Lecture 7 – Synaptic Transmission II -
... 5. NMDA receptors are blocked by external Mg2+, which binds to a site within the pore at negative resting potentials. Thus, current carried by AMPA and kainate receptors largely determines EPSP at negative resting potentials. However, during strong synaptic activity, the postsynaptic cell depolarize ...
... 5. NMDA receptors are blocked by external Mg2+, which binds to a site within the pore at negative resting potentials. Thus, current carried by AMPA and kainate receptors largely determines EPSP at negative resting potentials. However, during strong synaptic activity, the postsynaptic cell depolarize ...
14. Development and Plasticity
... To find the general principles of brain development is one of the major scientific quests in neuroscience Not all characteristics of the brain can be specified by a ...
... To find the general principles of brain development is one of the major scientific quests in neuroscience Not all characteristics of the brain can be specified by a ...
The Biology of Mind take 2
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
The Biology of Mind take
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
17- The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
... the nucleus and produces the energy needed to fuel neuron activity. The dendrites are short, thin fibers that stick out from the cell body. Dendrites receive impulses, or messages, from other neurons and send them to the cell body. The axon is a long fiber that carries the impulses away from the cel ...
... the nucleus and produces the energy needed to fuel neuron activity. The dendrites are short, thin fibers that stick out from the cell body. Dendrites receive impulses, or messages, from other neurons and send them to the cell body. The axon is a long fiber that carries the impulses away from the cel ...
Nervous System
... (2) Bipolar neuron – have two distinct processes, one dendrite and one axon with cell body between them. Rare, but found in special sense organs where they relay information about sight, smell, or hearing from receptor cells to neurons. ...
... (2) Bipolar neuron – have two distinct processes, one dendrite and one axon with cell body between them. Rare, but found in special sense organs where they relay information about sight, smell, or hearing from receptor cells to neurons. ...
sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
... stimulates the sodium gates to open at the very next point. The gates that have just opened and closed cannot be restimulated for a very brief period of time, (Recovery period) so the impulse moves in one direction only. ...
... stimulates the sodium gates to open at the very next point. The gates that have just opened and closed cannot be restimulated for a very brief period of time, (Recovery period) so the impulse moves in one direction only. ...
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Sensory neurons: (Afferent) Carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) toward the central nervous system. Motor neurons: (motoneurons) (Efferent) Carry signals away from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body. Receptors: Sense the environm ...
... Sensory neurons: (Afferent) Carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) toward the central nervous system. Motor neurons: (motoneurons) (Efferent) Carry signals away from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body. Receptors: Sense the environm ...
Biological Bases of Behavior: Neural Processing and the Endocrine
... 3) When a neuron fires , the first part of the axon opens it’s ‘gates’ (think manhole covers). 4) Positively charged sodium flows in. 5) This causes ‘depolarization’ – The inside and the outside of that part of the neuron are no longer charged differently. 6) This depolarization causes the next gate ...
... 3) When a neuron fires , the first part of the axon opens it’s ‘gates’ (think manhole covers). 4) Positively charged sodium flows in. 5) This causes ‘depolarization’ – The inside and the outside of that part of the neuron are no longer charged differently. 6) This depolarization causes the next gate ...
Slide ()
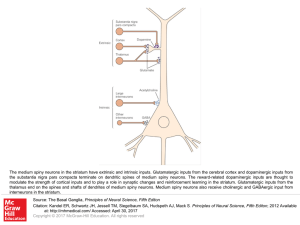
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
Neurons: A fish-eye view of the brain
... cells perform such magic? Surprisingly, we’re finding some answers to that question by studying the tiny, 10,000-neuron brains of the developing Danio rerio, known affectionately as the zebrafish. The stuff of brains What makes a brain powerful isn’t just its size or the number of neurons, but the w ...
... cells perform such magic? Surprisingly, we’re finding some answers to that question by studying the tiny, 10,000-neuron brains of the developing Danio rerio, known affectionately as the zebrafish. The stuff of brains What makes a brain powerful isn’t just its size or the number of neurons, but the w ...
Chapter 17:
... All neurons provide an all-or-none response: - in response to a stimulus, they either activate (fire) and provide a certain level of response, or don’t fire at all A neuron will only fire if it is stimulated with an intensity of at least threshold level Every action potential for a neuron is identic ...
... All neurons provide an all-or-none response: - in response to a stimulus, they either activate (fire) and provide a certain level of response, or don’t fire at all A neuron will only fire if it is stimulated with an intensity of at least threshold level Every action potential for a neuron is identic ...
The Nervous System - Appoquinimink High School
... 1. Use the book and your notes to create a foldable about the different types of neurons. 2. You may fold it anyway you like as long as on the outside you have three flaps (1 for each of the types of neurons) 3. The outside you will need to draw what each neuron looks like and label it. 4. The insi ...
... 1. Use the book and your notes to create a foldable about the different types of neurons. 2. You may fold it anyway you like as long as on the outside you have three flaps (1 for each of the types of neurons) 3. The outside you will need to draw what each neuron looks like and label it. 4. The insi ...
Chapter 3 - Morgan Community College
... Diversity in Neurons Both structural and functional features are used to ...
... Diversity in Neurons Both structural and functional features are used to ...
Chapter 17:
... All neurons provide an all-or-none response: - in response to a stimulus, they either activate (fire) and provide a certain level of response, or don’t fire at all A neuron will only fire if it is stimulated with an intensity of at least threshold level Every action potential for a neuron is identic ...
... All neurons provide an all-or-none response: - in response to a stimulus, they either activate (fire) and provide a certain level of response, or don’t fire at all A neuron will only fire if it is stimulated with an intensity of at least threshold level Every action potential for a neuron is identic ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint Notes
... _________________: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. ...
... _________________: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... 8) Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9) Describe the characteristics of an action potential. Explain the role of voltage-gated channels in this process. 10) Describe the two main factors that underlie the repolarizing phase of the action potential. 1 ...
... 8) Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9) Describe the characteristics of an action potential. Explain the role of voltage-gated channels in this process. 10) Describe the two main factors that underlie the repolarizing phase of the action potential. 1 ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... 8) Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9) Describe the characteristics of an action potential. Explain the role of voltage-gated channels in this process. 10) Describe the two main factors that underlie the repolarizing phase of the action potential. 1 ...
... 8) Explain the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting potential. 9) Describe the characteristics of an action potential. Explain the role of voltage-gated channels in this process. 10) Describe the two main factors that underlie the repolarizing phase of the action potential. 1 ...
Objectives: The student shall know the facts, understand the
... Active transport (primary & secondary); application to the resting neuron membrane and intestinal absorption of sodium, glucose, and water Water transport; definitions of solution osmolarity and tonicity Vesicular transport; endocytosis and exocytosis Components of electrochemical (passive) driving ...
... Active transport (primary & secondary); application to the resting neuron membrane and intestinal absorption of sodium, glucose, and water Water transport; definitions of solution osmolarity and tonicity Vesicular transport; endocytosis and exocytosis Components of electrochemical (passive) driving ...
Simulation of myelinated neuron with focus on conduction speed
... Myelin sheath is a protective coat around the axon of a neuron and acts as an insulator to the electrical signal that is conducted down the axon as a neuron fires. This increases the conduction speed of action potential and thus is a critical factor in maintaining the proper communication within the ...
... Myelin sheath is a protective coat around the axon of a neuron and acts as an insulator to the electrical signal that is conducted down the axon as a neuron fires. This increases the conduction speed of action potential and thus is a critical factor in maintaining the proper communication within the ...
Lecture 3 NS_2015
... potential of the postsynaptic membrane, determining excitation or inhibition The postsynaptic membrane has receptor proteins with 2 components: • A binding component/sites for ligands/neurotransmitters • An ionophore component that passes all the way through the postsynaptic membrane to the interior ...
... potential of the postsynaptic membrane, determining excitation or inhibition The postsynaptic membrane has receptor proteins with 2 components: • A binding component/sites for ligands/neurotransmitters • An ionophore component that passes all the way through the postsynaptic membrane to the interior ...
Neurotransmitters
... Neurotransmitters • Language of nervous system • 50 or more neurotransmitters have been identified • Most neurons make two or more neurotransmitters – Neurons can exert several influences ...
... Neurotransmitters • Language of nervous system • 50 or more neurotransmitters have been identified • Most neurons make two or more neurotransmitters – Neurons can exert several influences ...
The Nervous System
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.