psy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... 6. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a neuron, it triggers the release of chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ pe ...
... 6. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a neuron, it triggers the release of chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ pe ...
Lecture
... D. Only a very strong stimulus can stimulate the neuron during this phase. E. Resting potential. F. Absolute refractory period. G. Relative refractory period. ...
... D. Only a very strong stimulus can stimulate the neuron during this phase. E. Resting potential. F. Absolute refractory period. G. Relative refractory period. ...
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
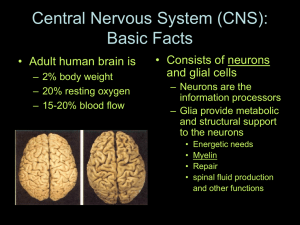
... Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
paper
... evoked potentials is correlated with spontaneous activity of spinal neurons in the cat E. Manjarrez, G. Rojas-Piloni, L. Martinez, D. Vazquez, D. Velez, I. Mendez, A. Flores Neuroscience Letters 323(2002):187-190 ...
... evoked potentials is correlated with spontaneous activity of spinal neurons in the cat E. Manjarrez, G. Rojas-Piloni, L. Martinez, D. Vazquez, D. Velez, I. Mendez, A. Flores Neuroscience Letters 323(2002):187-190 ...
Distinction of a left or right hand keypress
... Distinction of a left or right hand keypress Algorithm The algorithm used is based in a MLP neural network and a key feature extraction based in PCA (principal component analysis). The principal component analysis is computed for each channel, then the second principal mode is used (I have not used ...
... Distinction of a left or right hand keypress Algorithm The algorithm used is based in a MLP neural network and a key feature extraction based in PCA (principal component analysis). The principal component analysis is computed for each channel, then the second principal mode is used (I have not used ...
Gamma band activity in the nuclei of the Reticular Activating System
... Introduction: During activated states (waking and paradoxical sleep), EEG responses are characterized by low amplitude, high frequency oscillatory activity in the gamma band range (~20-100 Hz). Gamma frequency oscillations have been proposed to participate in conscious perception, problem solving, m ...
... Introduction: During activated states (waking and paradoxical sleep), EEG responses are characterized by low amplitude, high frequency oscillatory activity in the gamma band range (~20-100 Hz). Gamma frequency oscillations have been proposed to participate in conscious perception, problem solving, m ...
PETER SOMOGYI University of Oxford, United Kingdom Peter
... diagonal band nuclei (MSDB) innervate the hippocampus and/or related cortical areas and contribute to the coordination of network activity such as theta rhythmicity and high frequency ripple oscillations (SWR). Some of them exclusively innervate local cortical GABAergic interneurons. Individual MSDB ...
... diagonal band nuclei (MSDB) innervate the hippocampus and/or related cortical areas and contribute to the coordination of network activity such as theta rhythmicity and high frequency ripple oscillations (SWR). Some of them exclusively innervate local cortical GABAergic interneurons. Individual MSDB ...
Neural Development - Peoria Public Schools
... • Immature neurons have only the cell body and nucleus. • One axon develops on each neuron. a. Axon- outgrowth from the cell body that carries signals to another neuron. b. Chemical stimuli determine when they grow and which direction it grows in the embryo. ...
... • Immature neurons have only the cell body and nucleus. • One axon develops on each neuron. a. Axon- outgrowth from the cell body that carries signals to another neuron. b. Chemical stimuli determine when they grow and which direction it grows in the embryo. ...
Neural Network of C. elegans is a Small
... • The hermaphrodite version has a simple nervous system comprising about 302 neurons. • It’s neural network is completely mapped. • The pattern of connectivity portrays smallworld network characteristics. ...
... • The hermaphrodite version has a simple nervous system comprising about 302 neurons. • It’s neural network is completely mapped. • The pattern of connectivity portrays smallworld network characteristics. ...
Neuroscience - Instructional Resources
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
chapter_8_powerpoint_le07
... calculations at synapses, the sites at which neurons interact. While hundreds of neurotransmitters and receptors have been identified, they can be functionally classified into two types: excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will ...
... calculations at synapses, the sites at which neurons interact. While hundreds of neurotransmitters and receptors have been identified, they can be functionally classified into two types: excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will ...
The Nervous System
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
neuron and nervous system
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
Slide ()
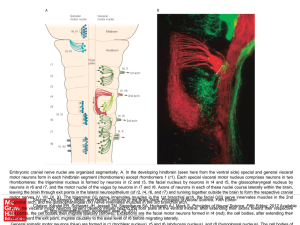
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
File - SSHS AP Psychology
... exceed to cause a neuron to fire All-or-none law= the neuron will fire or it won’t Absolute refractory period= time after a neuron has fired that it WILL NOT fire not matter what the impulse ...
... exceed to cause a neuron to fire All-or-none law= the neuron will fire or it won’t Absolute refractory period= time after a neuron has fired that it WILL NOT fire not matter what the impulse ...
abstract english
... The research in this thesis focuses on mechanisms that underlie brain waves (also called oscillations). Brain activity is often rhythmical, and depending on what a person is doing, waves of different frequency occur. In this thesis we describe processes which underlie brain waves typically observed ...
... The research in this thesis focuses on mechanisms that underlie brain waves (also called oscillations). Brain activity is often rhythmical, and depending on what a person is doing, waves of different frequency occur. In this thesis we describe processes which underlie brain waves typically observed ...
Slide ()
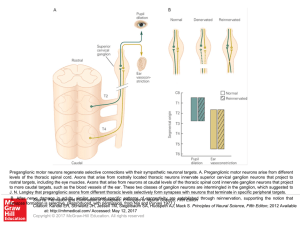
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
hwk-4-pg-521 - WordPress.com
... messages to effector tissues; interneurons transmit and integrate neural messages from the afferent neurons to the efferent neurons; effectors are the tissues where the appropriate response/stimulus takes place (for example, muscles, glands, and organs). (b) Afferent neurons, interneurons, efferent ...
... messages to effector tissues; interneurons transmit and integrate neural messages from the afferent neurons to the efferent neurons; effectors are the tissues where the appropriate response/stimulus takes place (for example, muscles, glands, and organs). (b) Afferent neurons, interneurons, efferent ...
ELEC 548
... required. This class will cover a range of techniques and their application to basic neuroscience and neural interfaces. This class will cover a range of techniques and their application to basic neuroscience and neural interfaces. Topics include an introduction to neurobiology and electrophysiology ...
... required. This class will cover a range of techniques and their application to basic neuroscience and neural interfaces. This class will cover a range of techniques and their application to basic neuroscience and neural interfaces. Topics include an introduction to neurobiology and electrophysiology ...
Nádasdy Zoltán Cal Tech
... Experimental evidence, such as task-dependent coherency between single-unit activity and local field potentials (LFPs), together with the dependency of action potential (AP) initiation on the subthreshold membrane oscillation (SMO) suggest that: i) the probability of action potentials is controlled ...
... Experimental evidence, such as task-dependent coherency between single-unit activity and local field potentials (LFPs), together with the dependency of action potential (AP) initiation on the subthreshold membrane oscillation (SMO) suggest that: i) the probability of action potentials is controlled ...
Slide ()
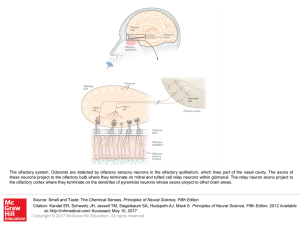
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
neural spike
... Which Model to Use for Cortical Spiking Neurons? To understand how the brain works, we need to combine experimental studies of animal and human nervous systems with numerical simulation of large-scale brain models. As we develop such large-scale brain models consisting of spiking neurons, we must f ...
... Which Model to Use for Cortical Spiking Neurons? To understand how the brain works, we need to combine experimental studies of animal and human nervous systems with numerical simulation of large-scale brain models. As we develop such large-scale brain models consisting of spiking neurons, we must f ...
Key - Cornell
... 4. Which characteristics of real neurons can you think of that leaky integrate-and-fire neurons do not model? Non-linearities in summation, refractory period 5. If one does not want to explicitly model action potential generation using Na+ and K+ channels, what is a good alternative? How is a refrac ...
... 4. Which characteristics of real neurons can you think of that leaky integrate-and-fire neurons do not model? Non-linearities in summation, refractory period 5. If one does not want to explicitly model action potential generation using Na+ and K+ channels, what is a good alternative? How is a refrac ...
Slide 1
... Which Model to Use for Cortical Spiking Neurons? To understand how the brain works, we need to combine experimental studies of animal and human nervous systems with numerical simulation of large-scale brain models. As we develop such large-scale brain models consisting of spiking neurons, we must f ...
... Which Model to Use for Cortical Spiking Neurons? To understand how the brain works, we need to combine experimental studies of animal and human nervous systems with numerical simulation of large-scale brain models. As we develop such large-scale brain models consisting of spiking neurons, we must f ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.