Oxidative Phosphorylation
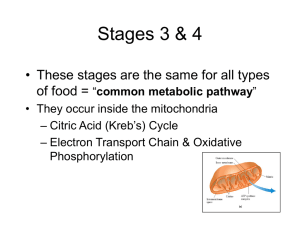
... • Citric acid cycle produces NADH & FADH2 • Electrons flow from NADH & FADH2 in the mitochondria (electron transport chain) generates energy in the form of ATP (oxidative phosphorylation). ...
... • Citric acid cycle produces NADH & FADH2 • Electrons flow from NADH & FADH2 in the mitochondria (electron transport chain) generates energy in the form of ATP (oxidative phosphorylation). ...
the Four Stages of Biochemical Energy Production
... Series of electron carriers Each carrier exists in oxidized or reduced form High energy electrons pass down the electron transport chain in a series of redox reactions These reactions are coupled with ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). They lose energy as they pass along the chain ...
... Series of electron carriers Each carrier exists in oxidized or reduced form High energy electrons pass down the electron transport chain in a series of redox reactions These reactions are coupled with ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). They lose energy as they pass along the chain ...
Cellular Respiration
... – reducing equivalents-3 NADH & 1 FADH2 • further oxidized in electron transport chain – 1 GTP-ATP equivalent Since two pyruvates are obtained from oxidation of glucose amounts need to be doubled for complete oxidation results ...
... – reducing equivalents-3 NADH & 1 FADH2 • further oxidized in electron transport chain – 1 GTP-ATP equivalent Since two pyruvates are obtained from oxidation of glucose amounts need to be doubled for complete oxidation results ...
Document
... • Water can pass through plasma membrane in 2 ways: – through lipid bilayer by simple diffusion – through aquaporins (integral membrane proteins) ...
... • Water can pass through plasma membrane in 2 ways: – through lipid bilayer by simple diffusion – through aquaporins (integral membrane proteins) ...
AnimalCellLabels.1.2
... are either found freely in the cytoplasm or attached to endoplasmic reticulum. Free ribosomes and bound ribosomes are interchangeable and the cell can change their numbers according to metabolic needs. Composed 25% of the cell's mass. Paired cylindrical organelles near the nucleus composed of nine t ...
... are either found freely in the cytoplasm or attached to endoplasmic reticulum. Free ribosomes and bound ribosomes are interchangeable and the cell can change their numbers according to metabolic needs. Composed 25% of the cell's mass. Paired cylindrical organelles near the nucleus composed of nine t ...
Biology 251 17 September 2015 Exam One FORM G KEY PRINT
... All the above are true e. Both a and c are true 23. What are the wastes produced by aerobic metabolism? a. ADP b. O2 c. CO2 d. Water e. Both c and d 24. Which of the following cause(s) electrical potentials on membranes? a. The uniform distribution of Na+ across membranes b. The differential permeab ...
... All the above are true e. Both a and c are true 23. What are the wastes produced by aerobic metabolism? a. ADP b. O2 c. CO2 d. Water e. Both c and d 24. Which of the following cause(s) electrical potentials on membranes? a. The uniform distribution of Na+ across membranes b. The differential permeab ...
Study Guide for Lecture Examination 3
... two sub-‐phases: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. The electron transport chain is a group of proteins and other particles embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The chain has two functi ...
... two sub-‐phases: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. The electron transport chain is a group of proteins and other particles embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The chain has two functi ...
Lecture 6 - The Plasma Membrane
... • Membranes must be fluid to work properly; they are usually about as fluid as salad oil ...
... • Membranes must be fluid to work properly; they are usually about as fluid as salad oil ...
Cellular respiration includes three pathways
... 39. _______________________________ and ______________________________________ respiration enables cells to produce ATP without the use of _________________________. 40. In_________________________________________, pyruvate is converted to ethanol in two steps. 41. Does fermentation result in the pr ...
... 39. _______________________________ and ______________________________________ respiration enables cells to produce ATP without the use of _________________________. 40. In_________________________________________, pyruvate is converted to ethanol in two steps. 41. Does fermentation result in the pr ...
Passive and active transport
... into the cell across the membrane and this needs a highly active glycolytic pathway to provide ATP needed to this transport. When we add fluoride which inhibits glycolysis, the intracellular conc of K+ will decrease and Na+ will rise. ...
... into the cell across the membrane and this needs a highly active glycolytic pathway to provide ATP needed to this transport. When we add fluoride which inhibits glycolysis, the intracellular conc of K+ will decrease and Na+ will rise. ...
Metabolism Objective Project
... (Student only needs to get three of these!) 1) Anaerobic is without the presence of oxygen, while aerobic is with 2) Anaerobic only makes 2 ATP per glucose molecule, aerobic makes between 30-32 3) In anaerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor is an organic molecule such as pyruvate. In aerob ...
... (Student only needs to get three of these!) 1) Anaerobic is without the presence of oxygen, while aerobic is with 2) Anaerobic only makes 2 ATP per glucose molecule, aerobic makes between 30-32 3) In anaerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor is an organic molecule such as pyruvate. In aerob ...
Ch 6 Cells Kelly
... - Fluid filled space enclosed by inner membrane (MATRIX) CONTAINS DNA, ribosomes, enzymes for cellular respiration • Site of cellular respiration - Break down sugars, fats, and other fuels in the presence of oxygen - Generate ATP • Cells with high energy needs (EX: muscle cells) have large numbers o ...
... - Fluid filled space enclosed by inner membrane (MATRIX) CONTAINS DNA, ribosomes, enzymes for cellular respiration • Site of cellular respiration - Break down sugars, fats, and other fuels in the presence of oxygen - Generate ATP • Cells with high energy needs (EX: muscle cells) have large numbers o ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide
... oxygen is released as waste hydrogen ions are transported across thylakoid membrane 38. _________________ captures energy and produces energy-carrying molecules chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight energized electrons are used to make NADPH NADPH is transferred to light-independent reactions 39. ...
... oxygen is released as waste hydrogen ions are transported across thylakoid membrane 38. _________________ captures energy and produces energy-carrying molecules chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight energized electrons are used to make NADPH NADPH is transferred to light-independent reactions 39. ...
D-Glucose is a carbohydrate which can be classified as which of the
... for ATP hydrolysis is -7.6 kcal/mol. Based on your answer to 14B, how many molecules of Cl- could theoretically be expelled for each ATP that is used? (2 points) ...
... for ATP hydrolysis is -7.6 kcal/mol. Based on your answer to 14B, how many molecules of Cl- could theoretically be expelled for each ATP that is used? (2 points) ...
Lecture 3a - Membs and Transport
... cross the membrane without help. Why not? This separates the extracellular fluid from the cytosol which is important for homeostasis Nonpolar molecules, fat soluble organic molecules (e.g. steroids), and water can ...
... cross the membrane without help. Why not? This separates the extracellular fluid from the cytosol which is important for homeostasis Nonpolar molecules, fat soluble organic molecules (e.g. steroids), and water can ...
CH 9 PowerPoint
... The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups: with one nucleotide containing an adenosine ring, and the other containing nicotinamide. In metabolism, NAD+ is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. Th ...
... The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups: with one nucleotide containing an adenosine ring, and the other containing nicotinamide. In metabolism, NAD+ is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. Th ...
Matrix: Citric Acid Cycle and Pyruvate Oxidation Mitochondrion A
... • Production of ATP as a result of electron transfer through carriers in the Electron Transport Chain – Electrons pass through a set of membrane-associated carriers by a series of redox reactions – Energy from electron transport powers the active transport of H+ to the intermembrane compartment of t ...
... • Production of ATP as a result of electron transfer through carriers in the Electron Transport Chain – Electrons pass through a set of membrane-associated carriers by a series of redox reactions – Energy from electron transport powers the active transport of H+ to the intermembrane compartment of t ...
Cell Structure and Function
... cells lacking a cell wall to resist osmotic lysis. Proteins and glycoproteins in the cytoplasmic membrane are quite diverse and function as: a. channel proteins to form pores for the free transport of small molecules and ions across the membrane b. carrier proteins for facilitated diffusion an ...
... cells lacking a cell wall to resist osmotic lysis. Proteins and glycoproteins in the cytoplasmic membrane are quite diverse and function as: a. channel proteins to form pores for the free transport of small molecules and ions across the membrane b. carrier proteins for facilitated diffusion an ...
Cellular Respiration
... of the cell and it has three parts associated with it: Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain. ...
... of the cell and it has three parts associated with it: Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain. ...
Cell Membrane Activity - Blair Community Schools
... clip into the soapy membrane so that it passes through to other side. Did the membrane seal around the pencil and clip and stay intact? ________ Next take the pencil or paper clip and dip it into the soapy solution. Why do you think the pencil or paper clip must be coated with soap solution in order ...
... clip into the soapy membrane so that it passes through to other side. Did the membrane seal around the pencil and clip and stay intact? ________ Next take the pencil or paper clip and dip it into the soapy solution. Why do you think the pencil or paper clip must be coated with soap solution in order ...
Metabolic Processes Unit
... d. It requires the addition of inorganic phosphate. e. None of the above statements is true. 16. The electron transport chain converts the potential energy collected by NADH and FADH2 into a. The kinetic energy of CO2 molecules. b. The kinetic energy of ATP molecules. c. The kinetic energy of water ...
... d. It requires the addition of inorganic phosphate. e. None of the above statements is true. 16. The electron transport chain converts the potential energy collected by NADH and FADH2 into a. The kinetic energy of CO2 molecules. b. The kinetic energy of ATP molecules. c. The kinetic energy of water ...
Evolutionary and Molecular Biology of Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
... Multi-subunit complexes must properly assemble in the (correct) membranes of the organelle ...
... Multi-subunit complexes must properly assemble in the (correct) membranes of the organelle ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.