
ANPS 019 Black 10-28
... How neurons and glia arranged? How does the CNS get its adult shape? How do we tell one part from another? What does each part of the brain do? Glial cells are smaller than neurons Many neurons synapsing on many neurons CNS: brain and spinal cord PNS: -special sensory -somatic: from muscles, joints, ...
... How neurons and glia arranged? How does the CNS get its adult shape? How do we tell one part from another? What does each part of the brain do? Glial cells are smaller than neurons Many neurons synapsing on many neurons CNS: brain and spinal cord PNS: -special sensory -somatic: from muscles, joints, ...
Document
... other lobes and utilizes this information to carry out body movement. The Panetal Lobe is located in middle of the brain. This associated with processing tactile sensory information such as pressure, touch, and pain. Another portion of the brain is the somatosensory cortex is essential to the proces ...
... other lobes and utilizes this information to carry out body movement. The Panetal Lobe is located in middle of the brain. This associated with processing tactile sensory information such as pressure, touch, and pain. Another portion of the brain is the somatosensory cortex is essential to the proces ...
Barry Jacobs presentation
... CRITICAL PERIODS • There are times during development when conditions must be right or it may be difficult or impossible to correct them later. • A young child who is abused or neglected may have great difficulty in successfully navigating adult social life. • If not corrected early on in life an i ...
... CRITICAL PERIODS • There are times during development when conditions must be right or it may be difficult or impossible to correct them later. • A young child who is abused or neglected may have great difficulty in successfully navigating adult social life. • If not corrected early on in life an i ...
Central Nervous System
... • Axons are bundled together and wrapped in CT, forming peripheral nerves, or nerves • Neuron cell bodies and axons are insulated from their surroundings by processes of glial cells: - satellite cells surround cell bodies in peripheral ganglia - every peripheral axon (unmyelinated or myelinated) is ...
... • Axons are bundled together and wrapped in CT, forming peripheral nerves, or nerves • Neuron cell bodies and axons are insulated from their surroundings by processes of glial cells: - satellite cells surround cell bodies in peripheral ganglia - every peripheral axon (unmyelinated or myelinated) is ...
Ch 49 Pract Test Nervous System
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 8
... 3. Multipolar neurons: several dendrites and one axon, includes motor neurons; bipolar neurons: one dendrite and one axon, found in the eye and nose; unipolar neurons: a single process that functions as an axon and a dendrite, includes most sensory neurons. 4. Astrocytes: participate with the endoth ...
... 3. Multipolar neurons: several dendrites and one axon, includes motor neurons; bipolar neurons: one dendrite and one axon, found in the eye and nose; unipolar neurons: a single process that functions as an axon and a dendrite, includes most sensory neurons. 4. Astrocytes: participate with the endoth ...
Introduction to Dissection
... together to maintain homeostasis. Understand the importance of maintaining a stable internal environment in the human body. ...
... together to maintain homeostasis. Understand the importance of maintaining a stable internal environment in the human body. ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Processes — fibers that extend from the cell body – can be microscopic or up to 3-4 feet in length ...
... • Processes — fibers that extend from the cell body – can be microscopic or up to 3-4 feet in length ...
nervous system text a - powerpoint presentation
... ganglia. Developmentally, this type of neuron starts out as a bipolar neuron. ...
... ganglia. Developmentally, this type of neuron starts out as a bipolar neuron. ...
Chap 2 Outline
... We can study the brain by using deep lesioning to destroy certain areas of the brain in laboratory animals, or by electrically stimulating those areas (ESB). The EEG machine allows researchers to look at the activity of the surface of the brain through the use of microelectrodes placed on the sc ...
... We can study the brain by using deep lesioning to destroy certain areas of the brain in laboratory animals, or by electrically stimulating those areas (ESB). The EEG machine allows researchers to look at the activity of the surface of the brain through the use of microelectrodes placed on the sc ...
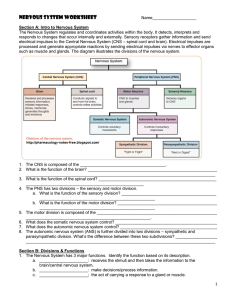
Nervous System Worksheet - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... connected to sensory receptors and the axons are connected to other neurons. The receptors change information from external sources, such as light waves or sound vibrations, into electrical impulses. In motor neurons, the dendrites are connected to other neurons, and the axons to effectors (muscles ...
... connected to sensory receptors and the axons are connected to other neurons. The receptors change information from external sources, such as light waves or sound vibrations, into electrical impulses. In motor neurons, the dendrites are connected to other neurons, and the axons to effectors (muscles ...
the nervous system powerpoint
... controled by motor area Right hemisphere controls left side of body Left hemisphere controls right side Motor nerves cross sides in spinal cord ...
... controled by motor area Right hemisphere controls left side of body Left hemisphere controls right side Motor nerves cross sides in spinal cord ...
PP text version
... many animals show cephalization: concentration of neurons and sensory organs in the head, nerve cord carries signals for rest of body ...
... many animals show cephalization: concentration of neurons and sensory organs in the head, nerve cord carries signals for rest of body ...
THE CONTROL SYSTEMS
... • Some are called somatic and control skeletal muscles • Some are called autonomic and control heartbeat, breathing, digestion, salivary glands. Spinal Cord by Brainpop ...
... • Some are called somatic and control skeletal muscles • Some are called autonomic and control heartbeat, breathing, digestion, salivary glands. Spinal Cord by Brainpop ...
CNS - Misericordia University
... time and are in stage 4 more than adults); Elderly have about the same total sleep time as adults but broken into smaller episodes, also spend less time in REM. Time spent in Stage 4 declines with age. • Person consistently deprived of REM may become ...
... time and are in stage 4 more than adults); Elderly have about the same total sleep time as adults but broken into smaller episodes, also spend less time in REM. Time spent in Stage 4 declines with age. • Person consistently deprived of REM may become ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Formation of new neurons from stem cells was not thought to occur in humans – 1992 a growth factor was found that stimulates adult mice brain cells to multiply – 1998 new neurons found to form within adult human hippocampus (area important for learning) ...
... • Formation of new neurons from stem cells was not thought to occur in humans – 1992 a growth factor was found that stimulates adult mice brain cells to multiply – 1998 new neurons found to form within adult human hippocampus (area important for learning) ...
Human Services Interpersonal Studies Multiple Choice Science Assessment Questions
... defense from injury or illness in animals (C) analyze the levels of organization in biological systems and relate the levels to each other and to the whole system 1. Charles thinks his time at the library has improved his mental functions. The ________ is the center of the nervous system that contro ...
... defense from injury or illness in animals (C) analyze the levels of organization in biological systems and relate the levels to each other and to the whole system 1. Charles thinks his time at the library has improved his mental functions. The ________ is the center of the nervous system that contro ...
11.4: The Peripheral Nervous System
... mainly conscious and voluntary part of the nervous system that controls body movements and carries signals from the CNS to skeletal muscles. The somatic system consists of 31 sets of spinal nerves. The autonomic system works with the endocrine system to react to changes in internal and external envi ...
... mainly conscious and voluntary part of the nervous system that controls body movements and carries signals from the CNS to skeletal muscles. The somatic system consists of 31 sets of spinal nerves. The autonomic system works with the endocrine system to react to changes in internal and external envi ...
The Nervous System
... • IX Glossopharyngeal nerve—sensory for taste; motor fibers to the pharynx • X Vagus nerves—sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and viscera • XI Accessory nerve—motor fibers to neck and upper back • XII Hypoglossal nerve—motor fibers to tongue ...
... • IX Glossopharyngeal nerve—sensory for taste; motor fibers to the pharynx • X Vagus nerves—sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and viscera • XI Accessory nerve—motor fibers to neck and upper back • XII Hypoglossal nerve—motor fibers to tongue ...
Neurons and Astrocytes
... needs some nerves — actually a lot of them. And it needs the spinal cord, which is a long bundle of nerves inside your spinal column, the vertebrae that protect it. It's the spinal cord and nerves — known as the nervous system — that let messages flow back and forth between the brain and body. – You ...
... needs some nerves — actually a lot of them. And it needs the spinal cord, which is a long bundle of nerves inside your spinal column, the vertebrae that protect it. It's the spinal cord and nerves — known as the nervous system — that let messages flow back and forth between the brain and body. – You ...
Cognitive Psychology
... by its firing rate - how many action potentials per second it generates. ...
... by its firing rate - how many action potentials per second it generates. ...
Nervous Tissue [PPT]
... axons in the CNS are myelinated by oligodendrocytes axons in the PNS are myelinated by Schwann cells ...
... axons in the CNS are myelinated by oligodendrocytes axons in the PNS are myelinated by Schwann cells ...
Nervous System
... fluid (which acts as a cushion) around the brain and spinal cord. Oligodendrocytes: Branched like astrocytes, but with less branches. They form myelin sheathes, which are used for insulation. ...
... fluid (which acts as a cushion) around the brain and spinal cord. Oligodendrocytes: Branched like astrocytes, but with less branches. They form myelin sheathes, which are used for insulation. ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.




















![Nervous Tissue [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000313628_1-63044c543d97a5d91f1cbdf37558ffd7-300x300.png)
