Dissecting sterol function during clathrin-dependent
... lipid bilayer solvent that can interact with peripheral proteins (Simons and Sampaio, 2011). The lipid bilayer results from the self-association of the lipids hydrophobic moieties and the interaction of the hydrophilic moieties with aqueous environments. The same principle acts at the subcellular le ...
... lipid bilayer solvent that can interact with peripheral proteins (Simons and Sampaio, 2011). The lipid bilayer results from the self-association of the lipids hydrophobic moieties and the interaction of the hydrophilic moieties with aqueous environments. The same principle acts at the subcellular le ...
Translocation of proteins across the cell envelope of Gram
... and the lipoprotein signal peptides (type II). A signal peptide usually is 14^25 amino acids long and consists of three identi¢able domains, i.e., the amino (N-), hydrophobic (H-), and carboxy-terminal (C-) regions. The N-region is rich in positively charged amino acids, and is followed by a hydroph ...
... and the lipoprotein signal peptides (type II). A signal peptide usually is 14^25 amino acids long and consists of three identi¢able domains, i.e., the amino (N-), hydrophobic (H-), and carboxy-terminal (C-) regions. The N-region is rich in positively charged amino acids, and is followed by a hydroph ...
Lysenin: A sphingomyelin specific pore
... lysenin and the LRPs. This discrepancy between the two lysenins is explained by the different tag proteins (maltose binding protein vs. six histidine residues) used in the experiments [29]. 3. Glycolipids inhibit lysenin binding to sphingomyelin, whereas cholesterol facilitates oligomerization of ly ...
... lysenin and the LRPs. This discrepancy between the two lysenins is explained by the different tag proteins (maltose binding protein vs. six histidine residues) used in the experiments [29]. 3. Glycolipids inhibit lysenin binding to sphingomyelin, whereas cholesterol facilitates oligomerization of ly ...
ZAMZAMI N, KROEMER G, 2001. The mitochondrion in apoptosis
... outer mitochondrial membranes, precedes the signs of necrotic or apoptotic cell death, including the apoptosis-specific activation of caspases. • MMP is a more accurate predictive parameter for cell death than caspase activation (which often is not required for cell death to occur and, in contrast, ...
... outer mitochondrial membranes, precedes the signs of necrotic or apoptotic cell death, including the apoptosis-specific activation of caspases. • MMP is a more accurate predictive parameter for cell death than caspase activation (which often is not required for cell death to occur and, in contrast, ...
Characterization of CIC transporter proteins Moradi, Hossein
... Cells need to accumulate compounds for different reasons and, thus need to transport solutes against their concentration gradient. This can be achieved in three ways. Firstly, the uphill transport of a solute is driven by the release of chemical energy from the hydrolyzation of ATP or pyrophosphate ...
... Cells need to accumulate compounds for different reasons and, thus need to transport solutes against their concentration gradient. This can be achieved in three ways. Firstly, the uphill transport of a solute is driven by the release of chemical energy from the hydrolyzation of ATP or pyrophosphate ...
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1768:
... S. pneumoniae contains mainly two glycolipids: monoglucosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) and galactosylglucosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG), and two acidic phospholipids: phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and cardiolipin (CL). The cell contains also one neutral lipid, diacylglycerol (DAG) (Fig. 2). For each of the wild ty ...
... S. pneumoniae contains mainly two glycolipids: monoglucosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) and galactosylglucosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG), and two acidic phospholipids: phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and cardiolipin (CL). The cell contains also one neutral lipid, diacylglycerol (DAG) (Fig. 2). For each of the wild ty ...
Chloroplast transit peptides: structure, function and evolution
... thylakoid targeting domain, which is C-terminal to the stromal targeting domain18. By contrast, a detailed study using deletion mutants of trFd have shown that the N-terminal region primarily interacts with MGDG, whereas the C-terminus mediates recognition of negatively charged phospholipids22. The ...
... thylakoid targeting domain, which is C-terminal to the stromal targeting domain18. By contrast, a detailed study using deletion mutants of trFd have shown that the N-terminal region primarily interacts with MGDG, whereas the C-terminus mediates recognition of negatively charged phospholipids22. The ...
Note - EtoosIndia
... The synthesis of ATP is coupled with electron transport system and creation of proton gradient across the membrane during photophosphorylation and oxidative phosphorlaion. Both are same but the difference is that during oxidative phosphorylation high H + ion concentration at intermembrane space/ p ...
... The synthesis of ATP is coupled with electron transport system and creation of proton gradient across the membrane during photophosphorylation and oxidative phosphorlaion. Both are same but the difference is that during oxidative phosphorylation high H + ion concentration at intermembrane space/ p ...
Cellular Respiration: Supplying Energy to Metabolic Reactions
... * Speed up many exergonic, catabolic reactions. You use HEAPS of ATP. Here are some estimates * 10 million molecules per muscle cell per second! * The average vertebrate consumes its own body weight in ATP every day! ...
... * Speed up many exergonic, catabolic reactions. You use HEAPS of ATP. Here are some estimates * 10 million molecules per muscle cell per second! * The average vertebrate consumes its own body weight in ATP every day! ...
13synthesis
... * Polar lipids are targeted to specific cell membrane. After the synthesis in the S.E.R. the polar lipids (phospho, sphingo, glyco lipids) they transferred to different cell membranes by Golgi apparatus in form of vesicles. ...
... * Polar lipids are targeted to specific cell membrane. After the synthesis in the S.E.R. the polar lipids (phospho, sphingo, glyco lipids) they transferred to different cell membranes by Golgi apparatus in form of vesicles. ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentation and O2 in cellular respiration ...
... • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentation and O2 in cellular respiration ...
The biosynthesis of peptidoglycan lipid
... & Strominger (1972) about 30 years ago and some of its properties were investigated. Its optimal pH for activity was near 7.5, the enzyme did not require any cation, was stimulated by nonionic Triton detergents, and failed to hydrolyze isopentenyl pyrophosphate. The gene for this activity, however, ...
... & Strominger (1972) about 30 years ago and some of its properties were investigated. Its optimal pH for activity was near 7.5, the enzyme did not require any cation, was stimulated by nonionic Triton detergents, and failed to hydrolyze isopentenyl pyrophosphate. The gene for this activity, however, ...
Polyphosphate-ATP Amplification Technology: Principle and its
... Fig. 2. Time course of bioluminescence during ATP amplification. (A) ATP amplification was started by adding a 2-µl ATP sample to 48 µl of a reaction mixture containing 0.16 µg of ADK-PPK, 10 µM AMP, 400 µM polyP, 8 mM MgCl2, and 60 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4). The reaction mixture was incubated at 37°C. A ...
... Fig. 2. Time course of bioluminescence during ATP amplification. (A) ATP amplification was started by adding a 2-µl ATP sample to 48 µl of a reaction mixture containing 0.16 µg of ADK-PPK, 10 µM AMP, 400 µM polyP, 8 mM MgCl2, and 60 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4). The reaction mixture was incubated at 37°C. A ...
Articulins and epiplasmins - Journal of Cell Science
... settled, and many of the filamentous systems described in protists do not fall into either actin or IF categories (see, for example, Honts and Williams, 1990; Levy et al., 1996). Protists are among the eukaryotes that possess the most elaborate cell shape and surface architecture. The latter is comp ...
... settled, and many of the filamentous systems described in protists do not fall into either actin or IF categories (see, for example, Honts and Williams, 1990; Levy et al., 1996). Protists are among the eukaryotes that possess the most elaborate cell shape and surface architecture. The latter is comp ...
The Cytoplasm-to-Vacuole Targeting Pathway: A Historical
... used for cell biology studies. Randy Schekman was giving a seminar on campus at that time, and I told him about our project. He suggested that we generate antibodies that only recognized prApe1 and carry out a screen looking for mutants that accumulate the precursor form of the protein. We did attem ...
... used for cell biology studies. Randy Schekman was giving a seminar on campus at that time, and I told him about our project. He suggested that we generate antibodies that only recognized prApe1 and carry out a screen looking for mutants that accumulate the precursor form of the protein. We did attem ...
Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 11e (Madigan/Martinko)
... destruction of the photosynthetic apparatus. Answer: TRUE 37) Phycobiliproteins are the main light-harvesting pigments of the cyanobacteria and the red algae. Answer: TRUE 38) Light-mediated ATP synthesis in all phototrophic organisms involves electron transport through a sequence of electron carrie ...
... destruction of the photosynthetic apparatus. Answer: TRUE 37) Phycobiliproteins are the main light-harvesting pigments of the cyanobacteria and the red algae. Answer: TRUE 38) Light-mediated ATP synthesis in all phototrophic organisms involves electron transport through a sequence of electron carrie ...
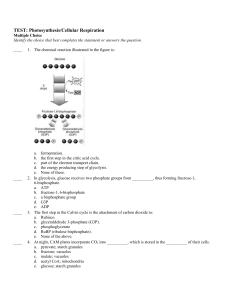
Use to make Test Corrections (Answer in complete sentence +10 pts
... d. electrons; proton e. water molecules; oxygen Which process does not match the starting materials? a. formation of acetyl CoAcitric acid, CO2, NADH b. citric acid cycleacetyl CoA, H2O, NAD+, FAD, ADP, Pi c. electron transport and chemiosmosisNADH, FADH2, O2, ADP, Pi d. glycolysisglucose, ATP, ...
... d. electrons; proton e. water molecules; oxygen Which process does not match the starting materials? a. formation of acetyl CoAcitric acid, CO2, NADH b. citric acid cycleacetyl CoA, H2O, NAD+, FAD, ADP, Pi c. electron transport and chemiosmosisNADH, FADH2, O2, ADP, Pi d. glycolysisglucose, ATP, ...
Dua`s Layer: its discovery, characteristics and applications
... along its circumference, further injection of air did not result in creation of another BB indicating that the DL is not a random separation of some posterior stromal lamellae of the corneal stroma. Characteristics of Dua’s layer (Description derived from the authors’ own recent publications referen ...
... along its circumference, further injection of air did not result in creation of another BB indicating that the DL is not a random separation of some posterior stromal lamellae of the corneal stroma. Characteristics of Dua’s layer (Description derived from the authors’ own recent publications referen ...
Structure of a glutamate transporter homologue from Pyrococcus
... Glutamate transporters are integral membrane proteins that catalyse the concentrative uptake of glutamate from the synapse to intracellular spaces by harnessing pre-existing ion gradients. In the central nervous system glutamate transporters are essential for normal development and function, and are ...
... Glutamate transporters are integral membrane proteins that catalyse the concentrative uptake of glutamate from the synapse to intracellular spaces by harnessing pre-existing ion gradients. In the central nervous system glutamate transporters are essential for normal development and function, and are ...
thèse - Université Evry Val d`Essonne
... proteins. mtDNA generally encodes catalytic subunits of the complexes of the respiratory chain with tRNA and rRNA components of the mitochondrial translation system, but it can also contain additional proteins; in S. cerevisiae, besides seven subunits of complexes involved in oxidative phosphorylati ...
... proteins. mtDNA generally encodes catalytic subunits of the complexes of the respiratory chain with tRNA and rRNA components of the mitochondrial translation system, but it can also contain additional proteins; in S. cerevisiae, besides seven subunits of complexes involved in oxidative phosphorylati ...
Mitochondrial membrane lipid remodeling in
... the mitochondrial electron transport chain, through which they are transferred to oxygen [7]. As electrons flow through a sequence of membrane-bound protein and non-protein carriers, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. Therefore, according to the chemiosmotic ...
... the mitochondrial electron transport chain, through which they are transferred to oxygen [7]. As electrons flow through a sequence of membrane-bound protein and non-protein carriers, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. Therefore, according to the chemiosmotic ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.