Nervous System
... Cell bodies are located in the CNS Monosynaptic, therefore very long Axons split into a cluster of axon terminals at the neuromuscular junction • Synaptic cleft between the motor neuron and the muscle is very narrow • Release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine • Effect on the muscle is always excita ...
... Cell bodies are located in the CNS Monosynaptic, therefore very long Axons split into a cluster of axon terminals at the neuromuscular junction • Synaptic cleft between the motor neuron and the muscle is very narrow • Release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine • Effect on the muscle is always excita ...
Physiology Lecture Outline: Membrane Potential and Neurophysiology
... The myelin sheath that covers some axon is made from the cytoplasm of glial cells (Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS). The myelin sheath is mostly composed of lipids and therefore is a good insulator, which is the same as saying it is a poor conductor of electrical charge. In ...
... The myelin sheath that covers some axon is made from the cytoplasm of glial cells (Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS). The myelin sheath is mostly composed of lipids and therefore is a good insulator, which is the same as saying it is a poor conductor of electrical charge. In ...
Tutorial 5: Sodium and Potassium Gradients at Rest
... Return to main tutorial page The first studies of the electrical characteristics of neurons were conducted in the 1930's using "giant" squid axons. The swimming mechanism of the squid (an aquatic animal found in the Atlantic Ocean) consists of an enlarged tubular structure or giant axon that is seve ...
... Return to main tutorial page The first studies of the electrical characteristics of neurons were conducted in the 1930's using "giant" squid axons. The swimming mechanism of the squid (an aquatic animal found in the Atlantic Ocean) consists of an enlarged tubular structure or giant axon that is seve ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... Local graded potentials, originating on cell dendrites or cell bodies, trigger specific cell functions (such as exocytosis of glandular secretions or ACh at a motor end plate) at the synaptic terminals of axons. The link between the two actions is the action potential. ...
... Local graded potentials, originating on cell dendrites or cell bodies, trigger specific cell functions (such as exocytosis of glandular secretions or ACh at a motor end plate) at the synaptic terminals of axons. The link between the two actions is the action potential. ...
in the central nervous system
... nervous systems Neurons can send electrical and chemical impulses (electrochemical impulses) The sending of impulses is the property of the neuron’s cell membrane Transmission not through the cytoplasm, but along the cell membrane ...
... nervous systems Neurons can send electrical and chemical impulses (electrochemical impulses) The sending of impulses is the property of the neuron’s cell membrane Transmission not through the cytoplasm, but along the cell membrane ...
When neurons form memories
... provided important new insights, it also raises new questions. The most important unresolved issue is probably whether the observed neocortical reactivations are truly a correlate of consolidation of declarative memory or whether ...
... provided important new insights, it also raises new questions. The most important unresolved issue is probably whether the observed neocortical reactivations are truly a correlate of consolidation of declarative memory or whether ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
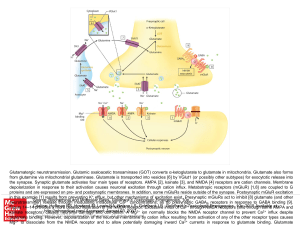
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
Biology 12 - The Nervous System Study Guide
... 24. How do neuro-poisons such as strychnine and nerve gas work? What are the symptoms of exposure? 25. How do narcotics such as heroin and morphine work? 26. Explain the biochemical events that occur when an impulse is transmitted through a reflex arc. Begin with the opening of the sodium gates in a ...
... 24. How do neuro-poisons such as strychnine and nerve gas work? What are the symptoms of exposure? 25. How do narcotics such as heroin and morphine work? 26. Explain the biochemical events that occur when an impulse is transmitted through a reflex arc. Begin with the opening of the sodium gates in a ...
Nervous System - Calgary Christian School
... The blood-brain barrier is important for maintaining the environment of neurons in the brain, but it also presents challenges for scientists who are investigating new treatments for brain disorders. If a medication cannot get into the brain, it cannot be effective. Researchers attempt to circumvent ...
... The blood-brain barrier is important for maintaining the environment of neurons in the brain, but it also presents challenges for scientists who are investigating new treatments for brain disorders. If a medication cannot get into the brain, it cannot be effective. Researchers attempt to circumvent ...
Chapter 28
... (2) why do they only flow in one direction? (a)Na+ channels are inactivated while K+ is diffusing out (b) If they can’t open, there can’t be an action potential iv) action potentials are all-or-none (1) they are always the same (2) there is no such thing as a strong or weak one (3) so how do we tell ...
... (2) why do they only flow in one direction? (a)Na+ channels are inactivated while K+ is diffusing out (b) If they can’t open, there can’t be an action potential iv) action potentials are all-or-none (1) they are always the same (2) there is no such thing as a strong or weak one (3) so how do we tell ...
CHAPTER 4
... Phenytoin (Dilantin) (Epamin) Dilantin is known to most doctors and many other people as a treatment for epilepsy. However, it has a wide range of pharmacologic effects other than its anticonvulsant activity. There have been more than 8,000 papers published on Dilantin and there have been clinical r ...
... Phenytoin (Dilantin) (Epamin) Dilantin is known to most doctors and many other people as a treatment for epilepsy. However, it has a wide range of pharmacologic effects other than its anticonvulsant activity. There have been more than 8,000 papers published on Dilantin and there have been clinical r ...
Too little
... 1. Resting potential…… • Draw the axon membrane at resting potential Na+ (sodium) is outside the membrane K+ (potassium) is inside the membrane too, but a mainly negative charge exists INSIDE the membrane. ...
... 1. Resting potential…… • Draw the axon membrane at resting potential Na+ (sodium) is outside the membrane K+ (potassium) is inside the membrane too, but a mainly negative charge exists INSIDE the membrane. ...
Action Potential Riddle Quiz
... Na+ & K+ Channels cannot be opened by a stimulus Na+/K+ Pump actively (ATP required) pumps Na+ out of & K+ into neuron (against/up their concentration gradients) Reestablishment of ion distribution of resting neuron ...
... Na+ & K+ Channels cannot be opened by a stimulus Na+/K+ Pump actively (ATP required) pumps Na+ out of & K+ into neuron (against/up their concentration gradients) Reestablishment of ion distribution of resting neuron ...
Nerve Impulses and Action Potential
... 6 Initial ionic conditions restored. The ionic conditions of the resting state are restored later by the activity of the sodium-potassium pump. Three sodium ions are ejected for every two potassium ions carried back into the cell. ...
... 6 Initial ionic conditions restored. The ionic conditions of the resting state are restored later by the activity of the sodium-potassium pump. Three sodium ions are ejected for every two potassium ions carried back into the cell. ...
Vocabulary Terms
... Axon: a long, fiber-like extension of a neuron that transmits signals from the cell body to the synapse. Brain: located in the skull, it is the organ that controls all body activities through the spinal cord and peripheral nerves of the nervous system. Codeine: a naturally occurring component (alkal ...
... Axon: a long, fiber-like extension of a neuron that transmits signals from the cell body to the synapse. Brain: located in the skull, it is the organ that controls all body activities through the spinal cord and peripheral nerves of the nervous system. Codeine: a naturally occurring component (alkal ...
MMNeuropharm2011
... Further investigations indicate that this AMPAR redistribution depends on PICK1, a trafficking protein specifically interacting with GluA2 (Bellone and Lüscher, 2006). Moreover, after the cocaine treatment the single channel conductance of sEPSCs almost doubled from 7.8 pS to 15 pS and evoked EPSCs we ...
... Further investigations indicate that this AMPAR redistribution depends on PICK1, a trafficking protein specifically interacting with GluA2 (Bellone and Lüscher, 2006). Moreover, after the cocaine treatment the single channel conductance of sEPSCs almost doubled from 7.8 pS to 15 pS and evoked EPSCs we ...
Document
... http://www.its.caltech.edu/~lester/Bi-1-2006/Lecture-images/Lecture-4-2006(History).ppt ...
... http://www.its.caltech.edu/~lester/Bi-1-2006/Lecture-images/Lecture-4-2006(History).ppt ...
01Integrated Normal Cells of CNS
... TYPES OF NEURONS Based on number of processes 2. Bipolar Neuron (spindle-shaped neuron): Has two processes (one arising from each pole of the cell body). One of them is the dendrite and the other is the axon, e.g. retina & olfactory epithelium. ...
... TYPES OF NEURONS Based on number of processes 2. Bipolar Neuron (spindle-shaped neuron): Has two processes (one arising from each pole of the cell body). One of them is the dendrite and the other is the axon, e.g. retina & olfactory epithelium. ...
THERIGHTBRAINPOWERPOINT
... where there is most oxygen. The brain takes about half a second to react to a stimulus, so this rapid scanning technique can clearly show the ebb and flow of activity in different parts of the brain as it reacts to various stimuli or undertakes different tasks. fMRI is proving to be the most rewardi ...
... where there is most oxygen. The brain takes about half a second to react to a stimulus, so this rapid scanning technique can clearly show the ebb and flow of activity in different parts of the brain as it reacts to various stimuli or undertakes different tasks. fMRI is proving to be the most rewardi ...
Competitive Learning Lecture 10
... An initially large neighborhood promotes a topology-preserving mapping" Smaller neighborhoods allows neurons to specialize in the latter stages of training" ...
... An initially large neighborhood promotes a topology-preserving mapping" Smaller neighborhoods allows neurons to specialize in the latter stages of training" ...
Neuronal cytoskeleton in synaptic plasticity and regeneration
... cells (Bazellieres et al. 2012), suggesting that the drebrin/EB3 pathway is canonical. Interestingly, microtubule invasion into dendritic spines is enhanced by over-expression of drebrin and, conversely, reduced by knockdown of drebrin (Merriam and Dent, personal communication). There is evidence th ...
... cells (Bazellieres et al. 2012), suggesting that the drebrin/EB3 pathway is canonical. Interestingly, microtubule invasion into dendritic spines is enhanced by over-expression of drebrin and, conversely, reduced by knockdown of drebrin (Merriam and Dent, personal communication). There is evidence th ...
Introduction to Neurotransmitters
... neurotransmitters which cross the synapse between the neurons • Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers which transmit information over the synapses from one neuron to another. ...
... neurotransmitters which cross the synapse between the neurons • Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers which transmit information over the synapses from one neuron to another. ...
Document
... • Alcohol has multiple effects on neurons. It alters neuron membranes, ion channels, enzymes, and receptors. • It binds directly to receptors for acetylcholine, serotonin, and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), and glutamate. • We will focus on GABA and its receptor. ...
... • Alcohol has multiple effects on neurons. It alters neuron membranes, ion channels, enzymes, and receptors. • It binds directly to receptors for acetylcholine, serotonin, and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), and glutamate. • We will focus on GABA and its receptor. ...
Mirror Neurons
... Uniview Worldwide Ltd warrants that it is fully entitled to enter into this Agreement and to grant the rights referred to in this Agreement. This Agreement shall be governed by English law, and the English courts shall be the courts of ...
... Uniview Worldwide Ltd warrants that it is fully entitled to enter into this Agreement and to grant the rights referred to in this Agreement. This Agreement shall be governed by English law, and the English courts shall be the courts of ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.