Non-coding RNA for ZM401, a Pollen
... H1 9 , XIS T, C R2 0 , wer e t h o u g h t t o fu n ct i o n as untranslatable RNAs, t he molecular mech anisms of th eir fu nct ion still remain un clear. Wat anabe and Yamamo to (1994) demonstrated that mei RNA contained no long ORF and formed a complex with Mei2 protein and performed an essential ...
... H1 9 , XIS T, C R2 0 , wer e t h o u g h t t o fu n ct i o n as untranslatable RNAs, t he molecular mech anisms of th eir fu nct ion still remain un clear. Wat anabe and Yamamo to (1994) demonstrated that mei RNA contained no long ORF and formed a complex with Mei2 protein and performed an essential ...
Ch.12 - Jamestown Public Schools
... Eukaryotic chromosomes have both DNA & protein, packed tightly together to form chromatin Chromatin - DNA that is tightly coiled around proteins (histones) ...
... Eukaryotic chromosomes have both DNA & protein, packed tightly together to form chromatin Chromatin - DNA that is tightly coiled around proteins (histones) ...
Intest Aid IB - SpeechNutrients.eu
... What is Nucleotide Nutrition? Nucleotides are organic compounds that form the essential building blocks for nucleic acids (information-containing molecules) such as DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribo Nucleic Acid). What are the functions of nucleotides? Besides being the building blocks for ...
... What is Nucleotide Nutrition? Nucleotides are organic compounds that form the essential building blocks for nucleic acids (information-containing molecules) such as DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribo Nucleic Acid). What are the functions of nucleotides? Besides being the building blocks for ...
DNA Structure and Function
... Polymers of nucleotide monomers: DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid • The heredity compound of life • Directs cellular activities ...
... Polymers of nucleotide monomers: DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid • The heredity compound of life • Directs cellular activities ...
Unfinished Material - Answer Key
... - RNA interference is a form of gene regulation that directly prevents mRNA from undergoing translation. - RNA polymerase is going to transcribe genes that code for RNAs that double back on themselves to form a hairpin structure. - The double stranded hairpin is going to be moved outside of the nucl ...
... - RNA interference is a form of gene regulation that directly prevents mRNA from undergoing translation. - RNA polymerase is going to transcribe genes that code for RNAs that double back on themselves to form a hairpin structure. - The double stranded hairpin is going to be moved outside of the nucl ...
Molecular Diagnosis Of Infectious Diseases
... transcribed into cDNA using virus-specific oligonucleotide primers Several different gene targets have been used for amplification including the matrix, HA, and NS protein genes ...
... transcribed into cDNA using virus-specific oligonucleotide primers Several different gene targets have been used for amplification including the matrix, HA, and NS protein genes ...
Part B - Modeling Transcription: How is RNA modified? Name:
... functions as part of an "attach here" sign for ribosomes. The other end of an mRNA molecule, the 3' end, is also modified before the message exits the nucleus. At the 3' end, an enzyme makes a poly(A) tail consisting of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides. Like the 5' cap, the poly(A) tail inh ...
... functions as part of an "attach here" sign for ribosomes. The other end of an mRNA molecule, the 3' end, is also modified before the message exits the nucleus. At the 3' end, an enzyme makes a poly(A) tail consisting of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides. Like the 5' cap, the poly(A) tail inh ...
Document
... RNA interference acts between the steps of transcription and translation. It has long been known that introduction of RNA into cells interferes with the function of the genes (3, 5). These effects have been proposed to result from the so called “antisense” mechanism that depends on hybridization bet ...
... RNA interference acts between the steps of transcription and translation. It has long been known that introduction of RNA into cells interferes with the function of the genes (3, 5). These effects have been proposed to result from the so called “antisense” mechanism that depends on hybridization bet ...
Chapter 10: How Proteins are Made
... • Some help arrange RNA polymerase in the correct position on promoter • Others (activators) bind to enhancers – Enhancers: non-coding segments of DNA involved in regulation of protein synthesis • Typically located 1000’s of nucleotide bases away from promoter ...
... • Some help arrange RNA polymerase in the correct position on promoter • Others (activators) bind to enhancers – Enhancers: non-coding segments of DNA involved in regulation of protein synthesis • Typically located 1000’s of nucleotide bases away from promoter ...
Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases and their Promoters
... • These are homologous to b’-, b-, and a-subunits • Both Rpb1 and b’-subunit binds DNA • Rpb2 and b-subunit are at or near the nucleotide-joining active site • Rpb3 does not resemble a-subunit – There is one 20-amino acid subunit of great similarity – 2 subunits are about same size - same stoichiome ...
... • These are homologous to b’-, b-, and a-subunits • Both Rpb1 and b’-subunit binds DNA • Rpb2 and b-subunit are at or near the nucleotide-joining active site • Rpb3 does not resemble a-subunit – There is one 20-amino acid subunit of great similarity – 2 subunits are about same size - same stoichiome ...
Transcription and Translation
... • RNA plays a central role in the life of the cell. We are mostly going to look at its role in protein synthesis, but RNA does many other things as well. • RNA can both store information (like DNA) and catalyze chemical reactions (like proteins). • One theory for the origin of life has it starting o ...
... • RNA plays a central role in the life of the cell. We are mostly going to look at its role in protein synthesis, but RNA does many other things as well. • RNA can both store information (like DNA) and catalyze chemical reactions (like proteins). • One theory for the origin of life has it starting o ...
Transcription and Translation
... • RNA plays a central role in the life of the cell. We are mostly going to look at its role in protein synthesis, but RNA does many other things as well. • RNA can both store information (like DNA) and catalyze chemical reactions (like proteins). • One theory for the origin of life has it starting o ...
... • RNA plays a central role in the life of the cell. We are mostly going to look at its role in protein synthesis, but RNA does many other things as well. • RNA can both store information (like DNA) and catalyze chemical reactions (like proteins). • One theory for the origin of life has it starting o ...
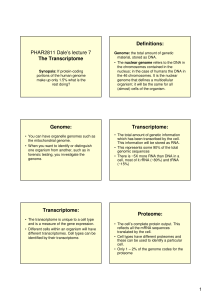
PHAR2811 Dale`s lecture 7 The Transcriptome Definitions: Genome
... that is capable of the RNase activity. • It was this enzyme that led scientists to the discovery of ribozymes; the RNA species capable of catalytic activity. ...
... that is capable of the RNase activity. • It was this enzyme that led scientists to the discovery of ribozymes; the RNA species capable of catalytic activity. ...
Slides PPT
... material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) cells of the organism. ...
... material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) cells of the organism. ...
CH 14 notes - Lincoln Park High School
... Explain how the languages of DNA and RNA are used to form polypeptides Explain how RNA is produced Explain how tRNA functions in the process of translation Describe the structure and function of ribosomes Explain how translation begins Describe the step-by-step process by which amino aci ...
... Explain how the languages of DNA and RNA are used to form polypeptides Explain how RNA is produced Explain how tRNA functions in the process of translation Describe the structure and function of ribosomes Explain how translation begins Describe the step-by-step process by which amino aci ...
Genes to Proteins Nucleic Acid Structure
... many times • Picture of histone‐ depleted chromosome: DNA strands have fallen off of scaffold ...
... many times • Picture of histone‐ depleted chromosome: DNA strands have fallen off of scaffold ...
Protein Synthesis - TangHua2012-2013
... At the end of each mRNA strand there are long chains of ____________________ bases (Adenine Tail, poly-A tail). ______________________________________________________________________________________. When enough protein is created the adenine tail ________________. This tells the body that this part ...
... At the end of each mRNA strand there are long chains of ____________________ bases (Adenine Tail, poly-A tail). ______________________________________________________________________________________. When enough protein is created the adenine tail ________________. This tells the body that this part ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein.
... Eukaryotic RNA polymerases differ from those of prokaryotes and require transcription factors. They differ in how transcription is terminated. Their ribosomes also are different. ...
... Eukaryotic RNA polymerases differ from those of prokaryotes and require transcription factors. They differ in how transcription is terminated. Their ribosomes also are different. ...
RNA Structure, Function, and Synthesis RNA - Rose
... RNA differs from DNA in both structural and functional respects. RNA has two major structural differences: each of the ribose rings contains a 2´-hydroxyl, and RNA uses uracil in place of thymine. RNA molecules are capable of base pairing, but generally will not form large regions of stable RNA-RNA ...
... RNA differs from DNA in both structural and functional respects. RNA has two major structural differences: each of the ribose rings contains a 2´-hydroxyl, and RNA uses uracil in place of thymine. RNA molecules are capable of base pairing, but generally will not form large regions of stable RNA-RNA ...
Chapter 4A
... Most cellular RNAs consist of a single strand. However, doublehelical regions are common in RNA where complementary sequence regions occur. Common types of RNA secondary structure elements are hairpins and stem-loop structures (Fig. 4.9a). Stem regions form A DNA-type double helices. The turns conne ...
... Most cellular RNAs consist of a single strand. However, doublehelical regions are common in RNA where complementary sequence regions occur. Common types of RNA secondary structure elements are hairpins and stem-loop structures (Fig. 4.9a). Stem regions form A DNA-type double helices. The turns conne ...
ap ch 17 powerpoint - Pregitzersninjascienceclasses
... Each tRNA carries a specific amino acid at one end At the other end is a nucleotide triplet called an anticodon. This base pairs with the mRNA. Made in nucleus, goes to cytoplasm Can be used repeatedly Short single strand of nucleotides ...
... Each tRNA carries a specific amino acid at one end At the other end is a nucleotide triplet called an anticodon. This base pairs with the mRNA. Made in nucleus, goes to cytoplasm Can be used repeatedly Short single strand of nucleotides ...
Document
... backbone at 180o • Actually a distorted ladder with poles closer to each other, on one side • Major/minor groove recognition ...
... backbone at 180o • Actually a distorted ladder with poles closer to each other, on one side • Major/minor groove recognition ...
Part II: How are antibiotics discovered
... a) Explain how a search for resistant mutants can give information as to the antibiotic’s target and mechanism of action. b) By adding the antibiotic (myx) at different times in a transcription reaction, the authors showed that myx inhibits RNA polymerase binding to double stranded DNA. Explain. ...
... a) Explain how a search for resistant mutants can give information as to the antibiotic’s target and mechanism of action. b) By adding the antibiotic (myx) at different times in a transcription reaction, the authors showed that myx inhibits RNA polymerase binding to double stranded DNA. Explain. ...
RNA world

The RNA world refers to the self-replicating ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules that were precursors to all current life on Earth. It is generally accepted that current life on Earth descends from an RNA world, although RNA-based life may not have been the first life to exist.RNA stores genetic information like DNA, and catalyzes chemical reactions like an enzyme protein. It may, therefore, have played a major step in the evolution of cellular life. The RNA world would have eventually been replaced by the DNA, RNA and protein world of today, likely through an intermediate stage of ribonucleoprotein enzymes such as the ribosome and ribozymes, since proteins large enough to self-fold and have useful activities would only have come about after RNA was available to catalyze peptide ligation or amino acid polymerization. DNA is thought to have taken over the role of data storage due to its increased stability, while proteins, through a greater variety of monomers (amino acids), replaced RNA's role in specialized biocatalysis.The RNA world hypothesis is supported by many independent lines of evidence, such as the observations that RNA is central to the translation process and that small RNAs can catalyze all of the chemical group and information transfers required for life. The structure of the ribosome has been called the ""smoking gun,"" as it showed that the ribosome is a ribozyme, with a central core of RNA and no amino acid side chains within 18 angstroms of the active site where peptide bond formation is catalyzed. Many of the most critical components of cells (those that evolve the slowest) are composed mostly or entirely of RNA. Also, many critical cofactors (ATP, Acetyl-CoA, NADH, etc.) are either nucleotides or substances clearly related to them. This would mean that the RNA and nucleotide cofactors in modern cells are an evolutionary remnant of an RNA-based enzymatic system that preceded the protein-based one seen in all extant life.Evidence suggests chemical conditions (including the presence of boron, molybdenum and oxygen) for initially producing RNA molecules may have been better on the planet Mars than those on the planet Earth. If so, life-suitable molecules, originating on Mars, may have later migrated to Earth via panspermia or similar process.