A Neural Network Model for the Representation of Natural Language
... My basic hypothesis is that the association among concepts is primarily an expression of domain-general cognitive mechanisms that depend on continuous learning of both previously presented linguistic input and everyday, direct experiential (i.e. sensory-physical) behaviors represented in natural lan ...
... My basic hypothesis is that the association among concepts is primarily an expression of domain-general cognitive mechanisms that depend on continuous learning of both previously presented linguistic input and everyday, direct experiential (i.e. sensory-physical) behaviors represented in natural lan ...
Accidental Reinforcement Can Cause Superstitious Behavior
... • A belief, not based on human reason or scientific knowledge, that future events may be influenced by one's behavior in some magical or mystical way. • Superstitious behavior: learned because it happened to be followed by a reinforcer, even though this behavior was not the cause of the reinforcer. ...
... • A belief, not based on human reason or scientific knowledge, that future events may be influenced by one's behavior in some magical or mystical way. • Superstitious behavior: learned because it happened to be followed by a reinforcer, even though this behavior was not the cause of the reinforcer. ...
Abstract View A HYBRID ELECTRO-DIFFUSION MODEL FOR NEURAL SIGNALING. ;
... of an action potential propagating through an unmyelinated axon, with discrete sodium and potassium channels modeled by a voltage-dependent Markov random process. For large diameter axons, the spatio-temporal dynamics of the membrane potential averaged over several runs converges to results obtained ...
... of an action potential propagating through an unmyelinated axon, with discrete sodium and potassium channels modeled by a voltage-dependent Markov random process. For large diameter axons, the spatio-temporal dynamics of the membrane potential averaged over several runs converges to results obtained ...
Nerve cord
... “Nerve net”: Simplest nervous system are a netlike arrangement of neurons throughout the body “Nerve cord”: Most complex have a nerve cord and a brain ...
... “Nerve net”: Simplest nervous system are a netlike arrangement of neurons throughout the body “Nerve cord”: Most complex have a nerve cord and a brain ...
Document
... What is an Operant Response? (2 points) What is Superstitious Behavior? (2 points) What is shaping? (2 points) How did B.F. Skinner discover operant conditioning? ...
... What is an Operant Response? (2 points) What is Superstitious Behavior? (2 points) What is shaping? (2 points) How did B.F. Skinner discover operant conditioning? ...
Observational Learning
... • Antisocial models- in one’s family or neighborhood, or on TV- may have antisocial effects. – “Copycat” threats or incidents in every state after Columbine High School massacre – Abusive parents might have aggressive children – Many men who beat their wives had wife-battering fathers • Intergenerat ...
... • Antisocial models- in one’s family or neighborhood, or on TV- may have antisocial effects. – “Copycat” threats or incidents in every state after Columbine High School massacre – Abusive parents might have aggressive children – Many men who beat their wives had wife-battering fathers • Intergenerat ...
Mollusks, Worms, Arthropods, Echinoderms
... system with mouth and anus First animals to have a fluid filled body cavity called a pseudocoelom- “false body cavity” ...
... system with mouth and anus First animals to have a fluid filled body cavity called a pseudocoelom- “false body cavity” ...
AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 9
... In order to trigger a neural impulse, excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must exceed a certain intensity, called a ________________________. Increasing a stimulus above this level will not increase the neural impulse's intensity. This phenomenon is called an ______-______-________________ r ...
... In order to trigger a neural impulse, excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must exceed a certain intensity, called a ________________________. Increasing a stimulus above this level will not increase the neural impulse's intensity. This phenomenon is called an ______-______-________________ r ...
E1 – Stimulus and response - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... junction between two nerve cell or between a nerve cell & an effector receive messages from motor neurons & produce a response to the stimuli ...
... junction between two nerve cell or between a nerve cell & an effector receive messages from motor neurons & produce a response to the stimuli ...
Unit Test Neuro: Core ( Topic 6.5) and Options E ( Topics 1,2,4) HL
... Explain how animal experiments, lesions and FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) scanning can be used in the identification of the brain part involved in specific functions. (3) ...
... Explain how animal experiments, lesions and FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) scanning can be used in the identification of the brain part involved in specific functions. (3) ...
Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience)
... Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience) Students need to understand the relationship between biology and behavior. We explore the range of techniques scientists have used to learn about brain function, from procedures such as ablation, direct stimulation, EEG, CAT scans, PET ...
... Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience) Students need to understand the relationship between biology and behavior. We explore the range of techniques scientists have used to learn about brain function, from procedures such as ablation, direct stimulation, EEG, CAT scans, PET ...
Marina Florack
... o Independent Variable: the factor manipulated (the cause) o Dependant Variable: behavior or mental process that is measured in response to the experiment (the effect) o Confounding Variables: any difference b/t the experimental group and control which affect the outcome (time, place, frequency, etc ...
... o Independent Variable: the factor manipulated (the cause) o Dependant Variable: behavior or mental process that is measured in response to the experiment (the effect) o Confounding Variables: any difference b/t the experimental group and control which affect the outcome (time, place, frequency, etc ...
Vertebrate versus invertebrate neural circuits
... show obvious differences in design principles, implying that some brain functions are not equivalent. However, many computational problems need to be solved by all brains. In these cases, insights obtained in one species will be instructive to understand brain functions in other species, even if the ...
... show obvious differences in design principles, implying that some brain functions are not equivalent. However, many computational problems need to be solved by all brains. In these cases, insights obtained in one species will be instructive to understand brain functions in other species, even if the ...
Information Processing SG
... Identify what a synapse is and how two joined neurons overcome a synapse. ...
... Identify what a synapse is and how two joined neurons overcome a synapse. ...
Option A.4 pt 2 - Peoria Public Schools
... • Compare and contrast reflex conditioning and operant conditioning. a. They are both types of learning. Reflex conditioning is initiated by the environment and experiences that occur before the response , operant conditioning is initiated by the animal testing out a behavior pattern and changes tha ...
... • Compare and contrast reflex conditioning and operant conditioning. a. They are both types of learning. Reflex conditioning is initiated by the environment and experiences that occur before the response , operant conditioning is initiated by the animal testing out a behavior pattern and changes tha ...
Animal Behavior and Ethology
... the “beta” member—they dominate everyone in the group except the alpha. Alpha members have first dibs on everything—mates, food, etc. Note: Since there is an order, known by all involved, it reduces the energy wasted and the risk from physical fighting for resources. Dominance hierarchies are charac ...
... the “beta” member—they dominate everyone in the group except the alpha. Alpha members have first dibs on everything—mates, food, etc. Note: Since there is an order, known by all involved, it reduces the energy wasted and the risk from physical fighting for resources. Dominance hierarchies are charac ...
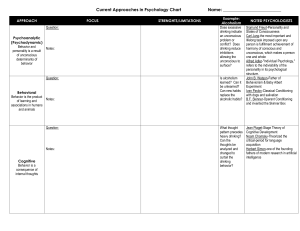
Current Approaches in Psychology Chart Name
... James Olds-the "reward" system in the brain Roger Sperry-showed that if the two hemispheres of the brain are separated by severing the corpus callosum (the large band of fibers that connects them) George Miller-The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two: Some Limits on our Capacity for Processing I ...
... James Olds-the "reward" system in the brain Roger Sperry-showed that if the two hemispheres of the brain are separated by severing the corpus callosum (the large band of fibers that connects them) George Miller-The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two: Some Limits on our Capacity for Processing I ...
Are animals smart? Things we can learn from animals.
... Characterized several instances of animal ...
... Characterized several instances of animal ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Signals: From Postsynaptic Potentials to Neural Networks One neuron, signals from thousands of other neurons Requires integration of signals PSPs add up, balance out Balance between IPSPs and EPSPs Neural networks Patterns of neural activity Interconnected neurons that fire together ...
... Signals: From Postsynaptic Potentials to Neural Networks One neuron, signals from thousands of other neurons Requires integration of signals PSPs add up, balance out Balance between IPSPs and EPSPs Neural networks Patterns of neural activity Interconnected neurons that fire together ...
NEW DIRECTIONS: Autism, Mirror Neurons, and Applied Behavior
... autism (Sanders, Murtha, Gupta, Murdoch, Raubeson, Willsey et al., 2012), but at present the causal evidence is not definitive. The discovery of the “mirror neuron” system (see Chapter 11) and its lack of development in autistic children suggest that these youngsters may benefit from intensive behav ...
... autism (Sanders, Murtha, Gupta, Murdoch, Raubeson, Willsey et al., 2012), but at present the causal evidence is not definitive. The discovery of the “mirror neuron” system (see Chapter 11) and its lack of development in autistic children suggest that these youngsters may benefit from intensive behav ...
STUDY GUIDE: UNIT III – BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR AP
... 13-1: What do split brains reveal about functions of our two brain hemispheres? Corpus callosum & split brains Right-left differences in the intact brain 13-2: The biology of Consciousness Cognitive neuroscience Dual processing ...
... 13-1: What do split brains reveal about functions of our two brain hemispheres? Corpus callosum & split brains Right-left differences in the intact brain 13-2: The biology of Consciousness Cognitive neuroscience Dual processing ...
An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology - Home
... Explain behavior in terms of a single cause Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Tendency to ignore information from other areas ...
... Explain behavior in terms of a single cause Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Tendency to ignore information from other areas ...
3 Types of nervous systems
... • They do not have a central nervous system. They just have a network of interconnected neurons running along the walls of their bodies. Network of neurons ...
... • They do not have a central nervous system. They just have a network of interconnected neurons running along the walls of their bodies. Network of neurons ...
Neuroethology

Neuroethology is the evolutionary and comparative approach to the study of animal behavior and its underlying mechanistic control by the nervous system. This interdisciplinary branch of behavioral neuroscience endeavors to understand how the central nervous system translates biologically relevant stimuli into natural behavior. For example, many bats are capable of echolocation which is used for prey capture and navigation. The auditory system of bats is often cited as an example for how acoustic properties of sounds can be converted into a sensory map of behaviorally relevant features of sounds. Neuroethologists hope to uncover general principles of the nervous system from the study of animals with exaggerated or specialized behaviors.As its name implies, neuroethology is a multidisciplinary field composed of neurobiology (the study of the nervous system) and ethology (the study of behavior in natural conditions). A central theme of the field of neuroethology, delineating it from other branches of neuroscience, is this focus on natural behavior. Natural behaviors may be thought of as those behaviors generated through means of natural selection (i.e. finding mates, navigation, locomotion, predator avoidance) rather than behaviors in disease states, or behavioral tasks that are particular to the laboratory.