Physiology Lecture 6
... little less negative than the equilibrium potential for K+ . Depolarization of a small region of an axon can be experimentally induced by a pair of stimulating electrodes that act as if they were injecting positive charges into the axon. If the depolarization is below a certain level, it will simply ...
... little less negative than the equilibrium potential for K+ . Depolarization of a small region of an axon can be experimentally induced by a pair of stimulating electrodes that act as if they were injecting positive charges into the axon. If the depolarization is below a certain level, it will simply ...
Nervous Tissue - Northland Community & Technical College
... White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and ...
... White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and ...
The Nervous System
... signals-Neurons are not connected to one another they are separated by tiny gaps called a synapse. The impulses changes to a chemical signal at the axon terminal, travels through the synapse, and then is picked up once again as an electrical signal by the dendrites. Nerve impulses travel in only one ...
... signals-Neurons are not connected to one another they are separated by tiny gaps called a synapse. The impulses changes to a chemical signal at the axon terminal, travels through the synapse, and then is picked up once again as an electrical signal by the dendrites. Nerve impulses travel in only one ...
The Nervous System
... neighbouring neuron through thousands of synapse. Some of the messages are excitatory (i.e. they tell the neuron to “fire”) while others may be inhibitory (i.e. they tell the neuron not to fire). Whether or not a neuron “fires” off an action potential at any particular instant depends on its abili ...
... neighbouring neuron through thousands of synapse. Some of the messages are excitatory (i.e. they tell the neuron to “fire”) while others may be inhibitory (i.e. they tell the neuron not to fire). Whether or not a neuron “fires” off an action potential at any particular instant depends on its abili ...
Cell body
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
Sensing the Environment
... other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron ...
... other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron ...
to Psychology 3
... the synapse; in the case of humans, neurotransmitters appear to signal across synapses 1. Sending Signals: Chemicals as Couriers - terms: (1) synaptic cleft: microscopic gap between the terminal button of one cell and the membrane of another, (2) presynaptic neuron - transmits the signal, (3) postsy ...
... the synapse; in the case of humans, neurotransmitters appear to signal across synapses 1. Sending Signals: Chemicals as Couriers - terms: (1) synaptic cleft: microscopic gap between the terminal button of one cell and the membrane of another, (2) presynaptic neuron - transmits the signal, (3) postsy ...
and GABA in the outer part of rat retina following acute high
... Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, 410013. ...
... Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, 410013. ...
Unit 3A Nervous System - Teacher Version
... • Synapse – the small gap between neurons which neurotransmitters travel across to send a message to the receiving neuron’s dendrites • Reuptake – the process of the sending neuron’s terminal buttons taking back excess neurotransmitters from the synaptic gap ...
... • Synapse – the small gap between neurons which neurotransmitters travel across to send a message to the receiving neuron’s dendrites • Reuptake – the process of the sending neuron’s terminal buttons taking back excess neurotransmitters from the synaptic gap ...
The vocabulary of nerve cells
... – The range of intensity of the stimulus must thus be coded into the possible range of frequencies of a neuron. The minimum detectable change in frequency depends on the constancy of firing of the signaling neuron (most neurons fire constantly). The absolute refractory period governs the maximum fre ...
... – The range of intensity of the stimulus must thus be coded into the possible range of frequencies of a neuron. The minimum detectable change in frequency depends on the constancy of firing of the signaling neuron (most neurons fire constantly). The absolute refractory period governs the maximum fre ...
Introduction
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
The Nervous System
... axomembrane as the nerve impulse occurs. • Action potential is an all-or-none phenomenon. • If a stimulus causes the axomembrane to depolarize to a certain level, which is called a threshold, an action potential occurs. • The action potential requires two types of gated channel proteins in the membr ...
... axomembrane as the nerve impulse occurs. • Action potential is an all-or-none phenomenon. • If a stimulus causes the axomembrane to depolarize to a certain level, which is called a threshold, an action potential occurs. • The action potential requires two types of gated channel proteins in the membr ...
Chapter 12 Nervous System Cells
... several knobs being activated simultaneously and stimulating different locations on the postsynaptic membrane, producing an action potential – Temporal summation—when synaptic knobs stimulate a postsynaptic neuron in rapid succession, their effects can summate over a brief period of time to produce ...
... several knobs being activated simultaneously and stimulating different locations on the postsynaptic membrane, producing an action potential – Temporal summation—when synaptic knobs stimulate a postsynaptic neuron in rapid succession, their effects can summate over a brief period of time to produce ...
rview
... A) It will either produce an action potential or not, depending entirely upon whether it is an excitatory or inhibitory neuron. B) It will integrate the incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals, with its rate of action potentials depending on the relative amount of each type of signal. C) It will ...
... A) It will either produce an action potential or not, depending entirely upon whether it is an excitatory or inhibitory neuron. B) It will integrate the incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals, with its rate of action potentials depending on the relative amount of each type of signal. C) It will ...
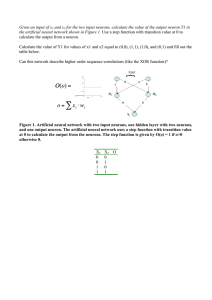
Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the
... input neuron to each layer that always has the value 1 (see figure 2). With this additional bias, calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0), (1,1), (1,0), and (0,1) and fill out the table below. Can this network describe higher order sequence correlations (like the XOR functio ...
... input neuron to each layer that always has the value 1 (see figure 2). With this additional bias, calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0), (1,1), (1,0), and (0,1) and fill out the table below. Can this network describe higher order sequence correlations (like the XOR functio ...
Minireview Embarrassed, but Not Depressed: Eye Opening Lessons
... Purkinje cell output that briefly disinhibits the deep nucleus neuron at only the appropriate time, sculpting the time course of the learned behavioral response. In a recent test of this hypothesis, Bao et al. (2002) took advantage of pharmacological manipulations that effectively disconnected Purki ...
... Purkinje cell output that briefly disinhibits the deep nucleus neuron at only the appropriate time, sculpting the time course of the learned behavioral response. In a recent test of this hypothesis, Bao et al. (2002) took advantage of pharmacological manipulations that effectively disconnected Purki ...
The Nervous System - Hartland High School
... Cells on the outside of the axons outside of the CNS that produce the myelin sheath by wrapping themselves tightly around the axon in a jelly-roll like fashion. Related to Schwann cells are three other structures of a neuron. i. Myelin Sheath – Myelin cover that encloses the axon ii. Neurilemma – pa ...
... Cells on the outside of the axons outside of the CNS that produce the myelin sheath by wrapping themselves tightly around the axon in a jelly-roll like fashion. Related to Schwann cells are three other structures of a neuron. i. Myelin Sheath – Myelin cover that encloses the axon ii. Neurilemma – pa ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... 11. Describe the diversity of animal nervous systems and provide examples. Explain how the structure of the nervous system relates to the ways animals interact with their environment. 12. Describe the general structure of the brain, spinal cord, and associated nerves of vertebrates. Describe the for ...
... 11. Describe the diversity of animal nervous systems and provide examples. Explain how the structure of the nervous system relates to the ways animals interact with their environment. 12. Describe the general structure of the brain, spinal cord, and associated nerves of vertebrates. Describe the for ...
Structure of the Nervous System
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
Practice makes perfect: a theoretical model of memory consolidation
... A brain area located at the lower back of the brain. Although its size is 10 times smaller than the cerebrum in humans, the number of neurons inside the cerebellum is almost 50% of the entire brain. The cerebellum plays an important role in motor learning and control, and when the cerebellum is dama ...
... A brain area located at the lower back of the brain. Although its size is 10 times smaller than the cerebrum in humans, the number of neurons inside the cerebellum is almost 50% of the entire brain. The cerebellum plays an important role in motor learning and control, and when the cerebellum is dama ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System, Part 2
... • Ca2+ concentration increases in presynaptic terminal and ostsynaptic neuron • Brief high-frequency stimulation partially depolarizes the postsynaptic neuron – Chemically gated channels (NMDA receptors) allow Ca2+ entry – Ca2+ activates kinase enzymes that promote more effective responses to subseq ...
... • Ca2+ concentration increases in presynaptic terminal and ostsynaptic neuron • Brief high-frequency stimulation partially depolarizes the postsynaptic neuron – Chemically gated channels (NMDA receptors) allow Ca2+ entry – Ca2+ activates kinase enzymes that promote more effective responses to subseq ...
The Nervous System
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment Resting neuron have a charge, or electrical potential, across their cell membranes. The inside of a neuron has a voltage of –70 millivolts (mV) compared to the outside. This difference is known as the resting poten ...
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment Resting neuron have a charge, or electrical potential, across their cell membranes. The inside of a neuron has a voltage of –70 millivolts (mV) compared to the outside. This difference is known as the resting poten ...
slides
... weight magnitude field of the LUT. • The integrate-and-fire array transceiver (IFAT) spatially and temporally integrates events. ...
... weight magnitude field of the LUT. • The integrate-and-fire array transceiver (IFAT) spatially and temporally integrates events. ...
Lecture #13 – Animal Nervous Systems
... At resting potential the neuron is NOT actively transmitting signals Maintained largely because cell membranes are more permeable to K+ than to Na+; more K+ leaves the cell than Na+ enters An ATP powered K+/Na+ pump continually restores the concentration gradients; this also helps to maintain the ...
... At resting potential the neuron is NOT actively transmitting signals Maintained largely because cell membranes are more permeable to K+ than to Na+; more K+ leaves the cell than Na+ enters An ATP powered K+/Na+ pump continually restores the concentration gradients; this also helps to maintain the ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.