The Superior Olivary Nucleus and Its Influence on Nucleus
... 20.4 and 10.9 nA current injections in a faster time scale. The resting membrane potential of this neuron was 259 mV. B, Function showing the relationship of current injected (in nanoamperes) and maximum membrane voltage deflection (in millivolts) for 23 SON cells (mean 6 SD). The slope of I–V f unc ...
... 20.4 and 10.9 nA current injections in a faster time scale. The resting membrane potential of this neuron was 259 mV. B, Function showing the relationship of current injected (in nanoamperes) and maximum membrane voltage deflection (in millivolts) for 23 SON cells (mean 6 SD). The slope of I–V f unc ...
Enhanced intrinsic excitability and EPSP
... increase the frequency, but not amplitude, of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents. ...
... increase the frequency, but not amplitude, of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents. ...
Print this article - University of Toronto Journal of Undergraduate Life
... The treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD) relies heavily on levodopa therapy. Although highly effective in ameliorating the debilitating symptoms of PD, levodopa treatment is largely associated with the development of abnormal involuntary movements. Several studies have suggested that these motor co ...
... The treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD) relies heavily on levodopa therapy. Although highly effective in ameliorating the debilitating symptoms of PD, levodopa treatment is largely associated with the development of abnormal involuntary movements. Several studies have suggested that these motor co ...
Multimodal imaging and the neural basis of EEG and fMRI
... into the cell on the return trip) causing a concentration gradient. Because ions have electrical charge, the concentration gradient creates an electrical potential (about -70 millivolt) between the inside and the outside of the cell. Neurotransmitter leads to the opening of ions channels through whi ...
... into the cell on the return trip) causing a concentration gradient. Because ions have electrical charge, the concentration gradient creates an electrical potential (about -70 millivolt) between the inside and the outside of the cell. Neurotransmitter leads to the opening of ions channels through whi ...
sympathetic division
... neuromuscular junctions of skeletal muscle • excitatory when ACh binding occurs ...
... neuromuscular junctions of skeletal muscle • excitatory when ACh binding occurs ...
Impairment of a parabolic bursting rhythm by the ectopic expression
... rhythm of R15. Previous studies on this topic have focused on two transient currents, designated ID (depolarizing) and IH (hyperpolarizing), both of which increment by a fixed amount after each action potential in a burst [1]. More recently, ISI (slow inward Ca2þ current) was proposed as a key requi ...
... rhythm of R15. Previous studies on this topic have focused on two transient currents, designated ID (depolarizing) and IH (hyperpolarizing), both of which increment by a fixed amount after each action potential in a burst [1]. More recently, ISI (slow inward Ca2þ current) was proposed as a key requi ...
No Slide Title
... • Two fundamental reasons – Sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers secrete different neurotransmitters – Target cells respond to the same neurotransmitter differently depending upon the type of receptor they have for it • All autonomic fibers secrete either acetylcholine or norepinephrine • There ar ...
... • Two fundamental reasons – Sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers secrete different neurotransmitters – Target cells respond to the same neurotransmitter differently depending upon the type of receptor they have for it • All autonomic fibers secrete either acetylcholine or norepinephrine • There ar ...
Synapse formation in developing neural circuits.
... synapses, or synaptic transmission. It is therefore befitting that the actual term ‘‘synapse’’ was not coined by a neuroanatomist, but by a physiologist named Charles Sherrington. Sherrington coined the term ‘‘synapse’’ to refer to the special connections from one nerve cell to another that facilita ...
... synapses, or synaptic transmission. It is therefore befitting that the actual term ‘‘synapse’’ was not coined by a neuroanatomist, but by a physiologist named Charles Sherrington. Sherrington coined the term ‘‘synapse’’ to refer to the special connections from one nerve cell to another that facilita ...
Spiking Neurons - Computing Science and Mathematics
... of spikes emitted by the receptor neuron increaseswith the force applied to the muscle. Another textbook example is the touch receptor in the leech [Kandel and Schwartz, 1991] . The stronger the touch stimulus , the more spikes occur during a stimulation period of 500 ms. These classical results sho ...
... of spikes emitted by the receptor neuron increaseswith the force applied to the muscle. Another textbook example is the touch receptor in the leech [Kandel and Schwartz, 1991] . The stronger the touch stimulus , the more spikes occur during a stimulation period of 500 ms. These classical results sho ...
THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM CHAPTER 5: 1.3.1 The
... (performed with a full and adequate supply of oxygen) types of exercise. On the other hand, fast twitch fibres are specifically adapted for high intensity and mainly anaerobic (performed without sufficient oxygen to cope with the energy demand) types of exercise. Describe some of the characteristics ...
... (performed with a full and adequate supply of oxygen) types of exercise. On the other hand, fast twitch fibres are specifically adapted for high intensity and mainly anaerobic (performed without sufficient oxygen to cope with the energy demand) types of exercise. Describe some of the characteristics ...
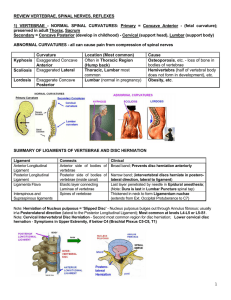
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... shows bilateral, mild hyperreflexia (scored 3). The physician suspects that this is not pathological but due to increased activation of Gamma motor neurons associated with nervousness and anxiety. Which of the following is an action of Gamma motor neurons that could produce the mild hyperreflexia? A ...
... shows bilateral, mild hyperreflexia (scored 3). The physician suspects that this is not pathological but due to increased activation of Gamma motor neurons associated with nervousness and anxiety. Which of the following is an action of Gamma motor neurons that could produce the mild hyperreflexia? A ...
Properties and Functional Role of Voltage
... glial cells that often wrap Purkinje cell dendrites. Purkinje cells were easily identified on the basis of their large size and distinctive morphology. Purkinje cells in the vermis were used for these experiments. Distance of the dendrite from which the patch was formed was measured from the center ...
... glial cells that often wrap Purkinje cell dendrites. Purkinje cells were easily identified on the basis of their large size and distinctive morphology. Purkinje cells in the vermis were used for these experiments. Distance of the dendrite from which the patch was formed was measured from the center ...
Fundamentals on Peripheral Nerves
... Although there are many different ways of classifying nerve fibers, in this course we will use only a very simple method based primarily on the direction of impulse transmission. Fundamentally, nerve fibers can be divided into AFFERENT FIBERS which conduct impulses toward the central nervous system ...
... Although there are many different ways of classifying nerve fibers, in this course we will use only a very simple method based primarily on the direction of impulse transmission. Fundamentally, nerve fibers can be divided into AFFERENT FIBERS which conduct impulses toward the central nervous system ...
The Central Nervous System
... • Rapid opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels • Na+ entry causes rapid depolarization ...
... • Rapid opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels • Na+ entry causes rapid depolarization ...
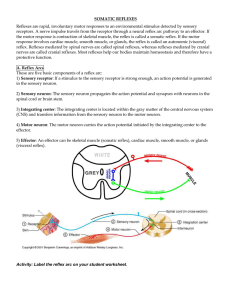
Reflex Activity/Lab
... Reflexes are rapid, involuntary motor responses to an environmental stimulus detected by sensory receptors. A nerve impulse travels from the receptor through a neural reflex arc pathway to an effector. If the motor response is contraction of skeletal muscle, the reflex is called a somatic reflex. If ...
... Reflexes are rapid, involuntary motor responses to an environmental stimulus detected by sensory receptors. A nerve impulse travels from the receptor through a neural reflex arc pathway to an effector. If the motor response is contraction of skeletal muscle, the reflex is called a somatic reflex. If ...
video slide - Course
... membrane. In this way, local currents of ions across the plasma membrane cause the action potential to be propagated along the length of the axon. ...
... membrane. In this way, local currents of ions across the plasma membrane cause the action potential to be propagated along the length of the axon. ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... • Two types of α (α1 and α2) • Two types of β (β1 and β2) • All act using G-proteins and second messenger systems. – β receptors use cAMP. – α receptors use a Ca2+ second messenger system. ...
... • Two types of α (α1 and α2) • Two types of β (β1 and β2) • All act using G-proteins and second messenger systems. – β receptors use cAMP. – α receptors use a Ca2+ second messenger system. ...
Muscle Coordination 1 Changes in Muscle Coordination with
... at which the task could be performed in an accurate and stable fashion (6). Are such changes in the stability of behaviour mediated by trained induced alterations in the efficiency with which motor actions are generated? One direct consequence of resistance training appears to be an increase in the ...
... at which the task could be performed in an accurate and stable fashion (6). Are such changes in the stability of behaviour mediated by trained induced alterations in the efficiency with which motor actions are generated? One direct consequence of resistance training appears to be an increase in the ...
MS word - University of Kentucky
... EPSPs, IPSPs, and the Neuromuscular Junction The abdominal extensor muscle preparation used to demonstrate the resting membrane potential is also ideal for demonstrating synaptic responses at neuromuscular junctions. In a general motorneural pathway, action potentials exiting the central nervous sys ...
... EPSPs, IPSPs, and the Neuromuscular Junction The abdominal extensor muscle preparation used to demonstrate the resting membrane potential is also ideal for demonstrating synaptic responses at neuromuscular junctions. In a general motorneural pathway, action potentials exiting the central nervous sys ...
Impact of correlated inputs to neurons
... membrane potentials of neighboring neurons were found to be highly correlated (Okun and Lampl 2008; Poulet and Petersen 2008; Gentet et al. 2010), but their spike responses were not (Gentet et al. 2010). Earlier theoretical work (de la Rocha et al. 2007; Shea-Brown et al. 2008; Tchumatchenko et al. ...
... membrane potentials of neighboring neurons were found to be highly correlated (Okun and Lampl 2008; Poulet and Petersen 2008; Gentet et al. 2010), but their spike responses were not (Gentet et al. 2010). Earlier theoretical work (de la Rocha et al. 2007; Shea-Brown et al. 2008; Tchumatchenko et al. ...
25. Organ of balance and hearing
... otolith-weighted matrix, stimulating the hair cells that stimulate the receptors of the vestibular nerve Vestibular nerve fibers conduct impulses to the brain and sense head position and a change in the pull of gravity Righting reflexes: muscular responses to restore the body and its parts to their ...
... otolith-weighted matrix, stimulating the hair cells that stimulate the receptors of the vestibular nerve Vestibular nerve fibers conduct impulses to the brain and sense head position and a change in the pull of gravity Righting reflexes: muscular responses to restore the body and its parts to their ...
Memory Maintenance in Synapses with Calcium
... points (the minima of U), one at r~0 - the DOWN state -, the other at r~1 - the UP state -, depending on the initial condition. This corresponds to a bistable synapse. 2. For intermediate calcium concentrations (c(t)whd ), the synapse is depressed, with a depression rate cd . 3. For large calcium co ...
... points (the minima of U), one at r~0 - the DOWN state -, the other at r~1 - the UP state -, depending on the initial condition. This corresponds to a bistable synapse. 2. For intermediate calcium concentrations (c(t)whd ), the synapse is depressed, with a depression rate cd . 3. For large calcium co ...
The concept of a reflex
... events in its own body and in the world around it. Information collected by sense organs is passed to the nervous system, which determines and initiates an appropriate response. The stimuli or the sensations are received by the nerves which are associated with special sensory cells called receptors ...
... events in its own body and in the world around it. Information collected by sense organs is passed to the nervous system, which determines and initiates an appropriate response. The stimuli or the sensations are received by the nerves which are associated with special sensory cells called receptors ...
Stretch reflexes. (Final).
... Signals sent to a whole muscle (like the biceps) causing it to contract, travel from the spinal cord through alpha motor neurons. When this occurs, only extrafusal muscle fibers would contract. Meanwhile, the intrafusal muscle fibers within the muscle spindles would go slack and information from the ...
... Signals sent to a whole muscle (like the biceps) causing it to contract, travel from the spinal cord through alpha motor neurons. When this occurs, only extrafusal muscle fibers would contract. Meanwhile, the intrafusal muscle fibers within the muscle spindles would go slack and information from the ...
Lecture #11 Brain and processing
... The Spinothalamic Pathway Third-order neurons Synapse in ventral nucleus group of the thalamus After the sensations have been sorted and processed, they are relayed to primary sensory ...
... The Spinothalamic Pathway Third-order neurons Synapse in ventral nucleus group of the thalamus After the sensations have been sorted and processed, they are relayed to primary sensory ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.