Central nervous system
... the neuron after sodium ions rush in • Sodium and potassium are actively transported back to their original positions = repolarization • Membrane is at rest again Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... the neuron after sodium ions rush in • Sodium and potassium are actively transported back to their original positions = repolarization • Membrane is at rest again Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Texts - mistergui
... heartening, scientists found that exercise jump-starts neurogenesis. Mice and rats that ran for a few weeks generally had about twice as many new neurons in their hippocampi as sedentary animals. Their brains, like other muscles, were bulking up. But it was the ineffable effect that exercise had on ...
... heartening, scientists found that exercise jump-starts neurogenesis. Mice and rats that ran for a few weeks generally had about twice as many new neurons in their hippocampi as sedentary animals. Their brains, like other muscles, were bulking up. But it was the ineffable effect that exercise had on ...
A leading centre for innovation, expertise, and discovery
... Neuroscientists at the Lunenfeld have developed a unique vision for this fascinating and important area, and their discoveries provide new insight and approaches to understanding diseases and injuries that affect nerve growth and function, including psychiatric disorders, Alzheimer’s disease, epilep ...
... Neuroscientists at the Lunenfeld have developed a unique vision for this fascinating and important area, and their discoveries provide new insight and approaches to understanding diseases and injuries that affect nerve growth and function, including psychiatric disorders, Alzheimer’s disease, epilep ...
Unit 8 Nervous System
... the dendrite of another Axosomatic- between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Less common Axoaxonic (axon to axon) ...
... the dendrite of another Axosomatic- between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Less common Axoaxonic (axon to axon) ...
Physiological Mechanisms of Behavior
... The human nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). The peripheral nervous system (nerves) extends from the central nervous system. See Figure 5.1 on page 139 in your textbook. Bloom begins his discussion with the smallest part of the brain, the neurons. ...
... The human nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). The peripheral nervous system (nerves) extends from the central nervous system. See Figure 5.1 on page 139 in your textbook. Bloom begins his discussion with the smallest part of the brain, the neurons. ...
DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD
... Dorsal part forms the ALAR plate , cell bodies in which form the dorsal gray columns. In transverse section, appear as Dorsal horn. Ventral part forms the BASAL plate, cell bodies of which form the ventral and lateral gray columns. In transverse section, appear as ventral and lateral horns respectiv ...
... Dorsal part forms the ALAR plate , cell bodies in which form the dorsal gray columns. In transverse section, appear as Dorsal horn. Ventral part forms the BASAL plate, cell bodies of which form the ventral and lateral gray columns. In transverse section, appear as ventral and lateral horns respectiv ...
The Brain, Biology, and Behavior
... cerebrum. Others are regarded as separate areas because their functions are quite different. ...
... cerebrum. Others are regarded as separate areas because their functions are quite different. ...
- Describe the roles of the different types of glial cells
... the tight junctions and prevent any leakage of unwanted substances into the brain. This helps create a very finely and tightly regulated environment and keeps out any potential toxins. Astrocytes also release various neurotrophic factors which regulate axonal growth and neuronal transport - Schwann ...
... the tight junctions and prevent any leakage of unwanted substances into the brain. This helps create a very finely and tightly regulated environment and keeps out any potential toxins. Astrocytes also release various neurotrophic factors which regulate axonal growth and neuronal transport - Schwann ...
Temporal Lobe
... response. Infected brain cells, white blood cells, and live and dead bacteria and fungi collect in an area of the brain. A membrane forms around this area and creates a mass. • While this immune response can protect the brain by isolating the infection, it can also do more harm than good. The brain ...
... response. Infected brain cells, white blood cells, and live and dead bacteria and fungi collect in an area of the brain. A membrane forms around this area and creates a mass. • While this immune response can protect the brain by isolating the infection, it can also do more harm than good. The brain ...
1 Introduction to Neurobiology Rudolf Cardinal NST 1B
... of the dendrites and the cell body, and propagated down the neuron’s single axon. Axons vary greatly in length; the longest in a human is about a metre long (and in a whale, many times this). At the very end of the axon it may divide into collaterals, which typically make synapses on the dendrites o ...
... of the dendrites and the cell body, and propagated down the neuron’s single axon. Axons vary greatly in length; the longest in a human is about a metre long (and in a whale, many times this). At the very end of the axon it may divide into collaterals, which typically make synapses on the dendrites o ...
12-2cut
... • Recall that there are two types of neurotransmitters: excitatory and inhibitory • So, synapses can be either excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the neurotransmitter produced • CNS neurons often receive input from many other neurons ...
... • Recall that there are two types of neurotransmitters: excitatory and inhibitory • So, synapses can be either excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the neurotransmitter produced • CNS neurons often receive input from many other neurons ...
Slide ()
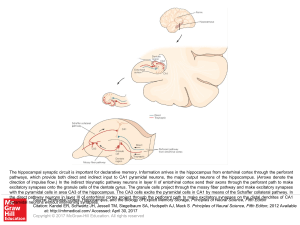
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
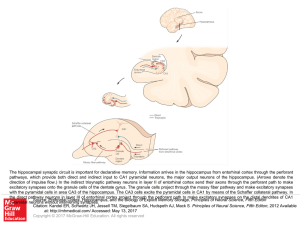
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Halle Berry as a Computational Brain Abstraction
... of this area in visual recognition tasks. Through cutting-‐edge experimentation with the depth electrodes, Quiroga's team found specific MTL neurons to respond selectively to specific people, places, and things. ...
... of this area in visual recognition tasks. Through cutting-‐edge experimentation with the depth electrodes, Quiroga's team found specific MTL neurons to respond selectively to specific people, places, and things. ...
Physiology - Soran University
... There are different types of neurons. They all carry electro-chemical nerve signals, but differ in structure (the number of processes, or axons, emanating from the cell body) and are found in different parts of the body. Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense recepto ...
... There are different types of neurons. They all carry electro-chemical nerve signals, but differ in structure (the number of processes, or axons, emanating from the cell body) and are found in different parts of the body. Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense recepto ...
Chapter 9
... o Structure: most inferior part of the brain stem; merges into spinal cord o Functions: heart rate control, blood pressure regulation, ...
... o Structure: most inferior part of the brain stem; merges into spinal cord o Functions: heart rate control, blood pressure regulation, ...
Chapter 2
... Describe the functions of neurons and glial cells, and distinguish among the three types of neurons. ...
... Describe the functions of neurons and glial cells, and distinguish among the three types of neurons. ...
Bosma Lab Bosma Lab
... Basic properties of neurons Neurons are organized into groups Neurons are usually localized into groups of cell bodies, which underlie the functions of the nervous system. The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord), and the peripheral nervous system (P ...
... Basic properties of neurons Neurons are organized into groups Neurons are usually localized into groups of cell bodies, which underlie the functions of the nervous system. The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord), and the peripheral nervous system (P ...
Jeopardy Bio Basis of Human Behavior
... Division of the NS that transmits commands for voluntary movement from the CNS to the muscles ...
... Division of the NS that transmits commands for voluntary movement from the CNS to the muscles ...
Development of the central nervous system
... Contributions of Neural Crest Cells and Placodes to Ganglia of the Cranial Nerve ...
... Contributions of Neural Crest Cells and Placodes to Ganglia of the Cranial Nerve ...
The Truth about Weed - Copley
... located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the brain primary role in the processing of memory and emotional reactions ...
... located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the brain primary role in the processing of memory and emotional reactions ...
The Nervous System How your body responds to a stimulus
... Each second, your body fires off about five trillion nerve impulses. • Your emotions, decisions, and physical actions all happen through nerve impulses traveling through neurons in your brain, spinal cord and ...
... Each second, your body fires off about five trillion nerve impulses. • Your emotions, decisions, and physical actions all happen through nerve impulses traveling through neurons in your brain, spinal cord and ...
TOC - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., ...
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., ...
The Journal of Neuroscience Journal Club SYMPOSIUM
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., ...
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.