Exam Name___________________________________
... 53) The sodium-potassium pump is called an electrogenic pump because it 53) ______ A) is used to drive the transport of other molecules against a concentration gradient. B) pumps equal quantities of Na+ and K+ across the membrane. C) pumps hydrogen ions out of the cell. D) contributes to the membran ...
... 53) The sodium-potassium pump is called an electrogenic pump because it 53) ______ A) is used to drive the transport of other molecules against a concentration gradient. B) pumps equal quantities of Na+ and K+ across the membrane. C) pumps hydrogen ions out of the cell. D) contributes to the membran ...
Midterm Exam Key
... a. a steep concentration gradient (high outside and low inside) is maintained by the Na+-glucose symport b. a steep concentration gradient (high outside and low inside) is maintained by the Na+K+ pump c. a steep concentration gradient (low outside and high inside) is maintained by the Na+glucose sym ...
... a. a steep concentration gradient (high outside and low inside) is maintained by the Na+-glucose symport b. a steep concentration gradient (high outside and low inside) is maintained by the Na+K+ pump c. a steep concentration gradient (low outside and high inside) is maintained by the Na+glucose sym ...
Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English
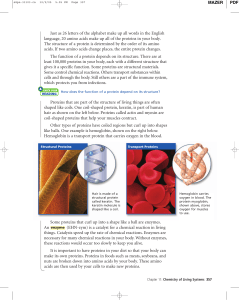
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
5IntracellTrans
... B. The protein eventually will move through the vesicular pathway. C. This occurs when proteins are transported into chloroplasts and mitochondria. D. The signal peptide is cleaved after the protein enters its target destination. E. transport requires the action of a “membrane transport complex.” 2. ...
... B. The protein eventually will move through the vesicular pathway. C. This occurs when proteins are transported into chloroplasts and mitochondria. D. The signal peptide is cleaved after the protein enters its target destination. E. transport requires the action of a “membrane transport complex.” 2. ...
Scientific Method
... lipid bilayer. The phosphate heads face the watery fluids inside the cell and outside the cell. Lipid tails are sandwiched inside the bilayer. The phospholipids in the cell membrane are constantly being formed and broken down by chemical reactions in living cells. The picture below illustrates the l ...
... lipid bilayer. The phosphate heads face the watery fluids inside the cell and outside the cell. Lipid tails are sandwiched inside the bilayer. The phospholipids in the cell membrane are constantly being formed and broken down by chemical reactions in living cells. The picture below illustrates the l ...
notes powerpoint
... rhythmic waves ( wavelengths) Entire range = electromagnetic spectrum Visible light drives photosynthesis ...
... rhythmic waves ( wavelengths) Entire range = electromagnetic spectrum Visible light drives photosynthesis ...
Chapter 5 Quiz: Cellular respiration and fermentation Mark your
... 11) NADH is converted to ATP in a process known as ___________________. a. ...
... 11) NADH is converted to ATP in a process known as ___________________. a. ...
Methods of Cell Transport, Such As Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active
... • Tonicity: the movement of water into and out of cells in response to the water concentration on the outside of the cell. Water moves from where it is in high concentration to where it is in low concentration until an equilibrium of the water concentration is reached. ...
... • Tonicity: the movement of water into and out of cells in response to the water concentration on the outside of the cell. Water moves from where it is in high concentration to where it is in low concentration until an equilibrium of the water concentration is reached. ...
Polarity and Medications
... packed cells that separate the blood and the fluid of the central nervous system (spinal cord and brain). Prevents harmful materials, such as pathogens, from moving to the brain. Non-polar materials (O2 and CO2) can diffuse through, but polar molecules such as glucose must have special channel p ...
... packed cells that separate the blood and the fluid of the central nervous system (spinal cord and brain). Prevents harmful materials, such as pathogens, from moving to the brain. Non-polar materials (O2 and CO2) can diffuse through, but polar molecules such as glucose must have special channel p ...
Cell Transport - Ms. Nevel's Biology Website
... with the cell membrane and forces the material outside the cell. ...
... with the cell membrane and forces the material outside the cell. ...
MEMBRANE POTENTIALS
... (b) inside negative > Na+ attracted (electrical gradient) BUT: (a) membrane channels closed (voltage gated) (b) Na+ pumps to outside ...
... (b) inside negative > Na+ attracted (electrical gradient) BUT: (a) membrane channels closed (voltage gated) (b) Na+ pumps to outside ...
Practice Lecture Exam 2
... The light-dependent reactions occur during the daylight hours; the light-independent reactions occur when it is dark. d. The light-dependent reactions produce water as a by-product; the light-independent reactions produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. e. The products of the light-dependent reac ...
... The light-dependent reactions occur during the daylight hours; the light-independent reactions occur when it is dark. d. The light-dependent reactions produce water as a by-product; the light-independent reactions produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. e. The products of the light-dependent reac ...
Cellular Energetics
... • ETC proteins embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane • ETC membrane proteins accept e- from NADH and FADH2 • e- are passed down the ETC via redox reactions until they reach the final e- acceptor (O2) to form water • No ATP is made by ETC; must be coupled to oxidative phosphorylation via chemi ...
... • ETC proteins embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane • ETC membrane proteins accept e- from NADH and FADH2 • e- are passed down the ETC via redox reactions until they reach the final e- acceptor (O2) to form water • No ATP is made by ETC; must be coupled to oxidative phosphorylation via chemi ...
Polypeptide: alpha-helix and beta
... Concept: Peptide chains tend to form orderly hydrogen-bonded arrangements. Materials: alpha-helix and beta-sheet models made by Prof. Ewing Procedure: Models may be used to help explain secondary protein structure. Related Information: Fibrous proteins are stringy, tough, and usually insoluble in ...
... Concept: Peptide chains tend to form orderly hydrogen-bonded arrangements. Materials: alpha-helix and beta-sheet models made by Prof. Ewing Procedure: Models may be used to help explain secondary protein structure. Related Information: Fibrous proteins are stringy, tough, and usually insoluble in ...
(B) Where CO 2
... Glucose(6 C’s) is split into 2 pyruvate molecules (each 2 C’s) Each Pyruvate is an acid Each step has a different enzyme. This is anerobic respiration (without using O2) Believed to be most ancient of metabolic processes since it does not need O2; found in all eukaryote & prokaryote cells. The enzym ...
... Glucose(6 C’s) is split into 2 pyruvate molecules (each 2 C’s) Each Pyruvate is an acid Each step has a different enzyme. This is anerobic respiration (without using O2) Believed to be most ancient of metabolic processes since it does not need O2; found in all eukaryote & prokaryote cells. The enzym ...
Ece 593 - Southern Illinois University Carbondale
... Membrane proteins • There are basically two classes of membrane proteins. They are; integral and peripheral membrane proteins. • Integral membrane proteins – Closely associated with the membrane lipids and cannot be extracted from the membrane without disrupting the lipid bilayer – They are amphipa ...
... Membrane proteins • There are basically two classes of membrane proteins. They are; integral and peripheral membrane proteins. • Integral membrane proteins – Closely associated with the membrane lipids and cannot be extracted from the membrane without disrupting the lipid bilayer – They are amphipa ...
Study Guide Answers
... 15. The sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport. 16. Moving very large particles out of the cell is called exocytosis. 17. In exocytosis, wastes are moved out of the cell in vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane. 18. Endocytosis involves moving large particles into the cell. 19. ...
... 15. The sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport. 16. Moving very large particles out of the cell is called exocytosis. 17. In exocytosis, wastes are moved out of the cell in vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane. 18. Endocytosis involves moving large particles into the cell. 19. ...
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, and Peroxisomes
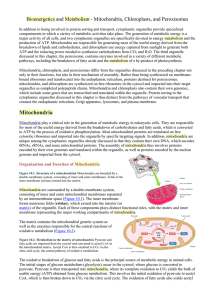
... Mitochondria contain their own genetic system, which is separate and distinct from the nuclear genome of the cell. Mitochondria are thought to have evolved from bacteria that developed a symbiotic relationship in which they lived within larger cells (endosymbiosis). This hypothesis has recently been ...
... Mitochondria contain their own genetic system, which is separate and distinct from the nuclear genome of the cell. Mitochondria are thought to have evolved from bacteria that developed a symbiotic relationship in which they lived within larger cells (endosymbiosis). This hypothesis has recently been ...
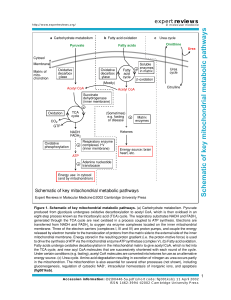
Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways
... membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the energy released by electron transfer to the translocation of protons from the matrix side to the external side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Energy stored in the resulting proton gradient (i.e. ...
... membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the energy released by electron transfer to the translocation of protons from the matrix side to the external side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Energy stored in the resulting proton gradient (i.e. ...
transport proteins
... important for cell to cell recognition • The membrane plays the key role in cell to cell recognition. – Cell to cell recognition is the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another. – This attribute is important in cell sorting and organization as tissues and organs in ...
... important for cell to cell recognition • The membrane plays the key role in cell to cell recognition. – Cell to cell recognition is the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another. – This attribute is important in cell sorting and organization as tissues and organs in ...
BIOL241cell3JUN2012
... • Carrier-‐mediated transport of ions and organic substrates into or out of the cell down their concentraDon gradient. SDll passive • Can also be called passive carrier-‐mediated transport Note: if energ ...
... • Carrier-‐mediated transport of ions and organic substrates into or out of the cell down their concentraDon gradient. SDll passive • Can also be called passive carrier-‐mediated transport Note: if energ ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.