nervous system 2012 - Junction Hill C
... to other cells by a fiber called an axon. Axons can be very short or quite long. You have some really long axons that extend almost 1 meter from your lower back to your toes ...
... to other cells by a fiber called an axon. Axons can be very short or quite long. You have some really long axons that extend almost 1 meter from your lower back to your toes ...
What is Psychology
... •Which cells are the nervous system’s communicators and how to they “talk”? •How do learning and experience alter the brain? •Why do neural impulses travel more slowly in children than adults? •What happens when neurotransmitters are too low or too high? ...
... •Which cells are the nervous system’s communicators and how to they “talk”? •How do learning and experience alter the brain? •Why do neural impulses travel more slowly in children than adults? •What happens when neurotransmitters are too low or too high? ...
Unit 2: Nervous System
... • Spinal cord = communication highway • All nerves communicate through Spine ...
... • Spinal cord = communication highway • All nerves communicate through Spine ...
3-2_UniqueFt_of_Neurons
... dendrites: neurons have multiple dendrites (which also can branch multiple times) that connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the de ...
... dendrites: neurons have multiple dendrites (which also can branch multiple times) that connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the de ...
Electrical Stimulation of the Brain
... Peripheral Nervous System PNS includes all nerves outside the brain and ...
... Peripheral Nervous System PNS includes all nerves outside the brain and ...
Grant Clay
... You should be able to answer the following questions: 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nat ...
... You should be able to answer the following questions: 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nat ...
II. ORGANIZATION OF THE HUMAN NERVOUS
... Cell Body – Contains the _nucleus______. Site of _metabolic_____ activity. Receives impulse from _dendrite______. Axon – Transmits impulses _away from the cell body______ to next cell. Usually a long, single fiber with many small tips called _axon terminals_________. Schwann Cells – Wrap aroun ...
... Cell Body – Contains the _nucleus______. Site of _metabolic_____ activity. Receives impulse from _dendrite______. Axon – Transmits impulses _away from the cell body______ to next cell. Usually a long, single fiber with many small tips called _axon terminals_________. Schwann Cells – Wrap aroun ...
File - CYPA Psychology
... Carl Wernicke (1848-1905): describes patient who cannot comprehend language but CAN produce it Damage to an area in the left TEMPORAL lobe Wernicke’s Aphasia ...
... Carl Wernicke (1848-1905): describes patient who cannot comprehend language but CAN produce it Damage to an area in the left TEMPORAL lobe Wernicke’s Aphasia ...
Biological Psychology A branch of psychology concerned with links
... A neural impulse (a brief electrical charge) that travels down an axon; The action potential is generated by movement of positively charged atoms through channels in the axon's membrane ...
... A neural impulse (a brief electrical charge) that travels down an axon; The action potential is generated by movement of positively charged atoms through channels in the axon's membrane ...
Introductory Assignment to the Nervous System
... organ coordinates most of the activities of the nervous system? Through what part of the body do most messages reach or leave the brain? The brain and spinal cord form what part of the nervous system? What connects the central nervous system to muscles and sense organs throughout the body? W ...
... organ coordinates most of the activities of the nervous system? Through what part of the body do most messages reach or leave the brain? The brain and spinal cord form what part of the nervous system? What connects the central nervous system to muscles and sense organs throughout the body? W ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... • Positive ions will flow into the neuron if not stopped or pumped out by the membrane. This is called the electrical potential, which is measured in millivolts. • The resting potential is the neuron’s usual charge, which is –70 millivolts. • When the resting potential has changed enough, about +10 ...
... • Positive ions will flow into the neuron if not stopped or pumped out by the membrane. This is called the electrical potential, which is measured in millivolts. • The resting potential is the neuron’s usual charge, which is –70 millivolts. • When the resting potential has changed enough, about +10 ...
Nerve Notes
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
Nervous System • Steers, controls and watches over our bodily
... Steers, controls and watches over our bodily functions and processes WHY?– to protect us, to keep us alive, and to fit in with the environment It is divided into a central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) – and a peripheral nervous system (periphery nerves) The peripheral system collects infor ...
... Steers, controls and watches over our bodily functions and processes WHY?– to protect us, to keep us alive, and to fit in with the environment It is divided into a central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) – and a peripheral nervous system (periphery nerves) The peripheral system collects infor ...
PPT Guide Brain Development
... There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ____________ and ____________ ...
... There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ____________ and ____________ ...
The Nervous System allows communication
... Magneto encephalography – is a noninvasive neurophysiological technique that is similar to the EEG but more accurate and measures deeply into the brain where speech and language centers are located. The “MEG” measures the magnetic fields generated by neuronal activity of the brain. John is pictured ...
... Magneto encephalography – is a noninvasive neurophysiological technique that is similar to the EEG but more accurate and measures deeply into the brain where speech and language centers are located. The “MEG” measures the magnetic fields generated by neuronal activity of the brain. John is pictured ...
File
... The dendrites receive the information from sensory cells which then is passed down to the cell body where the information is evaluated and on to the axon. Once the information is at axon it travel downs length of axon in form of electrical signal known as action potential. Once the electrical impuls ...
... The dendrites receive the information from sensory cells which then is passed down to the cell body where the information is evaluated and on to the axon. Once the information is at axon it travel downs length of axon in form of electrical signal known as action potential. Once the electrical impuls ...
A New Source for New Neurons : TheologyPlus : http://www
... learn a new trick: forming new neurons. Using stem cell reprogramming techniques, researchers learned that two factors—Sox2 and Mash1—would induce pericytes to change their developmental state and begin to function as newly-formed neurons. According to the article, “these induced neuronal cells acqu ...
... learn a new trick: forming new neurons. Using stem cell reprogramming techniques, researchers learned that two factors—Sox2 and Mash1—would induce pericytes to change their developmental state and begin to function as newly-formed neurons. According to the article, “these induced neuronal cells acqu ...
Lecture_31_2014_noquiz
... • Nerve = A long, tough strand of nervous tissue typically containing thousands of neurons wrapped in connective tissue; carries impulses between the central nervous system and some other part of the body. ...
... • Nerve = A long, tough strand of nervous tissue typically containing thousands of neurons wrapped in connective tissue; carries impulses between the central nervous system and some other part of the body. ...
The Nervous System
... Therefore maternal and environmental factors may impair brain development. Mothers that smoke impair the body’s ability to carry oxygen sufficiently which increased the chances of oxygen deprivation to the babies brain cells that are forming. Other severe congenital brain disorders include cerebral ...
... Therefore maternal and environmental factors may impair brain development. Mothers that smoke impair the body’s ability to carry oxygen sufficiently which increased the chances of oxygen deprivation to the babies brain cells that are forming. Other severe congenital brain disorders include cerebral ...
Nervous_System_PowerPoint
... Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord White matter: propagates sensory impulses from the periphery to the brain and motor impulses from the brain to the periphery Gray matter: receives and integrates incoming and outgoing info ...
... Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord White matter: propagates sensory impulses from the periphery to the brain and motor impulses from the brain to the periphery Gray matter: receives and integrates incoming and outgoing info ...
Slide ()
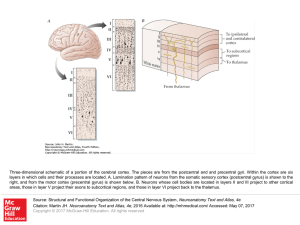
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.