Chapter 2 figures 2.7 to 2.12
... on the darker side (8 vs 16 units). The units of brightness were selected as an example. Stimulus image ...
... on the darker side (8 vs 16 units). The units of brightness were selected as an example. Stimulus image ...
Reuptake, or re-uptake, is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by
... senses, and in the manipulation of objects; portions of the parietal lobe are involved with visuospatial processing 3. Occipital lobe—sense of sight; lesions can produce hallucinations 4. Temporal lobe—senses of smell and sound, as well as processing of complex stimuli like faces and scenes. ...
... senses, and in the manipulation of objects; portions of the parietal lobe are involved with visuospatial processing 3. Occipital lobe—sense of sight; lesions can produce hallucinations 4. Temporal lobe—senses of smell and sound, as well as processing of complex stimuli like faces and scenes. ...
Ch 7 The Nervous System Notes
... Limbic System- receives input from association areas in cortex & passes signals cerebrum 2 parts: hippocampus- essential for formation of long term memories amygdala- center of emotions (eg fear) send signals to hypothalamus& medulla wh/ can activate “fight or flight” receives signals form olfactory ...
... Limbic System- receives input from association areas in cortex & passes signals cerebrum 2 parts: hippocampus- essential for formation of long term memories amygdala- center of emotions (eg fear) send signals to hypothalamus& medulla wh/ can activate “fight or flight” receives signals form olfactory ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... 3 Electrical potential forces positive ions to the center 4 Channels, or gates, along the axon open 5 Positive sodium enters through the channel, which depolarizes the neuron 6 Action Potential shoots down the axon 7 Mylination or a wider diameter of the axon causes a faster action potential 8 Actio ...
... 3 Electrical potential forces positive ions to the center 4 Channels, or gates, along the axon open 5 Positive sodium enters through the channel, which depolarizes the neuron 6 Action Potential shoots down the axon 7 Mylination or a wider diameter of the axon causes a faster action potential 8 Actio ...
Understanding the Gifted Learner`s Brain
... Attention is important for moving sensory memories to working memory. How do we get the brain to “pay attention”? There are many factors that influence attention, however the two over which we have the most control are: • Meaning – Whether or not the student can make sense of the information (Does ...
... Attention is important for moving sensory memories to working memory. How do we get the brain to “pay attention”? There are many factors that influence attention, however the two over which we have the most control are: • Meaning – Whether or not the student can make sense of the information (Does ...
Chapter 18: Neurologic Emergencies
... • Neurologic problems can be dangerous because depressed reflexes leave the airway and other body systems vulnerable. • The central nervous system has two major structures: the brain and the spinal cord. They communicate with a neural network to regulate breathing, pulse rate, blood pressure, and co ...
... • Neurologic problems can be dangerous because depressed reflexes leave the airway and other body systems vulnerable. • The central nervous system has two major structures: the brain and the spinal cord. They communicate with a neural network to regulate breathing, pulse rate, blood pressure, and co ...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... NOTE: You may be asked to identify any structure, cell, tissue, or organ labeled in the figures/pictures within this lab manual. In addition, you may be asked to name one function of each labeled item and one location within the human body where it can be found. You are only responsible for the spec ...
... NOTE: You may be asked to identify any structure, cell, tissue, or organ labeled in the figures/pictures within this lab manual. In addition, you may be asked to name one function of each labeled item and one location within the human body where it can be found. You are only responsible for the spec ...
CH. 2 (BIOLOGY)
... Motor Cortex: It initiates voluntary movements in specific parts of the body (right side of the brain controls the left side of the body, etc.) ...
... Motor Cortex: It initiates voluntary movements in specific parts of the body (right side of the brain controls the left side of the body, etc.) ...
Objectives included for the test File
... Explain how animal experiments, lesions and FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) scanning can be used in the identification of the brain part involved in specific functions.(Include one specific example of each.) Explain sympathetic and parasympathetic control of the heart rate, movements of ...
... Explain how animal experiments, lesions and FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) scanning can be used in the identification of the brain part involved in specific functions.(Include one specific example of each.) Explain sympathetic and parasympathetic control of the heart rate, movements of ...
Stimulus – Response: Reaction Time - Science
... Movements are controlled by the CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM - the brain, spinal column, and nerves. The central nervous system gets information from the outside through special systems called senses. (sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell). Your body has SENSORY RECEPTORS that produce electrical impulses ...
... Movements are controlled by the CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM - the brain, spinal column, and nerves. The central nervous system gets information from the outside through special systems called senses. (sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell). Your body has SENSORY RECEPTORS that produce electrical impulses ...
Nervous System and Senses - Avon Community School Corporation
... muscles › Autonomic nervous system- controls unconscious activities; connects to internal organs or structures ...
... muscles › Autonomic nervous system- controls unconscious activities; connects to internal organs or structures ...
Chapter 12 The Nervous System
... 3. Interpretation and analysis of impulses (brain, spinal cord) ...
... 3. Interpretation and analysis of impulses (brain, spinal cord) ...
Teacher Resource - Dale - American Physiological Society
... introduction to the nervous system anatomy and physiology, inquiry-based demonstrations and activities, and a take-home word search of vocabulary from the lesson. The introduction covered general principles of the central and peripheral nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, neurons, synap ...
... introduction to the nervous system anatomy and physiology, inquiry-based demonstrations and activities, and a take-home word search of vocabulary from the lesson. The introduction covered general principles of the central and peripheral nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, neurons, synap ...
the autonomic nervous system
... CELLS OF SYMPATHETICALLY INNERVATED ORGANS • ALPHA-2: PRESYNAPTIC TERMINALS OF CHOLINERGIC ...
... CELLS OF SYMPATHETICALLY INNERVATED ORGANS • ALPHA-2: PRESYNAPTIC TERMINALS OF CHOLINERGIC ...
The Role of Natriuretic Peptides in Hearing
... Formation and differentiation of the neural tube Tissue architecture of the central nervous system Differentiation of neurons/generation of neural diversity Pattern generation in the nervous system ...
... Formation and differentiation of the neural tube Tissue architecture of the central nervous system Differentiation of neurons/generation of neural diversity Pattern generation in the nervous system ...
Biology Nervous System - Educational Research Center
... − the human nervous system extends from the brain to various parts of the body. The student realizes that the nervous system: − controls most of our voluntary and nonvoluntary body functions. − controls cognitive abilities such as reasoning, learning and memory. − collects and processes information ...
... − the human nervous system extends from the brain to various parts of the body. The student realizes that the nervous system: − controls most of our voluntary and nonvoluntary body functions. − controls cognitive abilities such as reasoning, learning and memory. − collects and processes information ...
Neuron_Exercises_HPsychAY10
... You will do this by engaging in a series of ten-minute projects with a partner. You will complete the following “stations” and/or projects in whatever order seems best to you: 1. Create a diagram of the structure of the neuron using construction paper and crayons or pencils. 2. Answer the following ...
... You will do this by engaging in a series of ten-minute projects with a partner. You will complete the following “stations” and/or projects in whatever order seems best to you: 1. Create a diagram of the structure of the neuron using construction paper and crayons or pencils. 2. Answer the following ...
Slide ()
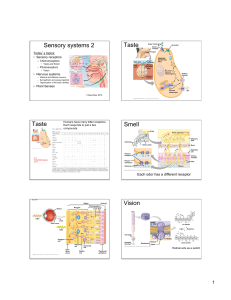
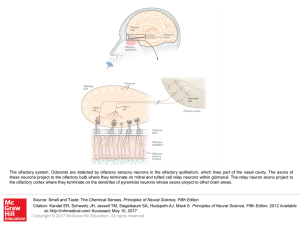
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Neurotransmitters
... the body, up the spinal cord, is processed by the brain, sent back down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
... the body, up the spinal cord, is processed by the brain, sent back down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
Lecture 1a - Division of Social Sciences
... Pia Mater (“Pious mother”) = pliant inner layer, conforms to brain & spine surface, includes blood vessels Meningitis = inflammation of Meninges Ventricles (hollow, inter-connected cavities) in brain, produce Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) - 2 Lateral and Third Ventricles in Forebrain, Cerebral Aqueduc ...
... Pia Mater (“Pious mother”) = pliant inner layer, conforms to brain & spine surface, includes blood vessels Meningitis = inflammation of Meninges Ventricles (hollow, inter-connected cavities) in brain, produce Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) - 2 Lateral and Third Ventricles in Forebrain, Cerebral Aqueduc ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.