File
... to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy ...
... to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy ...
AP UNIT 3
... • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
... • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
Choosing the Best Kinase Assay to Meet Your Research Needs
... Protein kinases are enzymes capable of transferring the γphosphate group from ATP to a serine, threonine or tyrosine residue in specific substrate proteins. These phosphorylation events modulate the activity of a vast number of proteins, including ion channels, transcription factors, phosphatases an ...
... Protein kinases are enzymes capable of transferring the γphosphate group from ATP to a serine, threonine or tyrosine residue in specific substrate proteins. These phosphorylation events modulate the activity of a vast number of proteins, including ion channels, transcription factors, phosphatases an ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through channels in ATP synthase • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy ...
... causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through channels in ATP synthase • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy ...
Microbial Metabolism
... the thousands of known enzymes has a characteristic threedimensional shape with a specific surface configuration as a result of its primary, secondary, and tertiary structures (see Figure 2.15, page 46). The unique configuration of each enzyme enables it to “find” the correct substrate from among th ...
... the thousands of known enzymes has a characteristic threedimensional shape with a specific surface configuration as a result of its primary, secondary, and tertiary structures (see Figure 2.15, page 46). The unique configuration of each enzyme enables it to “find” the correct substrate from among th ...
Chapter 9 Powerpoint
... • NADH passes the electrons to the electron transport chain • Unlike an uncontrolled reaction, the electron transport chain passes electrons in a series of steps instead of one explosive reaction • O2 pulls electrons down the chain in an energyyielding tumble • The energy yielded is used to regenera ...
... • NADH passes the electrons to the electron transport chain • Unlike an uncontrolled reaction, the electron transport chain passes electrons in a series of steps instead of one explosive reaction • O2 pulls electrons down the chain in an energyyielding tumble • The energy yielded is used to regenera ...
Overall energy conversion efficiency of a photosynthetic vesicle | eLife
... Computational Biology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, United States; 4Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, University of ...
... Computational Biology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, United States; 4Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, University of ...
mitochondrial biogenesis during
... systems but this is the first time that such a striking transition has been observed . It is interesting to note that treatment of L cells with ethidium bromide leads to progressive mitochondrial changes (Soslau and Nass, 1971) resulting, finally, in mitochondria which are morphologically very simil ...
... systems but this is the first time that such a striking transition has been observed . It is interesting to note that treatment of L cells with ethidium bromide leads to progressive mitochondrial changes (Soslau and Nass, 1971) resulting, finally, in mitochondria which are morphologically very simil ...
Communication - Department of Molecular Physiology and Biophysics
... syntrophin triplet suggesting that all the syntrophins including α- as well as β-type may directly bind to dystrophin (Fig. 2). Previous work by Ozawa's group indicated that one of 43-DAGs was overlaid by dystrophin fusion protein containing cysteinerich and C-terminal domains (16). This interaction ...
... syntrophin triplet suggesting that all the syntrophins including α- as well as β-type may directly bind to dystrophin (Fig. 2). Previous work by Ozawa's group indicated that one of 43-DAGs was overlaid by dystrophin fusion protein containing cysteinerich and C-terminal domains (16). This interaction ...
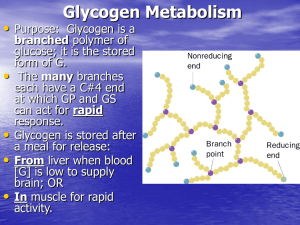
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... catalyzed by phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1). In muscle, phosphorylation of a regulatory glycogen binding protein, GM in response to insulin (which causes dephosphorylation of other Es) at site 1 activates PP1. This results in the opposite activities to the above (GS active to store the plentiful ...
... catalyzed by phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1). In muscle, phosphorylation of a regulatory glycogen binding protein, GM in response to insulin (which causes dephosphorylation of other Es) at site 1 activates PP1. This results in the opposite activities to the above (GS active to store the plentiful ...
The Ultrastructure of Megakaryocytes and Blood
... marginal zone actually takes place (Pease, ’55). The abundance of platelet granules and other organelles in platelets compared with their low frequency in the marginal zone, supports Yamada’s suggestion that, during platelet separation, demarcation membranes extend out toward the cell surface from t ...
... marginal zone actually takes place (Pease, ’55). The abundance of platelet granules and other organelles in platelets compared with their low frequency in the marginal zone, supports Yamada’s suggestion that, during platelet separation, demarcation membranes extend out toward the cell surface from t ...
Autophagy in Plasmodium, a multifunctional pathway?
... a component of the COPII vesicle machinery for trafficking between the ER and Golgi. Sar1 was shown to have similar localization to the ER and small vesicle compartments in P. falciparum blood stages as in yeast, at the ER site for secretion of proteins [67,68]. The role of other Atg protei ...
... a component of the COPII vesicle machinery for trafficking between the ER and Golgi. Sar1 was shown to have similar localization to the ER and small vesicle compartments in P. falciparum blood stages as in yeast, at the ER site for secretion of proteins [67,68]. The role of other Atg protei ...
Placental Transporters Relevant to Drug Distribution across the
... faces the fetal circulation. These two domains of the syncytiotrophoblast plasma membrane are functionally and structurally distinct. The brush-border membrane possesses a microvillous structure that effectively amplifies the surface area, whereas the basal membrane lacks this structural organizatio ...
... faces the fetal circulation. These two domains of the syncytiotrophoblast plasma membrane are functionally and structurally distinct. The brush-border membrane possesses a microvillous structure that effectively amplifies the surface area, whereas the basal membrane lacks this structural organizatio ...
Signal Peptidases
... cleaving signal peptides in bacteria. SPase I can process nonlipoprotein substrates that are exported by the SecYEG pathway or the twin arginine translocation (Tat) pathway. Lipoproteins that are exported by the Sec pathway are cleaved by SPase II. SPase IV cleaves type IV prepilins and prepilin-lik ...
... cleaving signal peptides in bacteria. SPase I can process nonlipoprotein substrates that are exported by the SecYEG pathway or the twin arginine translocation (Tat) pathway. Lipoproteins that are exported by the Sec pathway are cleaved by SPase II. SPase IV cleaves type IV prepilins and prepilin-lik ...
Nucleus-Encoded Genes for Plastid
... been retained, including the leucine biosynthesis pathway, which was only recently recognized in plant plastids. These two parasites represent different evolutionary trajectories in plastid metabolic adaptation. only by investigations of their metabolism or molecular biology that these plastids are ...
... been retained, including the leucine biosynthesis pathway, which was only recently recognized in plant plastids. These two parasites represent different evolutionary trajectories in plastid metabolic adaptation. only by investigations of their metabolism or molecular biology that these plastids are ...
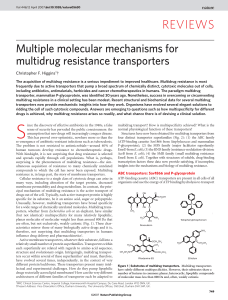
REVIEWS
... magnitude38. Recent structures of AcrB provide insights into the mechanism by which it, and presumably other RND transporters, works39–42. Gram-negative bacteria including E. coli have two cell membranes— a cytoplasmic membrane and an outer membrane—separated by the periplasmic space. Many antibioti ...
... magnitude38. Recent structures of AcrB provide insights into the mechanism by which it, and presumably other RND transporters, works39–42. Gram-negative bacteria including E. coli have two cell membranes— a cytoplasmic membrane and an outer membrane—separated by the periplasmic space. Many antibioti ...
Life 9e - Garvness
... Bloom’s Category: 2. Understanding 19. When a photon is absorbed by a molecule, the photon a. loses its ability to generate any energy. b. raises the molecule from a ground state of low energy to an excited state. c. affects the molecule in ways that are not clearly understood. d. causes a change in ...
... Bloom’s Category: 2. Understanding 19. When a photon is absorbed by a molecule, the photon a. loses its ability to generate any energy. b. raises the molecule from a ground state of low energy to an excited state. c. affects the molecule in ways that are not clearly understood. d. causes a change in ...
Oral Cavity
... • The food is broken down in the mouth by grinding action of the teeth, and is mixed with the saliva by the movements of the tongue and the action of the buccinator muscle. • The thoroughly mixed food is now formed into a bolus on the dorsum of the tongue and pushed upward and backward against the u ...
... • The food is broken down in the mouth by grinding action of the teeth, and is mixed with the saliva by the movements of the tongue and the action of the buccinator muscle. • The thoroughly mixed food is now formed into a bolus on the dorsum of the tongue and pushed upward and backward against the u ...
western blotting - New England Biolabs GmbH
... and positive (TPA-treated) Jurkat lysate, as well as purified recombinant tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. The importance of using a well-validated antibody and the inclusion of proper experimental controls is demonstrated by the cross-reactivity of the alternate providers’ antibodies in both negat ...
... and positive (TPA-treated) Jurkat lysate, as well as purified recombinant tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. The importance of using a well-validated antibody and the inclusion of proper experimental controls is demonstrated by the cross-reactivity of the alternate providers’ antibodies in both negat ...
Cellular Respiration
... receives a phosphate group. The product of this step is two molecules of a new three-carbon compound. As shown in Figure 7-3, the oxidation of G3P is accompanied by the reduction of two molecules of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD!) to NADH. NAD! is similar to NADP!, a compound involved in th ...
... receives a phosphate group. The product of this step is two molecules of a new three-carbon compound. As shown in Figure 7-3, the oxidation of G3P is accompanied by the reduction of two molecules of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD!) to NADH. NAD! is similar to NADP!, a compound involved in th ...
Early bioenergetic evolution
... finally (v) quinone-based (and Q-cycle-dependent) proton gradient generation. Of those five transitions, the first four are posited to have taken place at the vent. Ultimately, all of these bioenergetic processes depend, even today, upon CO2 reduction with low-potential ferredoxin (Fd), generated ei ...
... finally (v) quinone-based (and Q-cycle-dependent) proton gradient generation. Of those five transitions, the first four are posited to have taken place at the vent. Ultimately, all of these bioenergetic processes depend, even today, upon CO2 reduction with low-potential ferredoxin (Fd), generated ei ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration
... Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.