Key to Exam 2
... E. How does autoradiography differ from fluorography? • autoradiography is the exposure of film due to direct interactions of radiation with film • fluorography is an indirect exposure of the film resulting from fluorescence generated via the radiation interacting with a fluor (low energy) or a fluo ...
... E. How does autoradiography differ from fluorography? • autoradiography is the exposure of film due to direct interactions of radiation with film • fluorography is an indirect exposure of the film resulting from fluorescence generated via the radiation interacting with a fluor (low energy) or a fluo ...
Big Idea #2
... Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules in Photosystems I and II which are embedded in the thylakoid membranes. Electrons become excited and move down an electron transport chain from photosystem I to photosystem II. Their energy is used to pump H+ ions into the stroma. Electrons los ...
... Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules in Photosystems I and II which are embedded in the thylakoid membranes. Electrons become excited and move down an electron transport chain from photosystem I to photosystem II. Their energy is used to pump H+ ions into the stroma. Electrons los ...
General Biology Notes 9 The Cell Membrane (pages 204, 205, 208
... a. Diffusion is the natural tendency of solutes to move from an area where they are _______________ concentrated to an area where they are less _________________ b. This is a very important process because, as we will see, it is largely responsible for getting __________ and _____________ into the c ...
... a. Diffusion is the natural tendency of solutes to move from an area where they are _______________ concentrated to an area where they are less _________________ b. This is a very important process because, as we will see, it is largely responsible for getting __________ and _____________ into the c ...
lec04
... A. Membrane Composition and Structure • Biological membranes consist of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. The fluid mosaic model describes a phospholipid bilayer in which membrane proteins move laterally within the membrane. • Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane and ...
... A. Membrane Composition and Structure • Biological membranes consist of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. The fluid mosaic model describes a phospholipid bilayer in which membrane proteins move laterally within the membrane. • Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane and ...
Respiration and Lipid Metabolism Aerobic
... Seeds e.g. commercial oils: sunflower, soybean, peanut, cotton Fruits e.g. avocado, olives 2. Energy Storage – same as above 3. Energy harvest – chlorophylls & carotenoids 4. Membranes – phospholipids 5. Protection – waxes 6. Hormones – isopreness Æ precursors to some hormones (ABA & GA) metabolic p ...
... Seeds e.g. commercial oils: sunflower, soybean, peanut, cotton Fruits e.g. avocado, olives 2. Energy Storage – same as above 3. Energy harvest – chlorophylls & carotenoids 4. Membranes – phospholipids 5. Protection – waxes 6. Hormones – isopreness Æ precursors to some hormones (ABA & GA) metabolic p ...
Slide 1
... • A ____________ is a large molecule made up of many similar or identical subunits. • Water molecules associate with each other because they are held together by ___________ bonds. ...
... • A ____________ is a large molecule made up of many similar or identical subunits. • Water molecules associate with each other because they are held together by ___________ bonds. ...
Cellular Respiration
... with oxaloacetate to form citrate – coenzyme A is released to be reused Kreb’s cycle rearranges citrate to regenerate oxaloacetate giving off 2 CO2, 1 ATP and four electron carriers (1 FADH2 and 3 NADH) per pyruvate molecule ...
... with oxaloacetate to form citrate – coenzyme A is released to be reused Kreb’s cycle rearranges citrate to regenerate oxaloacetate giving off 2 CO2, 1 ATP and four electron carriers (1 FADH2 and 3 NADH) per pyruvate molecule ...
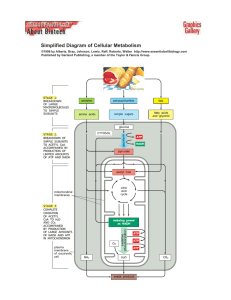
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
A Closer Look at Cell Membranes
... Many types of molecules and ions diffuse across a lipid bilayer only with the help of specific transport proteins. A. Passive Transport Requires no energy input Some passive transporters are open channels Other passive transporters are gated and change shape when a specific molecule binds to the ...
... Many types of molecules and ions diffuse across a lipid bilayer only with the help of specific transport proteins. A. Passive Transport Requires no energy input Some passive transporters are open channels Other passive transporters are gated and change shape when a specific molecule binds to the ...
Cell Membrane - Dickinson ISD
... The cytoplasm of a cell is at a certain concentration. The fluid surrounding the cell is at another concentration. Diffusion – movement of particles from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration. When the particles in the two areas have moved to where both areas are ...
... The cytoplasm of a cell is at a certain concentration. The fluid surrounding the cell is at another concentration. Diffusion – movement of particles from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration. When the particles in the two areas have moved to where both areas are ...
Chapter 11: Membrane transport
... Many proteins use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to fuel transport. (2) V-type ATPase Multimeric transporters often work in the reverse direction (ATP synthesis) F1Fo ATPase is the mitochondrial ATP synthase H+-ATPase of lysosomes acidify the organelle ...
... Many proteins use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to fuel transport. (2) V-type ATPase Multimeric transporters often work in the reverse direction (ATP synthesis) F1Fo ATPase is the mitochondrial ATP synthase H+-ATPase of lysosomes acidify the organelle ...
Photosynthesis - Crestwood Local Schools
... Energy from these photons zaps the e- and gives it more energy *this energy is used in 2 different processes in the light reactions: a.) Making ATP: ~ excited e- get replaced by splitting H2O molecules - H donates its e- and is left with H+ - O isn't used anymore so it leaves as O2 gas ~ excited e- ...
... Energy from these photons zaps the e- and gives it more energy *this energy is used in 2 different processes in the light reactions: a.) Making ATP: ~ excited e- get replaced by splitting H2O molecules - H donates its e- and is left with H+ - O isn't used anymore so it leaves as O2 gas ~ excited e- ...
Transport in Bacterial Cells
... • Higher potential energy of water • Higher concentration of water molecules that have free energy of movement ...
... • Higher potential energy of water • Higher concentration of water molecules that have free energy of movement ...
Name: Assignment: Cell #4: Structure of Cell Membranes Let`s take
... Let's take a look at the structure of the cell membrane. Surprisingly, this barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the outside is not thick, nor is it particularly sturdy. It is composed mostly of layers of special lipids called phospholipids. Phospholipids are a lot like triglycerides. ...
... Let's take a look at the structure of the cell membrane. Surprisingly, this barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the outside is not thick, nor is it particularly sturdy. It is composed mostly of layers of special lipids called phospholipids. Phospholipids are a lot like triglycerides. ...
ATP (energy)
... exchange for two K+ (potassium ions) – ATP (energy) is needed to make the protein change its shape so that Na+ and K+ can move through it and cross the membrane ...
... exchange for two K+ (potassium ions) – ATP (energy) is needed to make the protein change its shape so that Na+ and K+ can move through it and cross the membrane ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 30: Ion pumps in the membrane
... AspH+ can line up with the exit half channel and deprotonate. In effect, the Fo module is a nanoscale turbine powered by H+ moving down its electrochemical gradient, or a pump if the direction of rotation is reversed (Lehninger pp.680-683). ...
... AspH+ can line up with the exit half channel and deprotonate. In effect, the Fo module is a nanoscale turbine powered by H+ moving down its electrochemical gradient, or a pump if the direction of rotation is reversed (Lehninger pp.680-683). ...
221_exam_2_2003
... clear that microbes account for most of the “fixed” carbon on earth. Consequently, we have also discovered that microbes have evolved several mechanisms for “fixing” carbon dioxide. Briefly discuss three mechanisms of carbon dioxide fixation found in ...
... clear that microbes account for most of the “fixed” carbon on earth. Consequently, we have also discovered that microbes have evolved several mechanisms for “fixing” carbon dioxide. Briefly discuss three mechanisms of carbon dioxide fixation found in ...
TEXT S1- SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS In-solution digestion
... quantify every peptide from every protein in all samples, quantitative information about the complete proteome was not available in our proteomic datasets. For some proteins quantitative information was lacking or highly variable, making it impossible to determine whether these proteins were Bvg-reg ...
... quantify every peptide from every protein in all samples, quantitative information about the complete proteome was not available in our proteomic datasets. For some proteins quantitative information was lacking or highly variable, making it impossible to determine whether these proteins were Bvg-reg ...
Membrane Structure and Function POGIL
... • YOU are responsible for YOUR role!!! • I will be checking that you are performing your role. THIS is what influences your final grade as a group. TEAMWORK!! • When you get to a stop sign, make sure your team has all of the answers for each question and that they are consistent (NOT IDENTICAL). The ...
... • YOU are responsible for YOUR role!!! • I will be checking that you are performing your role. THIS is what influences your final grade as a group. TEAMWORK!! • When you get to a stop sign, make sure your team has all of the answers for each question and that they are consistent (NOT IDENTICAL). The ...
Cellular Transport WebQuest
... Passive Transport Thermal Motion Concentration Gradients Solutions Biological Membranes Scroll down to example #1 (how perfume spreads throughout a room) and read it. Next scroll down to example #2 (salt dissolving in water) and read it. Next scroll down to example #3 (diffusion will occur through a ...
... Passive Transport Thermal Motion Concentration Gradients Solutions Biological Membranes Scroll down to example #1 (how perfume spreads throughout a room) and read it. Next scroll down to example #2 (salt dissolving in water) and read it. Next scroll down to example #3 (diffusion will occur through a ...
Cellular Transport WebQuest
... Passive Transport Thermal Motion Concentration Gradients Solutions Biological Membranes Scroll down to example #1 (how perfume spreads throughout a room) and read it. Next scroll down to example #2 (salt dissolving in water) and read it. Next scroll down to example #3 (diffusion will occur through a ...
... Passive Transport Thermal Motion Concentration Gradients Solutions Biological Membranes Scroll down to example #1 (how perfume spreads throughout a room) and read it. Next scroll down to example #2 (salt dissolving in water) and read it. Next scroll down to example #3 (diffusion will occur through a ...
Chapter 7 Photosynthesis
... photosystem II) cooperate in the light reactions. Each type of photosystem has a characteristic reaction center. – Photosystem II, which functions first, is called P680 because its pigment absorbs light with a wavelength of 680 nm. – Photosystem I, which functions second, is called P700 because ...
... photosystem II) cooperate in the light reactions. Each type of photosystem has a characteristic reaction center. – Photosystem II, which functions first, is called P680 because its pigment absorbs light with a wavelength of 680 nm. – Photosystem I, which functions second, is called P700 because ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.