The role of the nervous system in detecting and
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
Chapter 2 – Biology of the Mind
... • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. • Discuss the infl uence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms). • Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on b ...
... • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. • Discuss the infl uence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms). • Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on b ...
Slide ()
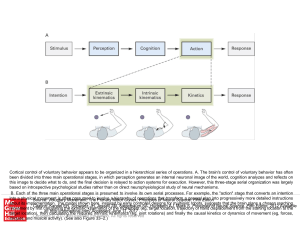
... Cortical control of voluntary behavior appears to be organized in a hierarchical series of operations. A. The brain's control of voluntary behavior has often been divided into three main operational stages, in which perception generates an internal neuronal image of the world, cognition analyzes and ...
... Cortical control of voluntary behavior appears to be organized in a hierarchical series of operations. A. The brain's control of voluntary behavior has often been divided into three main operational stages, in which perception generates an internal neuronal image of the world, cognition analyzes and ...
Bayesian Curve Fitting and Neuron Firing Patterns
... One of the most important techniques in learning about the functioning of the brain has involved examining neuronal activity in laboratory animals under varying experimental conditions. Neural information is represented and communicated through series of action potentials, or spike trains, and the c ...
... One of the most important techniques in learning about the functioning of the brain has involved examining neuronal activity in laboratory animals under varying experimental conditions. Neural information is represented and communicated through series of action potentials, or spike trains, and the c ...
Behavior can be learned
... The following questions are considered when analyzing animal behavior: • What is the stimulus that elicits the behavior and what is the physiological mechanism of the response? (proximate cause) • How do animal’s experiences influence the response? (proximate cause) • How does the behavior aid survi ...
... The following questions are considered when analyzing animal behavior: • What is the stimulus that elicits the behavior and what is the physiological mechanism of the response? (proximate cause) • How do animal’s experiences influence the response? (proximate cause) • How does the behavior aid survi ...
Habituation - WordPress.com
... Acquisition: Learning to pair a behavior with its consequence. Extinction: When a particular behavior stops being paired with a consequence. Spontaneous Recovery: Returning to a behavior for which you are no longer reinforced. Generalization: Assuming that similar behaviors will also generate the sa ...
... Acquisition: Learning to pair a behavior with its consequence. Extinction: When a particular behavior stops being paired with a consequence. Spontaneous Recovery: Returning to a behavior for which you are no longer reinforced. Generalization: Assuming that similar behaviors will also generate the sa ...
Introduction - Florida Atlantic University
... The corpus callosum is a bundle of axons that interconnects the two cerebral hemispheres Callotomy involves cutting the corpus callosum to ...
... The corpus callosum is a bundle of axons that interconnects the two cerebral hemispheres Callotomy involves cutting the corpus callosum to ...
Brumberg - QC Queens College
... individual elements of a cortical circuit and how they interact brings us a step closer to understanding the function of the circuit as a whole and ultimately its behavior in response to environmental stimuli. While the analogy applies to the neocortex, deciphering the cortical microcircuit is much ...
... individual elements of a cortical circuit and how they interact brings us a step closer to understanding the function of the circuit as a whole and ultimately its behavior in response to environmental stimuli. While the analogy applies to the neocortex, deciphering the cortical microcircuit is much ...
Ch. 3 Power point
... 1. Ex. Humpback whales and bubble blowing behavior (read p. 48-49) 2. Problem: Hypo science difficult to do with animal behavior (Size, space, care, etc. may be impractical) a. Can still do this type of science in wild (Read p. 49-Jane Goodall) b. Must often observe behaviors in ...
... 1. Ex. Humpback whales and bubble blowing behavior (read p. 48-49) 2. Problem: Hypo science difficult to do with animal behavior (Size, space, care, etc. may be impractical) a. Can still do this type of science in wild (Read p. 49-Jane Goodall) b. Must often observe behaviors in ...
The Process of Science: Studying Animal Behavior
... 2. Ex. Digger wasps all build nests same way, even if raised in isolation Ex. Bird nest building behavior B. Not completely isolated from environment, though 1. Ex. Wasp: needs right sandy nest building site, proper nutrition to grow up strong enough to build nest, physical skills must be developed ...
... 2. Ex. Digger wasps all build nests same way, even if raised in isolation Ex. Bird nest building behavior B. Not completely isolated from environment, though 1. Ex. Wasp: needs right sandy nest building site, proper nutrition to grow up strong enough to build nest, physical skills must be developed ...
9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... 5) What are the two major kinds of aggression in cats that can be elicited from electrical stimulation of the hypothalamus? How can we be sure that the kind that corresponds to predatory aggression is not due to increased hunger? 6) Describe an experiment that indicates connections to the motor syst ...
... 5) What are the two major kinds of aggression in cats that can be elicited from electrical stimulation of the hypothalamus? How can we be sure that the kind that corresponds to predatory aggression is not due to increased hunger? 6) Describe an experiment that indicates connections to the motor syst ...
C13 Lesson 2 extra credit
... 1. How are a stimulus and a response related? 2. How do the three different types of neurons function? 3. What is a nerve net? How many specialized neurons does a nerve net include? 4. What are the three functions of a brain? 5. How are animals with many sense organs able to process many stimuli at ...
... 1. How are a stimulus and a response related? 2. How do the three different types of neurons function? 3. What is a nerve net? How many specialized neurons does a nerve net include? 4. What are the three functions of a brain? 5. How are animals with many sense organs able to process many stimuli at ...
Review for Quiz 2 Fixed Action Pattern Types of neurons Anatomy of
... Define and know examples of the following types of rhythms Ultradian Infradian Circadian Circannual Exogenous vs. Endogenous rhythms Free running rhythms Entrainment & Zeitgeiber What is the SCN and where ...
... Define and know examples of the following types of rhythms Ultradian Infradian Circadian Circannual Exogenous vs. Endogenous rhythms Free running rhythms Entrainment & Zeitgeiber What is the SCN and where ...
Elicited Behavior Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can`t
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
File
... Ethology: study of animal behavior, specifically many species in natural environment; questions evolution and behaviors Behaviorism: behaviors can be modified by experience to respond to unnamed stimuli; Ivan Pavlov Proximate Causes: Immediate genetic, physiological, neurological, & developmental me ...
... Ethology: study of animal behavior, specifically many species in natural environment; questions evolution and behaviors Behaviorism: behaviors can be modified by experience to respond to unnamed stimuli; Ivan Pavlov Proximate Causes: Immediate genetic, physiological, neurological, & developmental me ...
Organization of Behavior
... act on central pattern generators changes in activity in brainstem "command" circuits directed by sensory input + or klinotaxis (single receptor compares stimulus over time) tropotaxis (paired receptors--simultaneous comparison) telotaxis (toward a goal--e.g. swim toward shore) not well studied in v ...
... act on central pattern generators changes in activity in brainstem "command" circuits directed by sensory input + or klinotaxis (single receptor compares stimulus over time) tropotaxis (paired receptors--simultaneous comparison) telotaxis (toward a goal--e.g. swim toward shore) not well studied in v ...
I. Innate vs. Learned Behavior
... B. Learned Behavior – also called acquired behavior; behavior that changes as a result of experience. Develop over time. 4 major types: habituation, classical conditioning, operant conditioning, insight learning 1. Habituation – process by which an animal decreases or stops its response to a repetit ...
... B. Learned Behavior – also called acquired behavior; behavior that changes as a result of experience. Develop over time. 4 major types: habituation, classical conditioning, operant conditioning, insight learning 1. Habituation – process by which an animal decreases or stops its response to a repetit ...
Animal Behavior Study Guide
... ____ 1. A forceful act used to dominate or control another animal ____ 2. An exchange of information ____ 3. An instinctive seasonal movement of animals ____ 4. An area that an animal defends from other members of its species ____ 5. Animals that are active during the night ____ 6. A group of animal ...
... ____ 1. A forceful act used to dominate or control another animal ____ 2. An exchange of information ____ 3. An instinctive seasonal movement of animals ____ 4. An area that an animal defends from other members of its species ____ 5. Animals that are active during the night ____ 6. A group of animal ...
Animal Behavior 09
... organisms more efficient. Often, there is a division-oflabor setup & most, if not all, of the organisms are related to one another. Therefore, by sticking together, it increases the chances that those genes of the individual (which are also in the collective group) go on to future generations. ...
... organisms more efficient. Often, there is a division-oflabor setup & most, if not all, of the organisms are related to one another. Therefore, by sticking together, it increases the chances that those genes of the individual (which are also in the collective group) go on to future generations. ...
Learning about Learning - by Directly Driving Networks of Neurons
... Associate Professor of Bioengineering University of Pittsburgh New behaviors require new patterns of neural activity among the population of neurons that control behavior. How can the brain find a pattern of activity appropriate for the desired behavior? Why does that learning process take time? To ...
... Associate Professor of Bioengineering University of Pittsburgh New behaviors require new patterns of neural activity among the population of neurons that control behavior. How can the brain find a pattern of activity appropriate for the desired behavior? Why does that learning process take time? To ...
Neuroethology

Neuroethology is the evolutionary and comparative approach to the study of animal behavior and its underlying mechanistic control by the nervous system. This interdisciplinary branch of behavioral neuroscience endeavors to understand how the central nervous system translates biologically relevant stimuli into natural behavior. For example, many bats are capable of echolocation which is used for prey capture and navigation. The auditory system of bats is often cited as an example for how acoustic properties of sounds can be converted into a sensory map of behaviorally relevant features of sounds. Neuroethologists hope to uncover general principles of the nervous system from the study of animals with exaggerated or specialized behaviors.As its name implies, neuroethology is a multidisciplinary field composed of neurobiology (the study of the nervous system) and ethology (the study of behavior in natural conditions). A central theme of the field of neuroethology, delineating it from other branches of neuroscience, is this focus on natural behavior. Natural behaviors may be thought of as those behaviors generated through means of natural selection (i.e. finding mates, navigation, locomotion, predator avoidance) rather than behaviors in disease states, or behavioral tasks that are particular to the laboratory.