Chapter 3 The Plasma Membrane: transport across cell membrane
... through which specific ions can diffuse down their electrochemical gradients. 3.Active transport Movement of a molecule across a membrane driven by energy. 4.Endocytosis Uptake of material into a cell by an invagination of a the plasma membrane and its internalization in a membrane-bounded vesicle. ...
... through which specific ions can diffuse down their electrochemical gradients. 3.Active transport Movement of a molecule across a membrane driven by energy. 4.Endocytosis Uptake of material into a cell by an invagination of a the plasma membrane and its internalization in a membrane-bounded vesicle. ...
powerpoint
... Mechanisms governing the secondary burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and basic pathways of cell death from hyperoxia. 1: Loss of plasma membrane integrity from lipid peroxidation by ROS. 2: ROS damage to the mitochondria membranes and deactivation of enzyme systems and cytochrome chain. 3: This ...
... Mechanisms governing the secondary burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and basic pathways of cell death from hyperoxia. 1: Loss of plasma membrane integrity from lipid peroxidation by ROS. 2: ROS damage to the mitochondria membranes and deactivation of enzyme systems and cytochrome chain. 3: This ...
Slide 1
... repeats of N-acetylglucosamine and Nacetylmuramic acid, with the latter cross-linked between strands by short peptides. Many sheets of peptidoglycan can be present, depending on the organism. ...
... repeats of N-acetylglucosamine and Nacetylmuramic acid, with the latter cross-linked between strands by short peptides. Many sheets of peptidoglycan can be present, depending on the organism. ...
9-2 Continues - Southgate Schools
... Every time 2 high-energy electrons transport down the electron transport chain, their energy is used to transport hydrogen ions (H+) across the membrane. ...
... Every time 2 high-energy electrons transport down the electron transport chain, their energy is used to transport hydrogen ions (H+) across the membrane. ...
CO2 would move across a plasma membrane more quickly than
... cell increase, and the CFTR channel is open, in what direction will chloride ions and water move across the cell membrane? • A. Chloride ions will move out of the cell, and water will move into the cell. • B. Both chloride ions and water will move out of the cell. • C. Chloride ions will move into t ...
... cell increase, and the CFTR channel is open, in what direction will chloride ions and water move across the cell membrane? • A. Chloride ions will move out of the cell, and water will move into the cell. • B. Both chloride ions and water will move out of the cell. • C. Chloride ions will move into t ...
What agents? What war?
... Used to do work (move stuff around) used for active transport to make/maintain ion and solute gradients Lots of other roles ...
... Used to do work (move stuff around) used for active transport to make/maintain ion and solute gradients Lots of other roles ...
Anionic proteins are trapped Inside the cell
... gradients across the cell membrane • Electrical force moves K+ into the cell (cell has more neg. charges) • Chemical gradient favors K+ to leave the cell (K+ concentration is low outside) • These forces reach a steady state ...
... gradients across the cell membrane • Electrical force moves K+ into the cell (cell has more neg. charges) • Chemical gradient favors K+ to leave the cell (K+ concentration is low outside) • These forces reach a steady state ...
Preview Sample 1
... hydrogen ions pass from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, activating ATP synthase. b. hydrogen ions pass from the intermembrane space to the mitochondrial matrix, activating ATP synthase. c. water passes from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, activating ATP synt ...
... hydrogen ions pass from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, activating ATP synthase. b. hydrogen ions pass from the intermembrane space to the mitochondrial matrix, activating ATP synthase. c. water passes from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, activating ATP synt ...
electron transport chain
... Electrons from these donors are passed through an electron transport chain to oxygen, which is reduced to water. This is a multi-step redox process that occurs on the mitochondrial inner membrane. The enzymes that catalyze these reactions have the remarkable ability to simultaneously create a proton ...
... Electrons from these donors are passed through an electron transport chain to oxygen, which is reduced to water. This is a multi-step redox process that occurs on the mitochondrial inner membrane. The enzymes that catalyze these reactions have the remarkable ability to simultaneously create a proton ...
Chapter 3: cells
... •These proteins usually act to anchor the cell to other cells or to anchor organelles inside the cell. •Integral proteins – span the entire membrane. •These proteins usually aid in transporting large molecule or ...
... •These proteins usually act to anchor the cell to other cells or to anchor organelles inside the cell. •Integral proteins – span the entire membrane. •These proteins usually aid in transporting large molecule or ...
CELL MEMBRANE
... • Lipids (and particles that are soluble in lipids) pass through with least difficulty. • The plasma membrane tends not to be permeable to polar molecules unless they are small. ...
... • Lipids (and particles that are soluble in lipids) pass through with least difficulty. • The plasma membrane tends not to be permeable to polar molecules unless they are small. ...
File
... factors that read stop codons Stop codons (UAA, UGA or UAG) are read by protein release factors FR1 recognizes UAA or UAG and RF2 recognizes UAA or UGA RF3 is a GTPase that mediates interactions between RF1 or RF2 and the ribosome RF1 and RF2 mimic tRNAs and promote hydrolytic attack on the ester li ...
... factors that read stop codons Stop codons (UAA, UGA or UAG) are read by protein release factors FR1 recognizes UAA or UAG and RF2 recognizes UAA or UGA RF3 is a GTPase that mediates interactions between RF1 or RF2 and the ribosome RF1 and RF2 mimic tRNAs and promote hydrolytic attack on the ester li ...
Document
... 1. Separate compartments within the cytoplasm formed by membranes 2. Mitochondrion = “thread granule”, major source of cell’s energy a. energy is taken from sugar, stored in molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) b. requires oxygen to make this exchange (aerobic metabolism) c. contained within ...
... 1. Separate compartments within the cytoplasm formed by membranes 2. Mitochondrion = “thread granule”, major source of cell’s energy a. energy is taken from sugar, stored in molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) b. requires oxygen to make this exchange (aerobic metabolism) c. contained within ...
Cell Respiration Notes Kelly
... to make CITRIC ACID Each glucose requires TWO turns of cycle 1 GLUCOSE produces: 6 CO2, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP, 8 NADH ...
... to make CITRIC ACID Each glucose requires TWO turns of cycle 1 GLUCOSE produces: 6 CO2, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP, 8 NADH ...
Cell Respiration Notes
... to make CITRIC ACID Each glucose requires TWO turns of cycle 1 GLUCOSE produces: 6 CO2, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP, 8 NADH ...
... to make CITRIC ACID Each glucose requires TWO turns of cycle 1 GLUCOSE produces: 6 CO2, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP, 8 NADH ...
Transport PRactice - Mayfield City Schools
... b. stop moving across the membrane. c. move across the membrane in both directions. d. move across the membrane to the inside of the cell. 4. Which type of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? …………………………….……….. 5. All of the following are examples of cell specialization EXCEPT ...
... b. stop moving across the membrane. c. move across the membrane in both directions. d. move across the membrane to the inside of the cell. 4. Which type of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? …………………………….……….. 5. All of the following are examples of cell specialization EXCEPT ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
... poker chips) called ___________. Each individual sac is called a ____________ • The fluid outside the thylakoids is called ____________ (similar to cytoplasm) • Found in plants & algae and used for the site of photosynthesis ...
... poker chips) called ___________. Each individual sac is called a ____________ • The fluid outside the thylakoids is called ____________ (similar to cytoplasm) • Found in plants & algae and used for the site of photosynthesis ...
electron transport
... Oxidative Phosphorylation? How many ATP made per electron pair through the chain? • e- transport chain yields 10 H+ pumped out per electron pair from NADH to oxygen • 4 H+ flow back into matrix per ATP to cytosol • 10/4 = 2.5 for electrons entering as NADH • For electrons entering as succinate (FADH ...
... Oxidative Phosphorylation? How many ATP made per electron pair through the chain? • e- transport chain yields 10 H+ pumped out per electron pair from NADH to oxygen • 4 H+ flow back into matrix per ATP to cytosol • 10/4 = 2.5 for electrons entering as NADH • For electrons entering as succinate (FADH ...
CHAPTER 6
... NADH Fed into Electron Transport? Most NADH used in electron transport is cytosolic and NADH doesn't cross the inner mitochondrial membrane • "Shuttle systems" effect electron movement without actually carrying NADH • Glycerophosphate shuttle stores electrons in glycerol-3-P, which transfers electro ...
... NADH Fed into Electron Transport? Most NADH used in electron transport is cytosolic and NADH doesn't cross the inner mitochondrial membrane • "Shuttle systems" effect electron movement without actually carrying NADH • Glycerophosphate shuttle stores electrons in glycerol-3-P, which transfers electro ...
CPP1
... protein of POR 1 (CPP1), an essential protein for chloroplast development, plays a role in the regulation of POR stability and function. CPP1 contains a J-like domain and three transmembrane domains and is localized in the thylakoid and envelope membranes, and interacts with POR isoforms in chloropl ...
... protein of POR 1 (CPP1), an essential protein for chloroplast development, plays a role in the regulation of POR stability and function. CPP1 contains a J-like domain and three transmembrane domains and is localized in the thylakoid and envelope membranes, and interacts with POR isoforms in chloropl ...
chapter7_Sections 5
... phosphorylation in mitochondria • Defects in any of the thousands of other proteins used by mitochondria (such as frataxin) may be involved in many ...
... phosphorylation in mitochondria • Defects in any of the thousands of other proteins used by mitochondria (such as frataxin) may be involved in many ...
CO 2 - cloudfront.net
... don’t keep burning energy unless we need to. • However, some mitochondria have a protein in the inner membrane that lets H+ ions move freely back across the membrane. These are called “Uncoupling proteins” because they decouple the production of ATP from the rest of the electron transport chain. Why ...
... don’t keep burning energy unless we need to. • However, some mitochondria have a protein in the inner membrane that lets H+ ions move freely back across the membrane. These are called “Uncoupling proteins” because they decouple the production of ATP from the rest of the electron transport chain. Why ...
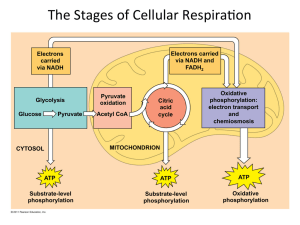
The Stages of Cellular RespiraWon
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
(Western) Blotting
... After proteins are transferred from gel to membrane, the membrane is blocked using 5% milk. Blocking prevents non-specific interactions After blocking, the membrane is incubated in primary antibody ...
... After proteins are transferred from gel to membrane, the membrane is blocked using 5% milk. Blocking prevents non-specific interactions After blocking, the membrane is incubated in primary antibody ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.