Cell Body - Cloudfront.net
... There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each vertebrae for a total of 31 pairs Spinal nerves are formed by the combination of the ventral and dorsal roots of the spinal cord Spinal nerves are named for the region from which they arise ...
... There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each vertebrae for a total of 31 pairs Spinal nerves are formed by the combination of the ventral and dorsal roots of the spinal cord Spinal nerves are named for the region from which they arise ...
Nervous System – Chapter 10
... 1. Central nervous system made of brain and spinal cord 2. Peripheral nervous system – branches 3. Autonomic nervous system – “cave man” response fight or flight B. Basic unit of the nervous system is the neuron 1. Neuroglial cells – cells that surround nervous tissue 2. Parts of Neuron: a. cell bod ...
... 1. Central nervous system made of brain and spinal cord 2. Peripheral nervous system – branches 3. Autonomic nervous system – “cave man” response fight or flight B. Basic unit of the nervous system is the neuron 1. Neuroglial cells – cells that surround nervous tissue 2. Parts of Neuron: a. cell bod ...
chapter nervous system i: basig strugture and function
... Identifu the changes in membrane potential associated with excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. ...
... Identifu the changes in membrane potential associated with excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. ...
The Nervous System - Florida International University
... N.B. Due to [unprogrammed] slide death, your slide box may not contain the required slide. If this is the case, notify an instructor and they will provide a replacement or suggest an alternative. If you end up borrowing a slide from one of your colleagues’, please don’t forget to return it to them. ...
... N.B. Due to [unprogrammed] slide death, your slide box may not contain the required slide. If this is the case, notify an instructor and they will provide a replacement or suggest an alternative. If you end up borrowing a slide from one of your colleagues’, please don’t forget to return it to them. ...
PNS and Transmission
... All of these lie close to a dendrite or the cell body of another neuron. • Pre-synaptic and Postsynaptic region. Between them is the Synaptic cleft. ...
... All of these lie close to a dendrite or the cell body of another neuron. • Pre-synaptic and Postsynaptic region. Between them is the Synaptic cleft. ...
Chapter 2 - Safford Unified School
... system conveys information between the CNS and sense organs and muscles. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls internal bodily processes such as heartbeat and respiration. The ANS contains two divisions, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic division speeds up mos ...
... system conveys information between the CNS and sense organs and muscles. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls internal bodily processes such as heartbeat and respiration. The ANS contains two divisions, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic division speeds up mos ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... • At the end of the axon, specializations called terminal buttons occur. • Here information is transferred to the dendrites of other neurones. Prof. Saeed Makarem ...
... • At the end of the axon, specializations called terminal buttons occur. • Here information is transferred to the dendrites of other neurones. Prof. Saeed Makarem ...
The Brain!
... connections at a rapid rate. The circuits that remain are more specific and efficient. The brain is one of the best examples of the “use it or lose it”•principle. Connections that are used repeatedly in the early years become permanent; while those that are not used are pruned. ...
... connections at a rapid rate. The circuits that remain are more specific and efficient. The brain is one of the best examples of the “use it or lose it”•principle. Connections that are used repeatedly in the early years become permanent; while those that are not used are pruned. ...
Functions of the Nervous System Functions of the
... Extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the first or second lumbar vertebra Provides a two-way conduction pathway to and from the brain 31 pairs of spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord Ends around vertebra L1 or L2 Cauda equina is a collection of spinal nerves at the inferior end ...
... Extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the first or second lumbar vertebra Provides a two-way conduction pathway to and from the brain 31 pairs of spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord Ends around vertebra L1 or L2 Cauda equina is a collection of spinal nerves at the inferior end ...
Structural Classification of the Nervous System
... Extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the first or second lumbar vertebra Provides a two-way conduction pathway to and from the brain 31 pairs of spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord Ends around vertebra L1 or L2 Cauda equina is a collection of spinal nerves at the inferior end ...
... Extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the first or second lumbar vertebra Provides a two-way conduction pathway to and from the brain 31 pairs of spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord Ends around vertebra L1 or L2 Cauda equina is a collection of spinal nerves at the inferior end ...
Slide ()
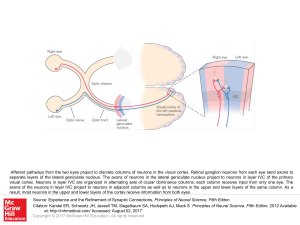
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
Motor Neuron - papbiobellaire
... Receptor CNS(brain, spinal cord) - optic (ear, eye, skin) b) motor nerve - consists entirely of motor neurons [ex:CNS effector (muscle or gland)] c) mixed nerve - consists of both sensory and motor neuron bundles neurons separated by connective tissues (spinal cord - all 31 pairs of spinal nerve ...
... Receptor CNS(brain, spinal cord) - optic (ear, eye, skin) b) motor nerve - consists entirely of motor neurons [ex:CNS effector (muscle or gland)] c) mixed nerve - consists of both sensory and motor neuron bundles neurons separated by connective tissues (spinal cord - all 31 pairs of spinal nerve ...
Katie Newhall Synchrony in stochastic pulse-coupled neuronal network models
... Synchrony in stochastic pulse-coupled neuronal network models Many pulse-coupled dynamical systems possess synchronous attracting states. Even stochastically driven model networks of Integrate and Fire neurons demonstrate synchrony over a large range of parameters. We study the interplay between ...
... Synchrony in stochastic pulse-coupled neuronal network models Many pulse-coupled dynamical systems possess synchronous attracting states. Even stochastically driven model networks of Integrate and Fire neurons demonstrate synchrony over a large range of parameters. We study the interplay between ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... a. 5 percent. b. 95 percent. c. 25 percent. d. 50 percent. e. 80 percent. The reproductive advantage enjoyed by organisms best suited to a particular environment is known as a. nurture. b. behavior genetics. c. self-regulation. d. natural selection. e. heritability. Males in their ________ are most ...
... a. 5 percent. b. 95 percent. c. 25 percent. d. 50 percent. e. 80 percent. The reproductive advantage enjoyed by organisms best suited to a particular environment is known as a. nurture. b. behavior genetics. c. self-regulation. d. natural selection. e. heritability. Males in their ________ are most ...
cranial nerves & pns
... the sympathetic nervous system, dominates in times of stress. It controls the "fight or flight" reaction, increasing blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate, and blood flow to the muscles. Another division, called the parasympathetic nervous system, has the opposite effect. It conserves energy by ...
... the sympathetic nervous system, dominates in times of stress. It controls the "fight or flight" reaction, increasing blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate, and blood flow to the muscles. Another division, called the parasympathetic nervous system, has the opposite effect. It conserves energy by ...
Notes_2-4_bcsd Biologic basis of behavior
... surgical removal, cutting of neural connections, or destruction by chemical applications -study of loss of function resulting from surgical removal of portions of the brain -measures subtle changes in brain electrical activity through electrodes placed on the head -allow for localization of function ...
... surgical removal, cutting of neural connections, or destruction by chemical applications -study of loss of function resulting from surgical removal of portions of the brain -measures subtle changes in brain electrical activity through electrodes placed on the head -allow for localization of function ...
psych mod 4 terms
... DNA, which is abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic Each cell contains 46 chromosomes in 23 pairs. 3. Gene- is a specific segment on the long strand of DNA that contains instructions for making proteins. Proteins are chemical building blocks from which all the parts of the brain and body are constructed ...
... DNA, which is abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic Each cell contains 46 chromosomes in 23 pairs. 3. Gene- is a specific segment on the long strand of DNA that contains instructions for making proteins. Proteins are chemical building blocks from which all the parts of the brain and body are constructed ...
Methods to Study the Brain
... • CT (computed tomography) scanning is a much-improved version of x-ray imaging. A CT scan takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a threedimensional image. ...
... • CT (computed tomography) scanning is a much-improved version of x-ray imaging. A CT scan takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a threedimensional image. ...
Methods to Study the Brain - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... • CT (computed tomography) scanning is a much-improved version of x-ray imaging. A CT scan takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a threedimensional image. ...
... • CT (computed tomography) scanning is a much-improved version of x-ray imaging. A CT scan takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a threedimensional image. ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... You could join two eight-studded Lego bricks 24 ways, and six bricks nearly 103 million ways. With some 40 billion neurons, each having roughly 10,000 contacts with other neurons, we end up with around 400 trillion synapses. A grain of sand size speck of your brain contains 100,000 neurons and one ...
... You could join two eight-studded Lego bricks 24 ways, and six bricks nearly 103 million ways. With some 40 billion neurons, each having roughly 10,000 contacts with other neurons, we end up with around 400 trillion synapses. A grain of sand size speck of your brain contains 100,000 neurons and one ...
Focus On Vocabulary Chapter 02
... (for example, the bricks) that make up a structure (for example, a house). The structure of our nervous system, or neural information system, is made up of neurons (they are its building blocks). To fathom our thoughts and actions, memories and moods, we must first understand how neurons work and co ...
... (for example, the bricks) that make up a structure (for example, a house). The structure of our nervous system, or neural information system, is made up of neurons (they are its building blocks). To fathom our thoughts and actions, memories and moods, we must first understand how neurons work and co ...
the neuron cheat sheet
... Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain at up to 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals trans ...
... Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain at up to 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals trans ...
glossary - HBO.com
... Amyloid precursor protein (APP)—the larger protein from which beta-amyloid is formed. ApoE gene—a gene that codes for a protein that carries cholesterol to and within cells; different forms of the ApoE gene are associated with differing risks for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. This gene may be refe ...
... Amyloid precursor protein (APP)—the larger protein from which beta-amyloid is formed. ApoE gene—a gene that codes for a protein that carries cholesterol to and within cells; different forms of the ApoE gene are associated with differing risks for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. This gene may be refe ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.