Dynamic Range Analysis of HH Model for Excitable Neurons
... signals and chemical messengers [1], [3]. The dendrites receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons in the body. This information is then passed to the cell body and on to the axon. Once the information has arrived at the axon, it travels through the length of the axon in the form of ...
... signals and chemical messengers [1], [3]. The dendrites receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons in the body. This information is then passed to the cell body and on to the axon. Once the information has arrived at the axon, it travels through the length of the axon in the form of ...
chapter 11 ppt additional
... A. Depolarization- change in which inner membrane becomes more positive compared to resting membrane B. Repolarization- membrane going back to the resting state C. Hyperpolarization- change in which membrane becomes more negative compared to resting membrane ...
... A. Depolarization- change in which inner membrane becomes more positive compared to resting membrane B. Repolarization- membrane going back to the resting state C. Hyperpolarization- change in which membrane becomes more negative compared to resting membrane ...
Slide ()
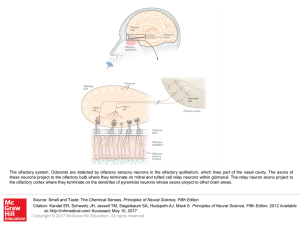
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Chemicals in and Around the Cell.
... many of the most difficult topics typically covered in the biopsychology course. Every module includes sections that explore relevant anatomy, physiological animations, and engaging case studies that bring behavioral neuroscience to life. At the end of each module, students can take an assessment th ...
... many of the most difficult topics typically covered in the biopsychology course. Every module includes sections that explore relevant anatomy, physiological animations, and engaging case studies that bring behavioral neuroscience to life. At the end of each module, students can take an assessment th ...
Increased leak conductance alters ISI variability.
... CV = standard deviation of ISI distribution/mean ISI ...
... CV = standard deviation of ISI distribution/mean ISI ...
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
... the mechanism behind various events. For example, How does drinking alcohol increase urinary output? How does muscle get bigger when it’s put under mechanical stress (i.e. ...
... the mechanism behind various events. For example, How does drinking alcohol increase urinary output? How does muscle get bigger when it’s put under mechanical stress (i.e. ...
Lecture 5
... epileptic seizures: wavelike electrical activity of a large number of neurons, often associated with loss of consciousness and involuntary body ...
... epileptic seizures: wavelike electrical activity of a large number of neurons, often associated with loss of consciousness and involuntary body ...
Sample
... many of the most difficult topics typically covered in the biopsychology course. Every module includes sections that explore relevant anatomy, physiological animations, and engaging case studies that bring behavioral neuroscience to life. At the end of each module, students can take an assessment th ...
... many of the most difficult topics typically covered in the biopsychology course. Every module includes sections that explore relevant anatomy, physiological animations, and engaging case studies that bring behavioral neuroscience to life. At the end of each module, students can take an assessment th ...
The Dialectics of Hebb and Homeostasis within
... compensation, is still not entirely clear. On a theoretical level, the existence of “firing rate set points” in neocortical neurons provides a means for circuits to self-tune excitability over long time-scales to prevent the development of hypo or hyperexcitable states (Turrigiano and Nelson, 2004). ...
... compensation, is still not entirely clear. On a theoretical level, the existence of “firing rate set points” in neocortical neurons provides a means for circuits to self-tune excitability over long time-scales to prevent the development of hypo or hyperexcitable states (Turrigiano and Nelson, 2004). ...
Final Exam Review Part II 1) The entire nervous system is divided
... 13) Both the depolarization and repolarization changes that occur during the action potential are produced by A) Ions moving across the cell membrane B) Small neuroglial cells that act as batteries for the neuron itself C) Negative stimuli D) Enzymes creating new ions 14) The two major ions involved ...
... 13) Both the depolarization and repolarization changes that occur during the action potential are produced by A) Ions moving across the cell membrane B) Small neuroglial cells that act as batteries for the neuron itself C) Negative stimuli D) Enzymes creating new ions 14) The two major ions involved ...
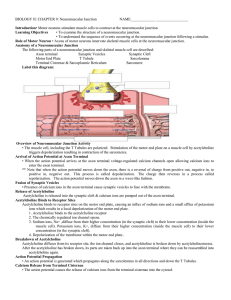
BIOLOGY II: CHAPTER 9: Neuromuscular Junction
... 3. Sodium ions, Na+ ,diffuse from their higher concentration (in the synaptic cleft) to their lower concentration (inside the muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of ...
... 3. Sodium ions, Na+ ,diffuse from their higher concentration (in the synaptic cleft) to their lower concentration (inside the muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of ...
A Neuron Play - Web Adventures
... student found that the basketball had somehow ended up in his/her hands. The whole world went into slow motion. Despite what some might say, this is what REALLY happened (put ball in hands of player). The dendrites in the sensory neurons of his/her hands were triggered by the touch of the ball in hi ...
... student found that the basketball had somehow ended up in his/her hands. The whole world went into slow motion. Despite what some might say, this is what REALLY happened (put ball in hands of player). The dendrites in the sensory neurons of his/her hands were triggered by the touch of the ball in hi ...
ANHB1102 Basic Principles of the Nervous System • The nervous
... - Action potential – momentary reversal of membrane potential. This change causes electrical signalling within neurons Resting Membrane Potential (RMP) - Inner part of the cell contains large number of ions, outside has same ions - In excitable cell, has more negatively charged inner membrane compar ...
... - Action potential – momentary reversal of membrane potential. This change causes electrical signalling within neurons Resting Membrane Potential (RMP) - Inner part of the cell contains large number of ions, outside has same ions - In excitable cell, has more negatively charged inner membrane compar ...
8a nerve cells 10a
... covering) of a neuron. DENDRITES function to receive the signal and carry the nerve conduction toward the cell body. SOMA (cell body) is where the nucleus, ribosomes, and most organelles are located AXON HILLOCK is the area on the soma where the action potential of the neuron builds up before it tra ...
... covering) of a neuron. DENDRITES function to receive the signal and carry the nerve conduction toward the cell body. SOMA (cell body) is where the nucleus, ribosomes, and most organelles are located AXON HILLOCK is the area on the soma where the action potential of the neuron builds up before it tra ...
Brain`s Building Blocks
... Alcohol affects the brain by imitating a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, GABA GABA Neurons ◦ GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA ...
... Alcohol affects the brain by imitating a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, GABA GABA Neurons ◦ GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA ...
axon
... fibers, but makes their job possible. When myelin or the nerve fiber is destroyed or damaged, the ability of the nerves to conduct electrical impulses to and from the brain is disrupted, and this produces the various symptoms of MS. ...
... fibers, but makes their job possible. When myelin or the nerve fiber is destroyed or damaged, the ability of the nerves to conduct electrical impulses to and from the brain is disrupted, and this produces the various symptoms of MS. ...
Biol 203 Lab Week 10 Nervous System Histology
... Sometimes the nerve fiber itself is damaged or broken. Myelin not only protects nerve fibers, but makes their job possible. When myelin or the nerve fiber is destroyed or damaged, the ability of the nerves to conduct electrical impulses to and from the brain is disrupted, and this produces the vario ...
... Sometimes the nerve fiber itself is damaged or broken. Myelin not only protects nerve fibers, but makes their job possible. When myelin or the nerve fiber is destroyed or damaged, the ability of the nerves to conduct electrical impulses to and from the brain is disrupted, and this produces the vario ...
Supplement to: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... Through the investigation of synaptic transmission between pairs of layer 5 pyramidal cells maintained in slices in vitro, we answer all three of these questions. First, we demonstrated that the amplitude of action potential evoked EPSPs between synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells is a c ...
... Through the investigation of synaptic transmission between pairs of layer 5 pyramidal cells maintained in slices in vitro, we answer all three of these questions. First, we demonstrated that the amplitude of action potential evoked EPSPs between synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells is a c ...
Nervous System
... that has been by using your senses, then your brain sends a message through neurons to muscles or other cells which work to perform the response. ...
... that has been by using your senses, then your brain sends a message through neurons to muscles or other cells which work to perform the response. ...
Supplement: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... Through the investigation of synaptic transmission between pairs of layer 5 pyramidal cells maintained in slices in vitro, we answer all three of these questions. First, we demonstrated that the amplitude of action potential evoked EPSPs between synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells is a c ...
... Through the investigation of synaptic transmission between pairs of layer 5 pyramidal cells maintained in slices in vitro, we answer all three of these questions. First, we demonstrated that the amplitude of action potential evoked EPSPs between synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells is a c ...
The Nervous System - OCPS TeacherPress
... Inactive until excited by stimulus (threshold = generator potential) ...
... Inactive until excited by stimulus (threshold = generator potential) ...
System Introduction to Sensory Physiology: Sensory- Motor
... 2) MRO1- slow adaptation- IK (Ca), Na/K pump! 3) MRO1 and MRO2 have similar generator potentials! 4) MRO2 adapts more quickly to depolarization! ...
... 2) MRO1- slow adaptation- IK (Ca), Na/K pump! 3) MRO1 and MRO2 have similar generator potentials! 4) MRO2 adapts more quickly to depolarization! ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.