Cellular Respiration
... with oxaloacetate to form citrate – coenzyme A is released to be reused Kreb’s cycle rearranges citrate to regenerate oxaloacetate giving off 2 CO2, 1 ATP and four electron carriers (1 FADH2 and 3 NADH) per pyruvate molecule ...
... with oxaloacetate to form citrate – coenzyme A is released to be reused Kreb’s cycle rearranges citrate to regenerate oxaloacetate giving off 2 CO2, 1 ATP and four electron carriers (1 FADH2 and 3 NADH) per pyruvate molecule ...
HB_Cell_Resp_KEYS_and_Review_Notes_12_BH
... The biochemical pathway that breaks down 2 acetyl CoA to produce 4CO2, 2ATP, 6NADH, and 2FADH2 ...
... The biochemical pathway that breaks down 2 acetyl CoA to produce 4CO2, 2ATP, 6NADH, and 2FADH2 ...
energy carrier!
... ETS (cytochrome chain) is a series of reduction/oxidation reactions Enzymes embedded in mitochondrial membranes ...
... ETS (cytochrome chain) is a series of reduction/oxidation reactions Enzymes embedded in mitochondrial membranes ...
Ch9 Review Sheet - Canvas by Instructure
... 19. Red blood cells do not contain mitochondria. Which stage or stages of sugar breakdown can take place in these cells? Explain your answer. 20. How is the process by which your body extracts energy from food similar to how a car's engine extracts energy from fuel? How is it different? 21. Explain ...
... 19. Red blood cells do not contain mitochondria. Which stage or stages of sugar breakdown can take place in these cells? Explain your answer. 20. How is the process by which your body extracts energy from food similar to how a car's engine extracts energy from fuel? How is it different? 21. Explain ...
Effects of Surface Modification of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane
... Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is considered as a clean and efficient energy conversion device for mobile and stationary applications. Among all the components of the PEMFC, the interface between the electrolyte and electrode catalyst plays an important role in determining the cell p ...
... Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is considered as a clean and efficient energy conversion device for mobile and stationary applications. Among all the components of the PEMFC, the interface between the electrolyte and electrode catalyst plays an important role in determining the cell p ...
BY 123 Mock Exam #2 Answer Key Chapters 8,9,10,12,13 Catabolic
... d. NADH supplies would be exhausted, and ATP synthesis would cease e. No proton gradient would be produced, and ATP synthesis would cease. Substrate-level phosphorylation: a. Involves the shifting of a phosphate group from ATP to a substrate b. Can use NADH or FADH2 c. Takes place only in the cytoso ...
... d. NADH supplies would be exhausted, and ATP synthesis would cease e. No proton gradient would be produced, and ATP synthesis would cease. Substrate-level phosphorylation: a. Involves the shifting of a phosphate group from ATP to a substrate b. Can use NADH or FADH2 c. Takes place only in the cytoso ...
Cellular Respiration
... A: Food, Oxygen, Water Q: WHY??? A: To make ATP so their cells can do cellular work. Ex. powering: active transport, cell division, protein synthesis. ...
... A: Food, Oxygen, Water Q: WHY??? A: To make ATP so their cells can do cellular work. Ex. powering: active transport, cell division, protein synthesis. ...
The Action Potential
... Some parts are more positive or more negative Membranes are used to keep the negatives and positives separate b/c they attract. ...
... Some parts are more positive or more negative Membranes are used to keep the negatives and positives separate b/c they attract. ...
Oliver Bawmann week 6
... If a membrane is selectively permeable then this means that it a barrier that only allows passage of specific things such as water, oxygen and nutrients. While some things pass fairly easy others have difficulty and need facilitation proteins or simply cannot pass through at all. By being selectivel ...
... If a membrane is selectively permeable then this means that it a barrier that only allows passage of specific things such as water, oxygen and nutrients. While some things pass fairly easy others have difficulty and need facilitation proteins or simply cannot pass through at all. By being selectivel ...
Assignment 5 Bioenergy/ Photosynthesis
... replace the electrons lost from the first pigment system (PSII). Remember PSII gave its electrons to the second pigment system (PSI). The H+ ion moves across the thylakoid membrane where the cytochrome complexes are embedded to cause a build-up of potential energy. This gradient energy is allowed to ...
... replace the electrons lost from the first pigment system (PSII). Remember PSII gave its electrons to the second pigment system (PSI). The H+ ion moves across the thylakoid membrane where the cytochrome complexes are embedded to cause a build-up of potential energy. This gradient energy is allowed to ...
File
... Glycolysis literally means "_________splitting." In glycolysis, the 6 carbon sugar glucose is split into 2 molecules of pyruvate, also called pyruvic acid. This process produces a net gain of ______ ATP molecules. The resulting molecules of pyruvate each have 3 carbon atoms. Glycolysis takes place i ...
... Glycolysis literally means "_________splitting." In glycolysis, the 6 carbon sugar glucose is split into 2 molecules of pyruvate, also called pyruvic acid. This process produces a net gain of ______ ATP molecules. The resulting molecules of pyruvate each have 3 carbon atoms. Glycolysis takes place i ...
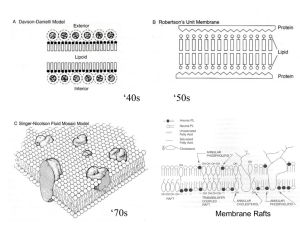
lecture 11
... bilayer would need to deform to prevent exposure of the hydrophobic amino acids to water. This would be energetically unfavorable. So, if the protein can “move” to a “raft” of different thickness, there would be a driving force for such partitioning. ...
... bilayer would need to deform to prevent exposure of the hydrophobic amino acids to water. This would be energetically unfavorable. So, if the protein can “move” to a “raft” of different thickness, there would be a driving force for such partitioning. ...
4 ADP + 4 Pi are converted to 2 ATP to produce a net gain of 2 ATP
... can be used to do work. This is analogous to water stored behind a dam How does the cell eliminate excess H? Each hydrogen atom is composed of 1 proton and 1 electron consequently, a transfer of H atoms is essentially a transfer of electrons These electron transfer reactions are called oxidation - r ...
... can be used to do work. This is analogous to water stored behind a dam How does the cell eliminate excess H? Each hydrogen atom is composed of 1 proton and 1 electron consequently, a transfer of H atoms is essentially a transfer of electrons These electron transfer reactions are called oxidation - r ...
„Biochemical reconstitution of protein complexes involved in
... Although it’s well understood that these proteins have to interact with each other, little is known about the molecular mechanism of this phenomena. Using available structural and biochemical data I predicted surface exposed residues critical for individual protein:protein interactions within tripar ...
... Although it’s well understood that these proteins have to interact with each other, little is known about the molecular mechanism of this phenomena. Using available structural and biochemical data I predicted surface exposed residues critical for individual protein:protein interactions within tripar ...
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... 5. Identify the inputs and outputs and location of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 7. Compare and contrast the structure and function of mitochondria and chloroplasts. ...
... 5. Identify the inputs and outputs and location of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 7. Compare and contrast the structure and function of mitochondria and chloroplasts. ...
11.17.11.ATP.synthase
... subunits within Fo transfer this rotation to the γ subunit which acts as a shaft connecting Fo to F1. Rotation of γ about the hexamer of α3β3 converts b subunits successively from O to T to L. ...
... subunits within Fo transfer this rotation to the γ subunit which acts as a shaft connecting Fo to F1. Rotation of γ about the hexamer of α3β3 converts b subunits successively from O to T to L. ...
Biology Chapter 4
... Chlorophyll is a molecule in chloroplasts that absorbs light energy Two MainTypes: chlorophyll A & B ...
... Chlorophyll is a molecule in chloroplasts that absorbs light energy Two MainTypes: chlorophyll A & B ...
Membranes & Channels PPT
... Uphill against the gradient Requires ATP • Secondary Active Transport Uphill against the gradient Hitches a ride with an ion going downhill ...
... Uphill against the gradient Requires ATP • Secondary Active Transport Uphill against the gradient Hitches a ride with an ion going downhill ...
Class Notes 2
... cell at 100 u/sec. When the cell is damaged, an action potential is generated and the streaming stops. Protoplasmic streaming is produced by actinomyosin as found in animal muscle. Streaming is inhibited when Ca++ moves into the cytoplasm activating a protein kinase that phosphorylates myosin so it ...
... cell at 100 u/sec. When the cell is damaged, an action potential is generated and the streaming stops. Protoplasmic streaming is produced by actinomyosin as found in animal muscle. Streaming is inhibited when Ca++ moves into the cytoplasm activating a protein kinase that phosphorylates myosin so it ...
Studying photosynthetic organisms from different angles
... Maryy Hamilton (([email protected]). y @ p ...
... Maryy Hamilton (([email protected]). y @ p ...
Cellular Respiration
... Autotrophs remove CO2 from environment and fix it into sugars (normally glucose) whereas heterotrophs consume those sugars and return them to the environment as CO2. O2 is “exhaled” from autotrophs and is required by autotrophs to break down sugars to remove the energy used to form ATP. 2. Write a b ...
... Autotrophs remove CO2 from environment and fix it into sugars (normally glucose) whereas heterotrophs consume those sugars and return them to the environment as CO2. O2 is “exhaled” from autotrophs and is required by autotrophs to break down sugars to remove the energy used to form ATP. 2. Write a b ...
Cellular Respiration
... time 2 high-energy electrons transport down the electron transport chain, their energy is used to transport hydrogen ions (H+) across the membrane H+ build up in the intermembrane space, making it positively charged The other side of the membrane is negatively charge ...
... time 2 high-energy electrons transport down the electron transport chain, their energy is used to transport hydrogen ions (H+) across the membrane H+ build up in the intermembrane space, making it positively charged The other side of the membrane is negatively charge ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... • The phospholipids organize themselves into a bilayer. • The interior of the membrane is fluid, which allows some molecules to move laterally in the membrane. ...
... • The phospholipids organize themselves into a bilayer. • The interior of the membrane is fluid, which allows some molecules to move laterally in the membrane. ...
+ -80 mV
... 1. The membrane conducts ions very poorly and allows the separation of ionic species. This results is a potential difference between the outside and the inside of the membrane. 2. The magnitude of the resting potential is determined by the selective permeability of the membrane to ionic species. 3. ...
... 1. The membrane conducts ions very poorly and allows the separation of ionic species. This results is a potential difference between the outside and the inside of the membrane. 2. The magnitude of the resting potential is determined by the selective permeability of the membrane to ionic species. 3. ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.