Annexins: multifunctional components of growth and adaptation
... partners and a broad range of roles within the cell. However, in contrast to their animal counterparts, the N-terminal region of all known plant annexins is short (;10 amino acids). The crystal structure of bell pepper annexin (AnxCa32) revealed that the short N-terminal ...
... partners and a broad range of roles within the cell. However, in contrast to their animal counterparts, the N-terminal region of all known plant annexins is short (;10 amino acids). The crystal structure of bell pepper annexin (AnxCa32) revealed that the short N-terminal ...
Insights into the Role of Specific Lipids in the
... (Moreau et al., 1998b; Vincent et al., 1999). Table I shows the enrichment of several marker enzyme activities in these purified fractions. The PM from Arabidopsis seedlings was purified by using a two-phase polyethylene glycol (PEG)-dextran partitioning system as explained in ‘‘Materials and Method ...
... (Moreau et al., 1998b; Vincent et al., 1999). Table I shows the enrichment of several marker enzyme activities in these purified fractions. The PM from Arabidopsis seedlings was purified by using a two-phase polyethylene glycol (PEG)-dextran partitioning system as explained in ‘‘Materials and Method ...
The `ins` and `outs` of flavonoid transport
... Anthocyanoplast: initially used to describe cytoplasmic membrane-bound vesicles containing high levels of anthocyanins and regarded as anthocyanin biosynthetic sites. However, later studies confused them with anthocyanic vacuolar inclusion (AVIs), which are more widely observed inside the vacuoles o ...
... Anthocyanoplast: initially used to describe cytoplasmic membrane-bound vesicles containing high levels of anthocyanins and regarded as anthocyanin biosynthetic sites. However, later studies confused them with anthocyanic vacuolar inclusion (AVIs), which are more widely observed inside the vacuoles o ...
Document
... 2. Production of AcoA --> glycolysis & FAoxidation 3. Oxidation of AcoA to CO2 & H2O --> KC & ETC Cellular Energetics ...
... 2. Production of AcoA --> glycolysis & FAoxidation 3. Oxidation of AcoA to CO2 & H2O --> KC & ETC Cellular Energetics ...
Ch13.doc
... below, -32.5kJ/mole in the EOC problem) which is clearly more than ATP + H2O ADP + Pi (30 kJ/mole) which means the usually ATP hydrolysis reaction can not drive the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from acetate + CoA. So, now check out Table 13-6, see below.. The ΔGo’ for ATP + H2O AMP + PPi is -45.6 kJ/ ...
... below, -32.5kJ/mole in the EOC problem) which is clearly more than ATP + H2O ADP + Pi (30 kJ/mole) which means the usually ATP hydrolysis reaction can not drive the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from acetate + CoA. So, now check out Table 13-6, see below.. The ΔGo’ for ATP + H2O AMP + PPi is -45.6 kJ/ ...
Chapter 8 Cellular Respiration
... Glycolysis 4 hydrogen (2 pair) atoms formed – First step in respiration picked up by 2NAD+ 2NADH + (2H+) ETS Occurs 2–ATP used in cytoplasm 4–ATP formedrequire oxygen Doesn’t ...
... Glycolysis 4 hydrogen (2 pair) atoms formed – First step in respiration picked up by 2NAD+ 2NADH + (2H+) ETS Occurs 2–ATP used in cytoplasm 4–ATP formedrequire oxygen Doesn’t ...
Selected Solutions to End of Chapter 13 Problems
... below, -32.5kJ/mole in the EOC problem) which is clearly more than ATP + H2O ADP + Pi (30 kJ/mole) which means the usually ATP hydrolysis reaction can not drive the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from acetate + CoA. So, now check out Table 13-6, see below.. The ΔGo’ for ATP + H2O AMP + PPi is -45.6 kJ/ ...
... below, -32.5kJ/mole in the EOC problem) which is clearly more than ATP + H2O ADP + Pi (30 kJ/mole) which means the usually ATP hydrolysis reaction can not drive the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from acetate + CoA. So, now check out Table 13-6, see below.. The ΔGo’ for ATP + H2O AMP + PPi is -45.6 kJ/ ...
Journal of Biological Chemistry
... upon amino acid incorporation into protein of the liver ribosome system (Table II) just as effectively as it does the decrease in hepatic ATP concentration induced by the same analogue (3). These results tend to implicate cellular BTP deficiency as being important in the inhibition of protein synthe ...
... upon amino acid incorporation into protein of the liver ribosome system (Table II) just as effectively as it does the decrease in hepatic ATP concentration induced by the same analogue (3). These results tend to implicate cellular BTP deficiency as being important in the inhibition of protein synthe ...
Complement - microbiology and immunology on-line
... • C-activation: alteration of C proteins such that they interact with the next component ...
... • C-activation: alteration of C proteins such that they interact with the next component ...
Bio426Lecture19Mar8 - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... 8400 kJ/mole hexose (for the red light example!) One mole of hexose (e.g. glucose or fructose) yields about 2800 kJ when it’s oxidized. (The heat of combustion) Efficiency = energy output/energy input = 2800kJ/8400kJ ...
... 8400 kJ/mole hexose (for the red light example!) One mole of hexose (e.g. glucose or fructose) yields about 2800 kJ when it’s oxidized. (The heat of combustion) Efficiency = energy output/energy input = 2800kJ/8400kJ ...
The Arabidopsis Rab5 Homologs Rha1 and Ara7 Localize to the
... tions of the different proteins were examined. As shown in Fig. 4, BiP:RFP (panels a–c) gave a network pattern as observed previously (Jin et al. 2001). Furthermore, F1-ATPaseγ:RFP (panels e–g) and RFP:SKL (panels i–k) gave punctate staining patterns as expected. None of these markers overlapped wit ...
... tions of the different proteins were examined. As shown in Fig. 4, BiP:RFP (panels a–c) gave a network pattern as observed previously (Jin et al. 2001). Furthermore, F1-ATPaseγ:RFP (panels e–g) and RFP:SKL (panels i–k) gave punctate staining patterns as expected. None of these markers overlapped wit ...
Protein targeting, translocation and Escherichia coli Proteomic analysis of substrate-pathway relationships
... So far, β-barrel membrane proteins have only been found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and mitochondria, and in the outer envelope of chloroplasts. β-barrel membrane proteins are composed of an even number of anti-parallel β-strands arranged in a barrel like structure. The amide and ...
... So far, β-barrel membrane proteins have only been found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and mitochondria, and in the outer envelope of chloroplasts. β-barrel membrane proteins are composed of an even number of anti-parallel β-strands arranged in a barrel like structure. The amide and ...
Enzymes of Glycolysis Are Functionally Associated
... targeting sequences (Emanuelsson et al., 2000). However, there is considerable disagreement between these methods regarding which proteins are mitochondrially targeted, and all of the programs mispredict a small proportion of proteins (Heazlewood et al., 2003). Furthermore, because these methods con ...
... targeting sequences (Emanuelsson et al., 2000). However, there is considerable disagreement between these methods regarding which proteins are mitochondrially targeted, and all of the programs mispredict a small proportion of proteins (Heazlewood et al., 2003). Furthermore, because these methods con ...
assembly of integral membrane proteins from the periplasm into the
... and Gross, 1996); the genes of periplasmic proteases such as DegP (HtrA); the genes of certain outer membrane lipoproteins, such as YfiO; genes of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), such as HtrM (RfaD), LpxD, and LpxA (Dartigalongue et al., 2001; Rouvière et al., 1995) ...
... and Gross, 1996); the genes of periplasmic proteases such as DegP (HtrA); the genes of certain outer membrane lipoproteins, such as YfiO; genes of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), such as HtrM (RfaD), LpxD, and LpxA (Dartigalongue et al., 2001; Rouvière et al., 1995) ...
12-Glycolysis2016-11-15 13:225.6 MB
... substrate directly to ADP. Oxidative: production of ATP molecules from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain Gylcolysis and Krebs cycle use substrate-level phosphorylation. Electron transport chain uses oxidative phosphorylation. ...
... substrate directly to ADP. Oxidative: production of ATP molecules from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain Gylcolysis and Krebs cycle use substrate-level phosphorylation. Electron transport chain uses oxidative phosphorylation. ...
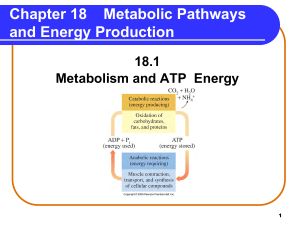
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... • protons (H+) from Complexes I, III, and IV move into the intermembrane space. • a proton gradient is created. • protons return to matrix through ATP synthase, a protein complex. • the flow of protons provides energy for ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). ADP + Pi + Energy ...
... • protons (H+) from Complexes I, III, and IV move into the intermembrane space. • a proton gradient is created. • protons return to matrix through ATP synthase, a protein complex. • the flow of protons provides energy for ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). ADP + Pi + Energy ...
ATP - RCSD
... oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • The citric acid cycle • is also called the Krebs cycle (after the GermanBritish researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), • completes the oxidation of organic molecules, and • generates many NA ...
... oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • The citric acid cycle • is also called the Krebs cycle (after the GermanBritish researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), • completes the oxidation of organic molecules, and • generates many NA ...
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical
... D) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase E) No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic. Answer: D Topic: Concept 9.4 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension ...
... D) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase E) No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic. Answer: D Topic: Concept 9.4 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension ...
Respiration - Biology Junction
... 3. The Krebs cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules: a closer look 4. The inner mitochondrial membrane couples electron transport to ATP synthesis: a closer look 5. Cellular respiration generates many ATP molecules for each sugar molecule it oxidizes: a review Copyright © ...
... 3. The Krebs cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules: a closer look 4. The inner mitochondrial membrane couples electron transport to ATP synthesis: a closer look 5. Cellular respiration generates many ATP molecules for each sugar molecule it oxidizes: a review Copyright © ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.