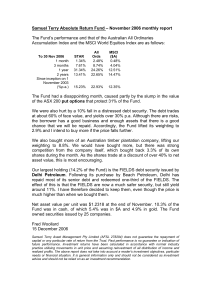
An Open Letter to Clients – January 2008
... interest rates go up property values can decline. And then, POP! There goes the housing market! Remember the loan made to someone who shouldn’t be borrowing money? That interest rate spiked upon renewal (typically a few years after the original purchase had been made). In some cases, such types of m ...
... interest rates go up property values can decline. And then, POP! There goes the housing market! Remember the loan made to someone who shouldn’t be borrowing money? That interest rate spiked upon renewal (typically a few years after the original purchase had been made). In some cases, such types of m ...
Interest Rate 1 Interest Rate Interest Rate What is the interest rate
... Essentially, 90 day Treasury bills mature and are extended in 13 weeks. Every week there is a 1/13th portion of the bill that is refunded. ...
... Essentially, 90 day Treasury bills mature and are extended in 13 weeks. Every week there is a 1/13th portion of the bill that is refunded. ...
Measuring the Duration of Liabilities
... • Interest rates shift in parallel fashion Short term interest rates tend to be more volatile than longer term rates ...
... • Interest rates shift in parallel fashion Short term interest rates tend to be more volatile than longer term rates ...
Section 5
... Large positive spread (Long-term rates are quite a bit higher than short-term rates) means that future interest rates should be higher. Negative spread (Short-term rates are higher than long-term rates) means that future interest rates should be lower. Often it is an indicator of an economic downtur ...
... Large positive spread (Long-term rates are quite a bit higher than short-term rates) means that future interest rates should be higher. Negative spread (Short-term rates are higher than long-term rates) means that future interest rates should be lower. Often it is an indicator of an economic downtur ...
1.1.2 SIMPLE INTEREST In practice, when calculating interest
... In the previous example, we see that to achieve a yield rate of 15% Jones pays 5022.46 and to achieve a yield rate of 12% Jones pays 5046.75. This inverse relationship between yield and price is typical of a “fixed-income” investment. A fixed-income investment is one for which the future payments ar ...
... In the previous example, we see that to achieve a yield rate of 15% Jones pays 5022.46 and to achieve a yield rate of 12% Jones pays 5046.75. This inverse relationship between yield and price is typical of a “fixed-income” investment. A fixed-income investment is one for which the future payments ar ...
Econ 204 Practice Qu..
... a. Money demand is sometimes called the liquidity preference function. b. An increase in interest rates will move left along the money demand curve c. An increase in output will shift the money demand curve to the right d. A decrease in price levels will shift the money demand curve to the left e. N ...
... a. Money demand is sometimes called the liquidity preference function. b. An increase in interest rates will move left along the money demand curve c. An increase in output will shift the money demand curve to the right d. A decrease in price levels will shift the money demand curve to the left e. N ...
A corporate bond maturing in 5 years carries a 10% coupon rate and
... percent which will result in interest charges of $7,000 per year. EBIT is projected to be $25,000 on sales of $270,000, and it expects to have a total assets turnover ratio of 3.0. The average tax rate will be 40 percent. What does Roland expect return on equity to be following the changes? 4. (20) ...
... percent which will result in interest charges of $7,000 per year. EBIT is projected to be $25,000 on sales of $270,000, and it expects to have a total assets turnover ratio of 3.0. The average tax rate will be 40 percent. What does Roland expect return on equity to be following the changes? 4. (20) ...
11 November 2008
... scheme such that the growth of the forest is continually subsidized at a rate σ while a decline in the forest is taxed at the same rate σ. Let the present value for the forest owner (over a full cycle) of such a subsidy/tax scheme be denoted N(T). -Show that N(T) is positive. -What does this imply f ...
... scheme such that the growth of the forest is continually subsidized at a rate σ while a decline in the forest is taxed at the same rate σ. Let the present value for the forest owner (over a full cycle) of such a subsidy/tax scheme be denoted N(T). -Show that N(T) is positive. -What does this imply f ...
Credit Risk
... Only considers two extreme cases (default/no default). Weights need not be stationary over time. Ignores hard to quantify factors including business cycle effects. Database of defaulted loans is not available to benchmark the model. Mortality rate models The probability of default is est ...
... Only considers two extreme cases (default/no default). Weights need not be stationary over time. Ignores hard to quantify factors including business cycle effects. Database of defaulted loans is not available to benchmark the model. Mortality rate models The probability of default is est ...
Chapter 14 - Capital Markets
... For nominal bonds, the risk is in higher inflation rates. For these bonds, the risk is in possible changes in government policy toward them. ...
... For nominal bonds, the risk is in higher inflation rates. For these bonds, the risk is in possible changes in government policy toward them. ...
interest rate options
... Depending on the agreed reference maturity periods, the current three-month or six-month market interest rate is compared against the agreed strike price every three or six months. If the market rate is higher than the strike price, the holder of the cap will be compensated for the difference. ad 2 ...
... Depending on the agreed reference maturity periods, the current three-month or six-month market interest rate is compared against the agreed strike price every three or six months. If the market rate is higher than the strike price, the holder of the cap will be compensated for the difference. ad 2 ...