Introduction to Psychology - Shoreline School District
... connect the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs ...
... connect the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs ...
APP Ch_3 Outline
... c. Dendrite – Parts of a Neuron that receives information. d. Axon – Long fiber that transmits information away to other neurons, muscles, or glands. e. Myelin Sheath – Insulating Material that encases some Axons. i. It speeds up to transmission of information. f. Terminal Button – Small knobs where ...
... c. Dendrite – Parts of a Neuron that receives information. d. Axon – Long fiber that transmits information away to other neurons, muscles, or glands. e. Myelin Sheath – Insulating Material that encases some Axons. i. It speeds up to transmission of information. f. Terminal Button – Small knobs where ...
Abstract
... Amazing abilities of our brain, such as sensation, cognition, learning, memory, and even consciousness are thought to be realized through complex interactions of streams of millisecond-order electrical spikes (known as action potentials) generated by billions of neurons. How can one investigate such ...
... Amazing abilities of our brain, such as sensation, cognition, learning, memory, and even consciousness are thought to be realized through complex interactions of streams of millisecond-order electrical spikes (known as action potentials) generated by billions of neurons. How can one investigate such ...
Co-ordination - BIFS IGCSE SCIENCE
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM is similar to sending a letter through the post i.e. takes longer to arrive but longer lasting ...
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM is similar to sending a letter through the post i.e. takes longer to arrive but longer lasting ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... are made by Schwanns cells or oligodendrocytes What is a Node of Ranvier? What is saltatory conduction? What is a synapse? ...
... are made by Schwanns cells or oligodendrocytes What is a Node of Ranvier? What is saltatory conduction? What is a synapse? ...
NEUROSCIENCE REVIEW
... Cesar was involved in a motorcycle accident and ever since he has had problems understanding what his parents, friends & teachers are saying. What area of his brain was most likely affected by the accident? ...
... Cesar was involved in a motorcycle accident and ever since he has had problems understanding what his parents, friends & teachers are saying. What area of his brain was most likely affected by the accident? ...
Label and discuss the significance of the Schwann cells/myelin
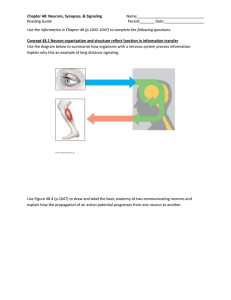
... Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer Use the diagram below to summarize how organisms with a nervous system process information. Explain why this an example of long distance signaling. ...
... Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer Use the diagram below to summarize how organisms with a nervous system process information. Explain why this an example of long distance signaling. ...
neuron - Cloudfront.net
... A “neuron”, or nerve cell is the basic unit Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the brain & spinal cord Interneurons: found within the brain & spinal cord; process impulses & pass response impulses to motor neurons Motor neurons: carry response impulses away from the brain or spinal cor ...
... A “neuron”, or nerve cell is the basic unit Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the brain & spinal cord Interneurons: found within the brain & spinal cord; process impulses & pass response impulses to motor neurons Motor neurons: carry response impulses away from the brain or spinal cor ...
The Nervous System
... incoming messages from other cells Axons—usually much longer than dendrites, convey outgoing messages from neurons to other cells ...
... incoming messages from other cells Axons—usually much longer than dendrites, convey outgoing messages from neurons to other cells ...
110 ~W~U~~ ~~~\W(Q)(UJ~
... nerves descend within the spinal canal to reach their point of exit from the vertebral column. The peripheral nervous system consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves and their branches, which connect the central nervous system to receptors, glands, and muscles throughout ...
... nerves descend within the spinal canal to reach their point of exit from the vertebral column. The peripheral nervous system consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves and their branches, which connect the central nervous system to receptors, glands, and muscles throughout ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind
... •After the signal passes through the gap, what happens to the neurotransmitter? • _____________, Or is broken down by an enzyme •So that the neuron is ready for another signal to cross the synaptic cleft Nervous System ...
... •After the signal passes through the gap, what happens to the neurotransmitter? • _____________, Or is broken down by an enzyme •So that the neuron is ready for another signal to cross the synaptic cleft Nervous System ...
PRACTICE QUIZ
... 10. The main difference between gustatory receptor cells and olfactory receptor cells is that _______________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Nasal mucus is produced by ______________________________________________________________ 12. Olfac ...
... 10. The main difference between gustatory receptor cells and olfactory receptor cells is that _______________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Nasal mucus is produced by ______________________________________________________________ 12. Olfac ...
ppt
... Resting potential does not change A small part of the axon reverses polarity Na+ ions rush out of the cell ...
... Resting potential does not change A small part of the axon reverses polarity Na+ ions rush out of the cell ...
Nervous System
... • Its rigid inner core is made up of gray matter – Gray matter is composed of dendrites, unmyelinated axons and the cell bodies of neurons ...
... • Its rigid inner core is made up of gray matter – Gray matter is composed of dendrites, unmyelinated axons and the cell bodies of neurons ...
nervousmedterm
... Blood pressure Temperature control Behavioral responses Water and electrolyte balance ...
... Blood pressure Temperature control Behavioral responses Water and electrolyte balance ...
Med Term Chapter 10
... the brain, making an individual partially or totally impaired in his ability to speak, write, or comprehend the commands. ...
... the brain, making an individual partially or totally impaired in his ability to speak, write, or comprehend the commands. ...
General design of the nervous system
... Peripheral nervous system connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Autonomic somatic The somatic nervous system includes all nerves controlling the muscular system and external sensory receptors. External sense organs (including skin) are receptors. Muscle fibers and gland cells a ...
... Peripheral nervous system connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Autonomic somatic The somatic nervous system includes all nerves controlling the muscular system and external sensory receptors. External sense organs (including skin) are receptors. Muscle fibers and gland cells a ...
Nervous System (Human): Introduction
... parts: the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and the nerves of the autonomic nervous system). Neurons These basic units of the nervous system intercommunicate electrochemically via synapses (junctions) between their proje ...
... parts: the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and the nerves of the autonomic nervous system). Neurons These basic units of the nervous system intercommunicate electrochemically via synapses (junctions) between their proje ...
OUTLINE FORMAT-Unit 3A Biological Basis of Behavior Directions
... Number and highlight the terms: 2. Answer this: How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? 16. synapse 17. synaptic gap/synaptic cleft 18. neurotransmitters ...
... Number and highlight the terms: 2. Answer this: How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? 16. synapse 17. synaptic gap/synaptic cleft 18. neurotransmitters ...
46 Chapter Review: Fill-in-the
... is a pattern of inheritance in which a trait is influenced by both genes and environmental factors. 13. The is the structure that is located above the brain stem and acts as a relay station for information flowing into or out of the higher brain centers. 14. The strip of tissue at the front ofthe pa ...
... is a pattern of inheritance in which a trait is influenced by both genes and environmental factors. 13. The is the structure that is located above the brain stem and acts as a relay station for information flowing into or out of the higher brain centers. 14. The strip of tissue at the front ofthe pa ...
Chapter 2
... – Depolarization= unfreezes or ungates the axon allowing the message to go through – Refractory period= resting period, when extra atoms are pushed out – Some signals excite and some inhibit ...
... – Depolarization= unfreezes or ungates the axon allowing the message to go through – Refractory period= resting period, when extra atoms are pushed out – Some signals excite and some inhibit ...
RAPID REVIEW The nervous system is made up of a complex
... these neurons act together in the spinal cord to form a reflex arc. The ability of the brain and spinal cord to change both in structure and function is referred to as neuroplasticity. One type of cell that facilitates these changes are stem cells. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is made up of a ...
... these neurons act together in the spinal cord to form a reflex arc. The ability of the brain and spinal cord to change both in structure and function is referred to as neuroplasticity. One type of cell that facilitates these changes are stem cells. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is made up of a ...
ANATOMY NEURO REVALIDA QUESTIONS
... Differentiate between the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. Give examples for each. Explain why cells in the PNS are able to regenerate and why cells in the CNS cannot A patient sustains an injury to his right cerebral hemisphere. Where will you expect his weakness? Why? Tell ...
... Differentiate between the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. Give examples for each. Explain why cells in the PNS are able to regenerate and why cells in the CNS cannot A patient sustains an injury to his right cerebral hemisphere. Where will you expect his weakness? Why? Tell ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.