Stimulus and response
... withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, motor neuron and effector. • E.1.4 Explain how animal responses can be affected by natural selection, using two examples. ...
... withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, motor neuron and effector. • E.1.4 Explain how animal responses can be affected by natural selection, using two examples. ...
Psychology 101 Exam 1
... 19) From a scientific perspective, a major problem with Psychodynamic theory is that it a. Focuses too much on sex b. It is difficult to test its principles c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _____ ...
... 19) From a scientific perspective, a major problem with Psychodynamic theory is that it a. Focuses too much on sex b. It is difficult to test its principles c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _____ ...
Introduction to Psychology - John Marshall High School
... when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
... when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
Nervous System
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
Human Nerve Chapter
... organ systems that integrate and coordinate with each other, the nervous and the endocrine systems. Nervous systems perform these basic functions: Receiving sensory input from the internal and external environments through receptors. Integrating the inputs in a central location to determine an appro ...
... organ systems that integrate and coordinate with each other, the nervous and the endocrine systems. Nervous systems perform these basic functions: Receiving sensory input from the internal and external environments through receptors. Integrating the inputs in a central location to determine an appro ...
Study Questions
... previously incorrect lever. The rationale for this strategy is that the action system would facilitate learning changes in the outcome but the habit system would interfere because it is slow to change. 9. Explain the conceptual model for actions and habits. An subject has an initial experience compo ...
... previously incorrect lever. The rationale for this strategy is that the action system would facilitate learning changes in the outcome but the habit system would interfere because it is slow to change. 9. Explain the conceptual model for actions and habits. An subject has an initial experience compo ...
behaviorism and operant conditioning
... Variable Ratio/Interval reinforcement at unpredictable response numbers/unpredictable amount of time ...
... Variable Ratio/Interval reinforcement at unpredictable response numbers/unpredictable amount of time ...
Biological Psychology
... Learning Objectives Chapters 1 and 3 Spring 2013 Chapter 1: Biopsychology as a Neuroscience Define biopsychology Describe the different disciplines that contribute to the field of neuroscience Key Terms: o Neurons o Neuroanatomy o Neuropathology o Neuropharmacology o Neuropsychology o Cognitiv ...
... Learning Objectives Chapters 1 and 3 Spring 2013 Chapter 1: Biopsychology as a Neuroscience Define biopsychology Describe the different disciplines that contribute to the field of neuroscience Key Terms: o Neurons o Neuroanatomy o Neuropathology o Neuropharmacology o Neuropsychology o Cognitiv ...
So, do worms sleep?
... Despite much progress in our understanding of C. elegans locomotion and navigation, little is known about the regulation of the absence of movement. Yet behavioral quiescent states are universal to the animal world, with the most famous and mysterious of these being sleep. The roundworm C. elegans i ...
... Despite much progress in our understanding of C. elegans locomotion and navigation, little is known about the regulation of the absence of movement. Yet behavioral quiescent states are universal to the animal world, with the most famous and mysterious of these being sleep. The roundworm C. elegans i ...
Text - Department of Physiology, UCLA
... the relationship between excitability and neuronal survival at different stages of life. We use a wide variety of experimental approaches to address these issues, including electrophysiology, imaging, biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and behavioral analysis. In the past few years, we have ...
... the relationship between excitability and neuronal survival at different stages of life. We use a wide variety of experimental approaches to address these issues, including electrophysiology, imaging, biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and behavioral analysis. In the past few years, we have ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint notes
... = the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms. ...
... = the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms. ...
Option A Neural Development Study Guide A1 A2
... The different parts of the brain have specific functions The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary processes The cerebral cortex forms a large part of the human brain and is folded so that it will fit within the cranium That cerebral hemispheres are responsible for higher order functions Tha ...
... The different parts of the brain have specific functions The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary processes The cerebral cortex forms a large part of the human brain and is folded so that it will fit within the cranium That cerebral hemispheres are responsible for higher order functions Tha ...
CHAPTER 5: SIMPLE NERVOUS SYSTEMS AND BEHAVIOR
... • Explicit or declarative memory: the recall of information about people, places, and objects, and it requires the medial temporal lobe and the hippocampus. • Implicit or procedural memory: perceptual/motor skills, habits, including classical and operant conditioning, habituation, and sensitization. ...
... • Explicit or declarative memory: the recall of information about people, places, and objects, and it requires the medial temporal lobe and the hippocampus. • Implicit or procedural memory: perceptual/motor skills, habits, including classical and operant conditioning, habituation, and sensitization. ...
File - BHS AP Psychology
... response to an action potential and these neurotransmitters are chemicals that carry the neural message across the synapse to other neurons during neural transmission allowing for one nerve to communicate with another. __________ Point 9: Synapse: Students should explain that neural transmission inv ...
... response to an action potential and these neurotransmitters are chemicals that carry the neural message across the synapse to other neurons during neural transmission allowing for one nerve to communicate with another. __________ Point 9: Synapse: Students should explain that neural transmission inv ...
The Nervous System – Use notebook paper if
... Draw a neuron and describe the three types of neurons. ...
... Draw a neuron and describe the three types of neurons. ...
PSY110 Psychology
... One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous ...
... One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous ...
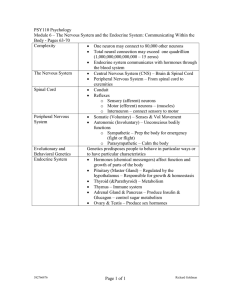
Module 6
... One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates by using hormones that travel through the blood system ...
... One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates by using hormones that travel through the blood system ...
Motivation
... Motivation is necessary for behavior but does not guarantee it. How we choose among competing goals is not well understood. Survival-related behavior is best understood. ...
... Motivation is necessary for behavior but does not guarantee it. How we choose among competing goals is not well understood. Survival-related behavior is best understood. ...
Introduction to the Symposium: Brain
... borrowed from other disciplines will also be described. ...
... borrowed from other disciplines will also be described. ...
Neuroethology

Neuroethology is the evolutionary and comparative approach to the study of animal behavior and its underlying mechanistic control by the nervous system. This interdisciplinary branch of behavioral neuroscience endeavors to understand how the central nervous system translates biologically relevant stimuli into natural behavior. For example, many bats are capable of echolocation which is used for prey capture and navigation. The auditory system of bats is often cited as an example for how acoustic properties of sounds can be converted into a sensory map of behaviorally relevant features of sounds. Neuroethologists hope to uncover general principles of the nervous system from the study of animals with exaggerated or specialized behaviors.As its name implies, neuroethology is a multidisciplinary field composed of neurobiology (the study of the nervous system) and ethology (the study of behavior in natural conditions). A central theme of the field of neuroethology, delineating it from other branches of neuroscience, is this focus on natural behavior. Natural behaviors may be thought of as those behaviors generated through means of natural selection (i.e. finding mates, navigation, locomotion, predator avoidance) rather than behaviors in disease states, or behavioral tasks that are particular to the laboratory.