here - STAO
... Neurotransmitters are molecules with very specific functions. By interacting with receptors on various postsynaptic membranes, certain actions are stimulated. There are quite a variety of other molecules that are structurally similar to various neurotransmitters. As you can imagine, if these molecul ...
... Neurotransmitters are molecules with very specific functions. By interacting with receptors on various postsynaptic membranes, certain actions are stimulated. There are quite a variety of other molecules that are structurally similar to various neurotransmitters. As you can imagine, if these molecul ...
The Nervous System - Ione Community Charter School
... activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
... activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
The Nervous System
... activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
... activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
Chapter 2 Powerpoint - Destiny High School
... • WE TALK OF THE BRAIN AND THE SPINAL CORD AS 2 DISTINCT STRUCTURES, BUT IN FACT, THERE IS NO CLEAR BOUNDARY BETWEEN THEM ...
... • WE TALK OF THE BRAIN AND THE SPINAL CORD AS 2 DISTINCT STRUCTURES, BUT IN FACT, THERE IS NO CLEAR BOUNDARY BETWEEN THEM ...
Neurons, Neurons, Neurons!
... When myelin is damaged, dense, scar-like tissue forms around nerve fibers throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spina ...
... When myelin is damaged, dense, scar-like tissue forms around nerve fibers throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spina ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... - serves sensory nerves, receptors (skin) sensory organs (head) & motor nerves that stimulate the skeletal muscle voluntary nervous system b. ...
... - serves sensory nerves, receptors (skin) sensory organs (head) & motor nerves that stimulate the skeletal muscle voluntary nervous system b. ...
File - Mr. Haan`s Science
... 1. Nervous system communicates by electrical and chemical signals 2. 3 overlapping functions a. Sensory input – sense receptors to monitor change in and out of body b. Integration – processes and interprets data to see what to do c. Motor output – causes response of effector organs ...
... 1. Nervous system communicates by electrical and chemical signals 2. 3 overlapping functions a. Sensory input – sense receptors to monitor change in and out of body b. Integration – processes and interprets data to see what to do c. Motor output – causes response of effector organs ...
Lecture 2
... • Whitish, fatty (protein-lipoid), segmented sheath around most long (NOT ALL) axons ...
... • Whitish, fatty (protein-lipoid), segmented sheath around most long (NOT ALL) axons ...
Introduction
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
... terms of information flow: Afferent neurons (sensory neurons) send signals into the central nervous system (CNS) for processing. The processed signal is sent out along efferent neurons to activate the required cellular response in effector cells. •The afferent and efferent neurons form the periphera ...
Biology Name____________________ Introduction to the Nervous
... DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM ...
... DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM ...
nervous system
... Somatic motor nerves relay information from the CNS to the skeletal muscles. A reflex arc is also an involuntary response of the somatic nervous system. ...
... Somatic motor nerves relay information from the CNS to the skeletal muscles. A reflex arc is also an involuntary response of the somatic nervous system. ...
neurons
... nervous system [PNS] consists of ‘the rest’ of the nervous system. The PNS gathers and sends information to and from the rest of the body. ...
... nervous system [PNS] consists of ‘the rest’ of the nervous system. The PNS gathers and sends information to and from the rest of the body. ...
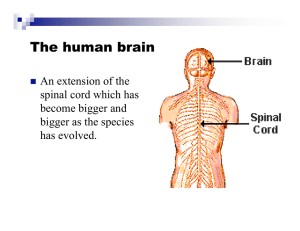
The human brain
... Typically a given neuron is connected to about ten thousand other neurons. The specific point of contact between the axon of one cell and a dendrite of another is called a ...
... Typically a given neuron is connected to about ten thousand other neurons. The specific point of contact between the axon of one cell and a dendrite of another is called a ...
MAPPINGS BETWEEN BRAINS - Wichita State University
... triggered only by specific stimuli falling on specific areas of the retina. • Once the lateral geniculate neurons are triggered, in returning to the visual cortex; if they are hypercomplex cells what happens next? ...
... triggered only by specific stimuli falling on specific areas of the retina. • Once the lateral geniculate neurons are triggered, in returning to the visual cortex; if they are hypercomplex cells what happens next? ...
The Nervous System - Marblehead High School
... Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
... Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
I. How Do Scientists Study the Nervous System?
... peripheral nervous system—consists of nerves that extend throughout the body outside the central nervous system ...
... peripheral nervous system—consists of nerves that extend throughout the body outside the central nervous system ...
Chapter 12 Notes Part 1 File
... – Neurilemma is formed by cytoplasm of Schwann cell (neurilemmocyte) wrapped around the myelin sheath; essential for nerve regrowth – Satellite cells are Schwann cells that cover and support cell bodies in the PNS ...
... – Neurilemma is formed by cytoplasm of Schwann cell (neurilemmocyte) wrapped around the myelin sheath; essential for nerve regrowth – Satellite cells are Schwann cells that cover and support cell bodies in the PNS ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... o Nerves (bundles of fibers of sensory and motor neurons) and o Ganglia (clusters of cell bodies of the neurons) Sensory neurons ...
... o Nerves (bundles of fibers of sensory and motor neurons) and o Ganglia (clusters of cell bodies of the neurons) Sensory neurons ...
The biological Approach
... The peripheral nervous system The PNS transmits messages, via millions of neurons (nerve cells), to and from the central nervous system. It is divided into: • The autonomic nervous system (ANS) This system governs vital functions in the body such as breathing, heart rate, digestion and stress respo ...
... The peripheral nervous system The PNS transmits messages, via millions of neurons (nerve cells), to and from the central nervous system. It is divided into: • The autonomic nervous system (ANS) This system governs vital functions in the body such as breathing, heart rate, digestion and stress respo ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon collaterals Axonal terminal – branched terminus of an axon ...
... Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon collaterals Axonal terminal – branched terminus of an axon ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.