RESPIRATORY DRUGS 1. ANTITUSSIVES
... brainstem which causes contraction of the muscles needed to cough. The type of cough produced depends on the location of the stimulated receptors and whether or not mucus is brought up with the cough (productive or non productive). -Antitussives given to animals are centrally acting. They suppress t ...
... brainstem which causes contraction of the muscles needed to cough. The type of cough produced depends on the location of the stimulated receptors and whether or not mucus is brought up with the cough (productive or non productive). -Antitussives given to animals are centrally acting. They suppress t ...
AANEM Glossary of Terms in Neuromuscular
... end of the spike and the time when the membrane potential is restored to its resting value. The membrane during this period may be depolarized or hyperpolarized at different times. akinesia Lack or marked delay of intended movement, often observed in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Often used syn ...
... end of the spike and the time when the membrane potential is restored to its resting value. The membrane during this period may be depolarized or hyperpolarized at different times. akinesia Lack or marked delay of intended movement, often observed in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Often used syn ...
34. Organ of balance and hearing
... otolith-weighted matrix, stimulating the hair cells that stimulate the receptors of the vestibular nerve Vestibular nerve fibers conduct impulses to the brain and sense head position and a change in the pull of gravity Righting reflexes: muscular responses to restore the body and its parts to their ...
... otolith-weighted matrix, stimulating the hair cells that stimulate the receptors of the vestibular nerve Vestibular nerve fibers conduct impulses to the brain and sense head position and a change in the pull of gravity Righting reflexes: muscular responses to restore the body and its parts to their ...
PREFERENTIAL POTENTIATION OF WEAKER INPUTS TO PRIMARY
... All work presented within this thesis represents the collective effort of many wonderful minds. Some of those minds have contributed to this thesis directly, with ideas, technical assistance, or by helping with the write-up. Others have helped through less direct means, such as by motivating, inspir ...
... All work presented within this thesis represents the collective effort of many wonderful minds. Some of those minds have contributed to this thesis directly, with ideas, technical assistance, or by helping with the write-up. Others have helped through less direct means, such as by motivating, inspir ...
Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity Orchestrates the Response of Pyramidal
... the differential impact of pyramidal cell population bursts on post-synaptic pyramidal cells receiving depressing synapses, and on a class of interneuron that receives facilitating synapses. In experiment a significant shift of the order of one hundred milliseconds is seen between the response of th ...
... the differential impact of pyramidal cell population bursts on post-synaptic pyramidal cells receiving depressing synapses, and on a class of interneuron that receives facilitating synapses. In experiment a significant shift of the order of one hundred milliseconds is seen between the response of th ...
Nutrient and energy intakes for the European Community
... potassium excretion or urinary Na:K excretion ratios 4 . An adequate potassium intake is needed to achieve effective homoeostasis of sodium. Young normotensive men on a potassium intake of 10 mmoYd (390 mgld) were less able to excrete an imposed sodium excess than when they had a potassium intake of ...
... potassium excretion or urinary Na:K excretion ratios 4 . An adequate potassium intake is needed to achieve effective homoeostasis of sodium. Young normotensive men on a potassium intake of 10 mmoYd (390 mgld) were less able to excrete an imposed sodium excess than when they had a potassium intake of ...
Nicotinic Receptors in Addiction Pathways
... have a critical role in controlling local dopamine release (Exley and Cragg, 2008) and exhibit marked differences in subunit composition across brain regions (Livingstone and Wonnacott, 2009). The ventral striatum, or nucleus accumbens, is a major output for reinforced behavior and is the target of ...
... have a critical role in controlling local dopamine release (Exley and Cragg, 2008) and exhibit marked differences in subunit composition across brain regions (Livingstone and Wonnacott, 2009). The ventral striatum, or nucleus accumbens, is a major output for reinforced behavior and is the target of ...
3-Morpholinylsydnonimine Inhibits Glutamatergic Transmission in
... produced a significant increase in the amplitude of EPSCs by 25.6 ⫾ 3.9% (n ⫽ 4, p ⬍ 0.05, paired Student’s t test), as reported previously (Huang et al., 2003). It is intriguing that the effect of SIN-1 at a higher dose on EPSC amplitude was drastically different. Applied at 1 mM, SIN-1 consistentl ...
... produced a significant increase in the amplitude of EPSCs by 25.6 ⫾ 3.9% (n ⫽ 4, p ⬍ 0.05, paired Student’s t test), as reported previously (Huang et al., 2003). It is intriguing that the effect of SIN-1 at a higher dose on EPSC amplitude was drastically different. Applied at 1 mM, SIN-1 consistentl ...
Mucosal Wave Movement
... –auditory feedback –sensory input learning speech – not essential for everyday use. –Prelingually deaf ...
... –auditory feedback –sensory input learning speech – not essential for everyday use. –Prelingually deaf ...
the physiology of a lepidopteran muscle receptor
... latencies revealed ganglionic delays over and above axon conduction time of 1-2 msec, in such cases. In contrast, it was not possible to show any ganglionic delay when recording from muscles responding in a 1:1 manner at over 100 stimuli/sec.; such high-frequency following was seen only with stimula ...
... latencies revealed ganglionic delays over and above axon conduction time of 1-2 msec, in such cases. In contrast, it was not possible to show any ganglionic delay when recording from muscles responding in a 1:1 manner at over 100 stimuli/sec.; such high-frequency following was seen only with stimula ...
A Learning Rule for the Emergence of Stable Dynamics and Timing
... in networks in which each neurons received 1 (black), 2 (red), or 4 (blue) from other excitatory neurons. With nEx 3 Ex ⫽ 1, synaptic scaling converges to a state in which each neuron achieves it’s target level of activity. Note that this represents a feed-forward network. Small degrees of recurrenc ...
... in networks in which each neurons received 1 (black), 2 (red), or 4 (blue) from other excitatory neurons. With nEx 3 Ex ⫽ 1, synaptic scaling converges to a state in which each neuron achieves it’s target level of activity. Note that this represents a feed-forward network. Small degrees of recurrenc ...
Changes in muscle coordination with training
... Stability and adaptability. To appreciate the potentially beneficial effects of increases in strength in complex natural tasks, it is necessary to also consider the context in which muscle actions are performed. Tasks encountered in daily living seldom involve a single muscle. The potential contribu ...
... Stability and adaptability. To appreciate the potentially beneficial effects of increases in strength in complex natural tasks, it is necessary to also consider the context in which muscle actions are performed. Tasks encountered in daily living seldom involve a single muscle. The potential contribu ...
The Nervous System
... • Nervous system communication can be conceptualized as working through a twostep process: 1. signal movement down a neuron’s axon 2. signal movement from this axon to a second cell across a structure known as a synapse ...
... • Nervous system communication can be conceptualized as working through a twostep process: 1. signal movement down a neuron’s axon 2. signal movement from this axon to a second cell across a structure known as a synapse ...
Sources
... induced coma and loss of protective reflexes resulting from the administration of one or more general anesthetic agents. A variety of medications may be administered, with the overall aim of ensuring unconsciousness, amnesia, analgesia, relaxation of skeletal muscles, and loss of control of reflexes ...
... induced coma and loss of protective reflexes resulting from the administration of one or more general anesthetic agents. A variety of medications may be administered, with the overall aim of ensuring unconsciousness, amnesia, analgesia, relaxation of skeletal muscles, and loss of control of reflexes ...
Dynamic Stochastic Synapses as Computational Units
... of this model in section 3. We focus here on computations on short spike trains, which have not been addressed previously in the literature. 2 A Model for the Temporal Dynamics of a Single Synapse Single excitatory synapses in the mammalian cortex exhibit binary responses. At each release site, eith ...
... of this model in section 3. We focus here on computations on short spike trains, which have not been addressed previously in the literature. 2 A Model for the Temporal Dynamics of a Single Synapse Single excitatory synapses in the mammalian cortex exhibit binary responses. At each release site, eith ...
Auto-structure of presynaptic activity defines postsynaptic firing
... We have studied then the Fano factor F FC as a measure of clustering of synchronous activity for renewal processes with Gamma- and log-normal -distributed interspike intervals. The Fano factor of the coincidence count distribution for pairs of processes with identical spike-rates is represented in F ...
... We have studied then the Fano factor F FC as a measure of clustering of synchronous activity for renewal processes with Gamma- and log-normal -distributed interspike intervals. The Fano factor of the coincidence count distribution for pairs of processes with identical spike-rates is represented in F ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... • Looking at the luminal membrane of these cells, we see that they lack a brush border, in contrast to the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule. However, they do have a limited number of short microvilli containing many ion channels and secondary active transport molecules. • Notice that this sec ...
... • Looking at the luminal membrane of these cells, we see that they lack a brush border, in contrast to the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule. However, they do have a limited number of short microvilli containing many ion channels and secondary active transport molecules. • Notice that this sec ...
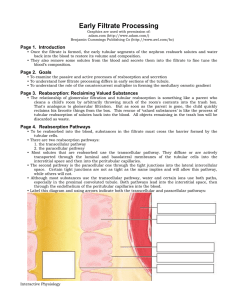
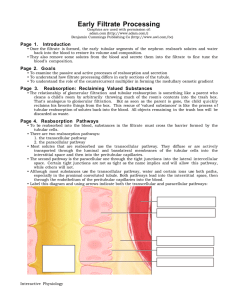
Early Filtrate Processing
... • Looking at the luminal membrane of these cells, we see that they lack a brush border, in contrast to the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule. However, they do have a limited number of short microvilli containing many ion channels and secondary active transport molecules. • Notice that this sec ...
... • Looking at the luminal membrane of these cells, we see that they lack a brush border, in contrast to the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule. However, they do have a limited number of short microvilli containing many ion channels and secondary active transport molecules. • Notice that this sec ...
Chapter 15
... • how can different autonomic neurons have different effects? constricting some vessels but dilating others – effects determined by types of neurotransmitters released and types of receptors found on target cells ...
... • how can different autonomic neurons have different effects? constricting some vessels but dilating others – effects determined by types of neurotransmitters released and types of receptors found on target cells ...
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Reflexes
... adrenal medulla, and in neuromuscular junctions – All cells with nicotinic receptors are excited by ACh – muscarinic receptors- occur on all gland, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscles cells that receive cholinergic innervation – some cells with muscarinic receptors are excited while others are inhibi ...
... adrenal medulla, and in neuromuscular junctions – All cells with nicotinic receptors are excited by ACh – muscarinic receptors- occur on all gland, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscles cells that receive cholinergic innervation – some cells with muscarinic receptors are excited while others are inhibi ...
Course Objectives
... o Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contractions. o Explain how muscle fibers are stimulated to contract by describing events that occur at the neuromuscular junction. o Describe how an action potential is generated. o Follow the events of excitation-contraction coupling that lead to cro ...
... o Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contractions. o Explain how muscle fibers are stimulated to contract by describing events that occur at the neuromuscular junction. o Describe how an action potential is generated. o Follow the events of excitation-contraction coupling that lead to cro ...
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor-like Molecules in the Retina
... The left half-sections were reacted for AChR-like immunoreactivity (through step 10, above), and both right and left halves were reacted for HRP. The matching sections were then reassembled photographitally, thus producing a reconstituted tectal slice in which the retinal Droiection aDDeared on the ...
... The left half-sections were reacted for AChR-like immunoreactivity (through step 10, above), and both right and left halves were reacted for HRP. The matching sections were then reassembled photographitally, thus producing a reconstituted tectal slice in which the retinal Droiection aDDeared on the ...
Nervous System Power Point
... Components of a synapse. Diagram shows synaptic knob or axon terminal of presynaptic neuron, the plasma membrane of a postsynaptic neuron, and a synaptic cleft. On the arrival of an action potential at a synaptic knob, neurotransmitter molecules are released from vesicles in the knob into the synapt ...
... Components of a synapse. Diagram shows synaptic knob or axon terminal of presynaptic neuron, the plasma membrane of a postsynaptic neuron, and a synaptic cleft. On the arrival of an action potential at a synaptic knob, neurotransmitter molecules are released from vesicles in the knob into the synapt ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.