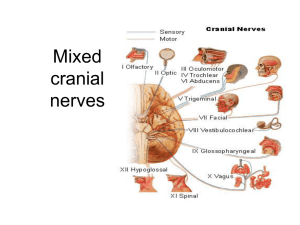
Animal Physiology, Chapter 10
... muscles • The effectors of the ANS are cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands ...
... muscles • The effectors of the ANS are cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands ...
Post-Operative Time Effects after Sciatic Nerve Crush on the
... numerical density of alpha motoneurons. The present results, are based on using method which provides absolute estimates of cell number rather than ratios [15, 19, 20]. This method has been rapidly gaining acceptance, because not only it is the most efficient quantification method, but also unbiased ...
... numerical density of alpha motoneurons. The present results, are based on using method which provides absolute estimates of cell number rather than ratios [15, 19, 20]. This method has been rapidly gaining acceptance, because not only it is the most efficient quantification method, but also unbiased ...
brainstem
... terminate in the dorsal horn cells • Ventral Corticospinal Tract – Originates in the pyramidal cells (motor area of the cortex) Impulses related to equilibrium and antigravity reflexes • Vestibulospinal Tract – Fibers originate in the vestibular nuclei of the medulla and terminate at level of the sa ...
... terminate in the dorsal horn cells • Ventral Corticospinal Tract – Originates in the pyramidal cells (motor area of the cortex) Impulses related to equilibrium and antigravity reflexes • Vestibulospinal Tract – Fibers originate in the vestibular nuclei of the medulla and terminate at level of the sa ...
A cellular mechanism for cortical associations: an organizing
... that although small (sub-threshold) signals contribute only to their respective spike initiation zones, the fact that input has reached threshold in one zone is quickly signaled to the other zone. This provides the possibility for associative interactions within the neuron by which the activity of o ...
... that although small (sub-threshold) signals contribute only to their respective spike initiation zones, the fact that input has reached threshold in one zone is quickly signaled to the other zone. This provides the possibility for associative interactions within the neuron by which the activity of o ...
Modelling fast stimulus-response association learning along the
... Fast SR learning is traditionally presented as an associative learning process following the Hebbian principle “what fires together, wires together”. For instance, if a neuron activated by the stimulus has weak connections with several neurons that can drive different responses, the activation of a ...
... Fast SR learning is traditionally presented as an associative learning process following the Hebbian principle “what fires together, wires together”. For instance, if a neuron activated by the stimulus has weak connections with several neurons that can drive different responses, the activation of a ...
PDF file - Izhikevich
... the general architectural principles of neocortex, Pearson et al. (1987) simulated a model of a cortical somatosensory area. They showed that patterned input resulted in the formation of neuronal groups within the simulated cortical sheet, in accord with the theory of neuronal group selection (TNGS; ...
... the general architectural principles of neocortex, Pearson et al. (1987) simulated a model of a cortical somatosensory area. They showed that patterned input resulted in the formation of neuronal groups within the simulated cortical sheet, in accord with the theory of neuronal group selection (TNGS; ...
JEB Classics - Journal of Experimental Biology
... ␥-efferent (Leksell, 1945). Stimulation of these axons caused no detectable contraction but excited an afferent discharge from the spindles. This was seen as a means by which the response of the spindles to muscle length change could be modified by the central nervous system. At the same time it had ...
... ␥-efferent (Leksell, 1945). Stimulation of these axons caused no detectable contraction but excited an afferent discharge from the spindles. This was seen as a means by which the response of the spindles to muscle length change could be modified by the central nervous system. At the same time it had ...
39_LectureSlides
... *Prison nursing home: with open cribs, a lively environment and extensive interaction with the mother, (even though she lived in the prison next door) *Foundling home with nurses caring for several babies: where cribs were shielded, there was no intimate interaction with the mother or other caregive ...
... *Prison nursing home: with open cribs, a lively environment and extensive interaction with the mother, (even though she lived in the prison next door) *Foundling home with nurses caring for several babies: where cribs were shielded, there was no intimate interaction with the mother or other caregive ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... • The axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron (axodendritic) • The axon of one neuron and the soma of another neuron (axosomic) • The axon of one neuron and the axon of another neuron (axoaxonic) • The axon of a neuron and a muscle ...
... • The axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron (axodendritic) • The axon of one neuron and the soma of another neuron (axosomic) • The axon of one neuron and the axon of another neuron (axoaxonic) • The axon of a neuron and a muscle ...
The Spinal Interneurons and Properties of
... Mg 2⫹ saline so the NMDAR-mediated component of glutamatergic excitation would be clear. Possible RB neurons showed no response or a single spike to skin stimulation and no input during fictive swimming (Clarke et al., 1984). Possible dlc interneurons showed a short-latency EPSP to skin stimulation ...
... Mg 2⫹ saline so the NMDAR-mediated component of glutamatergic excitation would be clear. Possible RB neurons showed no response or a single spike to skin stimulation and no input during fictive swimming (Clarke et al., 1984). Possible dlc interneurons showed a short-latency EPSP to skin stimulation ...
Resting Potential
... • Ion channels that respond to ntm are called chemically gated channels (as opposed to those that are voltage-gated & are involved in sending A.P.) • Changes in chem. gated channels create local changes called synaptic potentials (a small, temporary change in the potential charge of a neuron) • They ...
... • Ion channels that respond to ntm are called chemically gated channels (as opposed to those that are voltage-gated & are involved in sending A.P.) • Changes in chem. gated channels create local changes called synaptic potentials (a small, temporary change in the potential charge of a neuron) • They ...
Neurotransmitters
... These channels open and close rapidly providing a means for rapid activation or rapid inhibition of postsynaptic neurons. There might be EPSP’s firing at the same time as IPSP’s. Add up all the charges from the excitatory and inhibitory potentials to see which one wins! Temporal summation: same pres ...
... These channels open and close rapidly providing a means for rapid activation or rapid inhibition of postsynaptic neurons. There might be EPSP’s firing at the same time as IPSP’s. Add up all the charges from the excitatory and inhibitory potentials to see which one wins! Temporal summation: same pres ...
Comparative analysis of the baseline spike activity of
... random interspike intervals accounted for only 1.3% of cells (Fig. 2, I). Analysis of histograms of interspike intervals for neurons in the fastigial nucleus in normal conditions showed a predominance of polymodal neurons (64.5%) (Fig. 3, B, III). There were significantly fewer mono- and bimodal neu ...
... random interspike intervals accounted for only 1.3% of cells (Fig. 2, I). Analysis of histograms of interspike intervals for neurons in the fastigial nucleus in normal conditions showed a predominance of polymodal neurons (64.5%) (Fig. 3, B, III). There were significantly fewer mono- and bimodal neu ...
Somatosensory Systems: Pain and Temperature - Dr
... B. First-Order Neurons. Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion, with their central axon forming the dorsolateral fasciculus (Lissauer’s tract). In Lissauer’s tract the incoming fibers divide into ascending and descending branches. Most branches are ascending. All branches ultimately syna ...
... B. First-Order Neurons. Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion, with their central axon forming the dorsolateral fasciculus (Lissauer’s tract). In Lissauer’s tract the incoming fibers divide into ascending and descending branches. Most branches are ascending. All branches ultimately syna ...
Bayesian Retrieval In Associative Memories With Storage Errors
... errors in the initial patterns presented or if there are errors in the synaptic weight matrix [12]. Both sorts of error are highly likely in large-scale hardware implementations in silicon or optical devices and also in networks of biological neurons. With the notable exception of [13], one of the m ...
... errors in the initial patterns presented or if there are errors in the synaptic weight matrix [12]. Both sorts of error are highly likely in large-scale hardware implementations in silicon or optical devices and also in networks of biological neurons. With the notable exception of [13], one of the m ...
A visual processing task: Retina and V1
... spike is produced the preceding stimulus is recorded. The average gives the spike triggered average. Right: the spike triggered average thus constructed for simple cells in V1. From (Rieke et al., 1996) and from (Jones and Palmer, 1987). in which cell receive mainly input from either right or left e ...
... spike is produced the preceding stimulus is recorded. The average gives the spike triggered average. Right: the spike triggered average thus constructed for simple cells in V1. From (Rieke et al., 1996) and from (Jones and Palmer, 1987). in which cell receive mainly input from either right or left e ...
Initiation of the arousal response
... effects are common. The following analysis is neither exhaustive nor altogether precise, since arcane technical details that would add discriminatory levels of information have been omitted. The brain systems or axes most discussed in this context are those regulating arousal, memory, emotion, moti ...
... effects are common. The following analysis is neither exhaustive nor altogether precise, since arcane technical details that would add discriminatory levels of information have been omitted. The brain systems or axes most discussed in this context are those regulating arousal, memory, emotion, moti ...
On the Role of the Pontine Brainstem in Vocal Pattern Generation: A
... the Society for Neuroscience, and the specifications of the German Animal Welfare Law for the prevention of cruelty to animals. Care was taken to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering. All three experimental animals behaved normally to human caretakers and to other animals in the c ...
... the Society for Neuroscience, and the specifications of the German Animal Welfare Law for the prevention of cruelty to animals. Care was taken to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering. All three experimental animals behaved normally to human caretakers and to other animals in the c ...