Physiology 28.1: The human body has 5 levels of organization. 1
... 2. What are the two types of photoreceptors in the eye, and to what kind of vision do they contribute? 3. How do hair cells generate the signals needed to produce hearing? 4. What are the different types of receptors (specialized neurons) and what are their functions? 29.6: The endocrine system prod ...
... 2. What are the two types of photoreceptors in the eye, and to what kind of vision do they contribute? 3. How do hair cells generate the signals needed to produce hearing? 4. What are the different types of receptors (specialized neurons) and what are their functions? 29.6: The endocrine system prod ...
The Nervous System
... Describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information (brings information together) to produce a response. ...
... Describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information (brings information together) to produce a response. ...
Central Nervous System
... 3. The Hindbrain. • This consists of two main divisions: • a) The Metencephalon: Consists of two main structures: • i) The cerebellum: Receives information from sensory systems, the muscles, and the vestibular system. It coordinates this information to produce smooth movements. • Damage to the cere ...
... 3. The Hindbrain. • This consists of two main divisions: • a) The Metencephalon: Consists of two main structures: • i) The cerebellum: Receives information from sensory systems, the muscles, and the vestibular system. It coordinates this information to produce smooth movements. • Damage to the cere ...
Brain and Behavior
... Actions of the brain underlie all behavior. What we call mind is a range of functions carried out by the brain. ...
... Actions of the brain underlie all behavior. What we call mind is a range of functions carried out by the brain. ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Integration- interneurons integrate (analyze and interpret). Greatest complexity in neural circuits cells. Motor output- leaves CNS via motor neurons that communicate with effector cells (muscle or endocrine cells) ...
... Integration- interneurons integrate (analyze and interpret). Greatest complexity in neural circuits cells. Motor output- leaves CNS via motor neurons that communicate with effector cells (muscle or endocrine cells) ...
17-01-05 1 Golgi - stained neurons Neuronal function
... - vary in length … a few 10’s of microns, to many cm. - contain microtubules and microtubule binding proteins - relatively constant diameter in any neuron - always have specialized areas that release neurotransmitter -- terminal or en passant ...
... - vary in length … a few 10’s of microns, to many cm. - contain microtubules and microtubule binding proteins - relatively constant diameter in any neuron - always have specialized areas that release neurotransmitter -- terminal or en passant ...
File - Mr. Jacobson`s Site
... Reflex arc-the simplest type of nerve circuit Has to be at least one sensory neuron and one motor neuron ...
... Reflex arc-the simplest type of nerve circuit Has to be at least one sensory neuron and one motor neuron ...
Chemistry of Psychology - Point Loma High School
... Used by more neurons than any other Lots in Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus Too much Glutamate = causes neurons to die Plays a role in allowing and supporting synaptic connections allows messages to cross synapse efficiently Important for learning & memory (p98) Peptides= Endorphins Hund ...
... Used by more neurons than any other Lots in Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus Too much Glutamate = causes neurons to die Plays a role in allowing and supporting synaptic connections allows messages to cross synapse efficiently Important for learning & memory (p98) Peptides= Endorphins Hund ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and
... A. The nervous system originates from a dorsal neural tube and neural crest, which begin as a layer of neuroepithelial cells that ultimately become the CNS. B. Differentiation of neuroepithelial cells occurs largely in the second month of development. C. Growth of an axon toward its target appears t ...
... A. The nervous system originates from a dorsal neural tube and neural crest, which begin as a layer of neuroepithelial cells that ultimately become the CNS. B. Differentiation of neuroepithelial cells occurs largely in the second month of development. C. Growth of an axon toward its target appears t ...
Control and Coordination
... increase in diameter of pupil, which allows more light in. When we come out of the dark room into broad day light the diameter of the pupil decreases allowing less light to enter into the eyes. Both these functions occur under the influence of the autonomic nervous system. ...
... increase in diameter of pupil, which allows more light in. When we come out of the dark room into broad day light the diameter of the pupil decreases allowing less light to enter into the eyes. Both these functions occur under the influence of the autonomic nervous system. ...
Slide ()
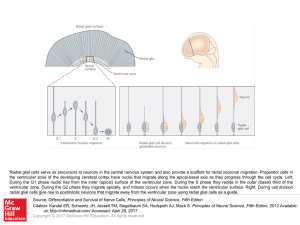
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
Sample test
... d. none of these _____14. An infant’s responses to stimuli are coarse and undifferentiated because nerve fibers a. have not yet appeared b. are incapable of carrying impulses c. have not yet developed connections to the brain d. are not completely myelinated ____15. . autoimmune disease that attacks ...
... d. none of these _____14. An infant’s responses to stimuli are coarse and undifferentiated because nerve fibers a. have not yet appeared b. are incapable of carrying impulses c. have not yet developed connections to the brain d. are not completely myelinated ____15. . autoimmune disease that attacks ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
MTC42: control of smooth muscle 11/10/07
... o Parasympathetic – arising from the brain stem (cranio-sacral) o Enteric – surrounding the gastrointestinal tract Cell bodies of ANS preganglionic neurons are found in the brain stem and spinal cord (within the CNS) and send axons (now part of the PNS) out to make synaptic contact with peripheral n ...
... o Parasympathetic – arising from the brain stem (cranio-sacral) o Enteric – surrounding the gastrointestinal tract Cell bodies of ANS preganglionic neurons are found in the brain stem and spinal cord (within the CNS) and send axons (now part of the PNS) out to make synaptic contact with peripheral n ...
The Autonomic Nervous System - Ashland Independent Schools
... Active under normal, restful conditions Prepares body for normal activities Maintains homeostasis ...
... Active under normal, restful conditions Prepares body for normal activities Maintains homeostasis ...
Chapter 17: Nervous System - Johnston Community College
... Each type of drug has been found to either promote or prevent the action of a particular neurotransmitter. Medications that counter drug effects work by affecting the release, reception, or breakdown of dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for mood. ...
... Each type of drug has been found to either promote or prevent the action of a particular neurotransmitter. Medications that counter drug effects work by affecting the release, reception, or breakdown of dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for mood. ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM REVIEW QUESTIONS:
... Sympathetic chain ganglia: Found either side of the spinal column, “sympathetic nerves”. Targets thoracic cavity organs and head (eg: heart, lungs, salivary glands etc) ...
... Sympathetic chain ganglia: Found either side of the spinal column, “sympathetic nerves”. Targets thoracic cavity organs and head (eg: heart, lungs, salivary glands etc) ...
File - Schuette Science
... Example: vertebrae of the spine; sliding joint 3. Freely movable joints: allows the widest range of motion. The following are examples of these joints: a.. pivot joint: bones rotate around each other. Example: skull attaches to vertebral column b. ball-and-socket joint: ball shaped end of one bone f ...
... Example: vertebrae of the spine; sliding joint 3. Freely movable joints: allows the widest range of motion. The following are examples of these joints: a.. pivot joint: bones rotate around each other. Example: skull attaches to vertebral column b. ball-and-socket joint: ball shaped end of one bone f ...
Unit M - Notes #1 Neurons - Mr. Lesiuk
... -Conduct a nerve impulse away from the cell body. 4. Myelin Sheath -Protective lipid coating of Schwann cells (type of neuroglial cell) forms insulating layer around longer axons and dendrites. OMIT "Larger __________" 5. Nodes of Ranvier -Interrupted areas of the Myelin Sheath due to gaps between o ...
... -Conduct a nerve impulse away from the cell body. 4. Myelin Sheath -Protective lipid coating of Schwann cells (type of neuroglial cell) forms insulating layer around longer axons and dendrites. OMIT "Larger __________" 5. Nodes of Ranvier -Interrupted areas of the Myelin Sheath due to gaps between o ...
A Data Mining Survey of the Allen Brain Atlas
... anatomical database called the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas has been conducted to reveal a detailed analysis of these neuromodulatory systems. The Allen Mouse Brain Atlas is an interactive, genome-wide image database of gene expression. A combination of RNA in situ hybridization data, detailed Reference ...
... anatomical database called the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas has been conducted to reveal a detailed analysis of these neuromodulatory systems. The Allen Mouse Brain Atlas is an interactive, genome-wide image database of gene expression. A combination of RNA in situ hybridization data, detailed Reference ...
Artificial Intelligence, Expert Systems, and DSS
... Artificial neural networks are information technology inspired by studies of the brain and nervous system ANNs are used to simulate the massively parallel processes that are effectively used in the brain for learning, and storing information and knowledge ...
... Artificial neural networks are information technology inspired by studies of the brain and nervous system ANNs are used to simulate the massively parallel processes that are effectively used in the brain for learning, and storing information and knowledge ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.