form with developing neurons Unused synapses are ...
Modeling Synaptic Plasticity
... Synapses are the structures through which neurons communicate, and the loci of information storage in neural circuits. Synapses store information (‘learn’) thanks to synaptic plasticity: the efficacy of the communication between the two neurons connected by the synapse can change, as a function of t ...
... Synapses are the structures through which neurons communicate, and the loci of information storage in neural circuits. Synapses store information (‘learn’) thanks to synaptic plasticity: the efficacy of the communication between the two neurons connected by the synapse can change, as a function of t ...
Neurons
... Memory centered on the hippocampus. Hippocampus is responsible for getting together the contextual features of a situation and create a representation of every experience. Animal studies 1. Rats (have similar anatomy of hippocampus) ...
... Memory centered on the hippocampus. Hippocampus is responsible for getting together the contextual features of a situation and create a representation of every experience. Animal studies 1. Rats (have similar anatomy of hippocampus) ...
abstract
... of 5HT was determined in the rat brain in an effort to gain an insight into the mechanism of action of this drug. This was done by determining its effect on the activity of tryptophan hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of 5HT in serotonergic neurons. The enzyme activity was de ...
... of 5HT was determined in the rat brain in an effort to gain an insight into the mechanism of action of this drug. This was done by determining its effect on the activity of tryptophan hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of 5HT in serotonergic neurons. The enzyme activity was de ...
Neuroimaging Tutorial
... fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its strengths and weaknesses. I’ll focus on fMRI and PET. fMRI and PET are des ...
... fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its strengths and weaknesses. I’ll focus on fMRI and PET. fMRI and PET are des ...
Artificial Intelligence, Expert Systems, and DSS
... Outputs are 0 or 1 If the activation (accumulated weighted input) is larger than threshold the unit generates a signal ...
... Outputs are 0 or 1 If the activation (accumulated weighted input) is larger than threshold the unit generates a signal ...
Abstract View OPTICAL RECORDING OF THE TRITONIA SWIMMING CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR. ;
... 2. Advanced Technology R&D Center, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Amagasaki, Japan We recorded action potential activity from the isolated brain of the nudibranch seaslug Tritonia diomedea during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their burs ...
... 2. Advanced Technology R&D Center, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Amagasaki, Japan We recorded action potential activity from the isolated brain of the nudibranch seaslug Tritonia diomedea during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their burs ...
KC Kajander GJ Giesler, Jr. KJ Gingrich JH Byrne YS Chan J
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
Perception, learning and memory - Max-Planck
... individual neurons and synapses, but much less about their coordinated action in ensembles of millions. The brain derives its magic from coordinated activity on the large scale and high degrees of specialization on the small scale7. Networks, neurons and molecular constituents need to be studied in ...
... individual neurons and synapses, but much less about their coordinated action in ensembles of millions. The brain derives its magic from coordinated activity on the large scale and high degrees of specialization on the small scale7. Networks, neurons and molecular constituents need to be studied in ...
Unit 2 Review
... 6. A neuron either fires or it doesn’t. There is no in between. This phenomenon is called _______________________________. 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
... 6. A neuron either fires or it doesn’t. There is no in between. This phenomenon is called _______________________________. 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
Slide ()
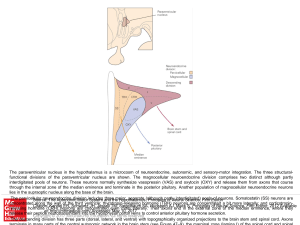
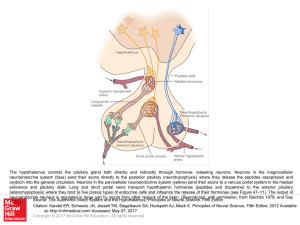
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
7-9_BrainDev_ValaczkaiR
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
Brain Structure and Functioning in Relation to Outdoor Space
... base for developing a method called electroencephalography ...
... base for developing a method called electroencephalography ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.