Scientists study Pavlovian conditioning in neural
... Schnitzer lab. "We need that as humans, animals amazing work but we still haven't had a glimpse of need that. When we associate certain stimuli with how neural ensembles encode a long-term their possible dangerous outcomes, it helps us to memory," said Mark Schnitzer, associate professor avoid dange ...
... Schnitzer lab. "We need that as humans, animals amazing work but we still haven't had a glimpse of need that. When we associate certain stimuli with how neural ensembles encode a long-term their possible dangerous outcomes, it helps us to memory," said Mark Schnitzer, associate professor avoid dange ...
Slide ()
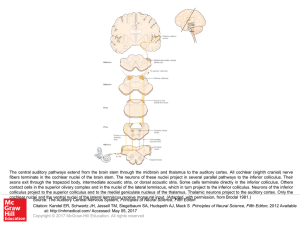
... The central auditory pathways extend from the brain stem through the midbrain and thalamus to the auditory cortex. All cochlear (eighth cranial) nerve fibers terminate in the cochlear nuclei of the brain stem. The neurons of these nuclei project in several parallel pathways to the inferior colliculu ...
... The central auditory pathways extend from the brain stem through the midbrain and thalamus to the auditory cortex. All cochlear (eighth cranial) nerve fibers terminate in the cochlear nuclei of the brain stem. The neurons of these nuclei project in several parallel pathways to the inferior colliculu ...
Q: A.1 Answer (b) neurolemma Q: A.2 Answer (d) Pons
... (a) Keeps us informed about the outside world through sense organs. (b) Enables us to remember, think and reason out. (c) Controls and harmonizes all voluntary muscular activities such as running, holding, writing (d) Regulates involuntary activities such as breathing, beating of the heart without o ...
... (a) Keeps us informed about the outside world through sense organs. (b) Enables us to remember, think and reason out. (c) Controls and harmonizes all voluntary muscular activities such as running, holding, writing (d) Regulates involuntary activities such as breathing, beating of the heart without o ...
Toxicology of the Nervous System
... Glutamate activates two types of ion channels (AMPA and NMDA) Cell Death is associated with excessive calcium entry through NMDA receptors ...
... Glutamate activates two types of ion channels (AMPA and NMDA) Cell Death is associated with excessive calcium entry through NMDA receptors ...
ANS_jh - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Monitor temperature, pain, irritation, chemical changes and stretch in the visceral organs Brain interprets as hunger, fullness, pain, nausea, well-being Receptors widely scattered – localization poor (e.g. which part is giving you the gas pain?) Visceral sensory fibers run within autonomic nerves ...
... Monitor temperature, pain, irritation, chemical changes and stretch in the visceral organs Brain interprets as hunger, fullness, pain, nausea, well-being Receptors widely scattered – localization poor (e.g. which part is giving you the gas pain?) Visceral sensory fibers run within autonomic nerves ...
Development of Nervous System
... Brain and spinal cord. Both contain fluid-filled spaces which contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The central canal of the spinal cord is continuous with the ventricles of the brain. White matter is composed of bundles of myelinated axons ...
... Brain and spinal cord. Both contain fluid-filled spaces which contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The central canal of the spinal cord is continuous with the ventricles of the brain. White matter is composed of bundles of myelinated axons ...
Nervous System Task Exploration
... cause neurological disease. For example, untreated high blood pressure may cause a stroke, which is a sudden loss of blood supply to a region of the brain resulting in the death of brain cells. Although initially the disease presents itself as a cardiac problem, it ends up becoming a significant neu ...
... cause neurological disease. For example, untreated high blood pressure may cause a stroke, which is a sudden loss of blood supply to a region of the brain resulting in the death of brain cells. Although initially the disease presents itself as a cardiac problem, it ends up becoming a significant neu ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... the sensory receptor to the central nervous system. Second order neuron – carries the information from the central nervous system to the thalamus. Information traveling along second order neurons deccussates from one side of the CNS to the other side of the CNS. Third order neuron – carries sensory ...
... the sensory receptor to the central nervous system. Second order neuron – carries the information from the central nervous system to the thalamus. Information traveling along second order neurons deccussates from one side of the CNS to the other side of the CNS. Third order neuron – carries sensory ...
Nervous System
... gives animals capacity for quick response (endocrine hormones act more slowly, long term) ...
... gives animals capacity for quick response (endocrine hormones act more slowly, long term) ...
Human Nervous System
... • Is the space between two neurons or between a neuron and a receptor organ. ...
... • Is the space between two neurons or between a neuron and a receptor organ. ...
NEURONS
... EX- light, gravity, food, etc. *The ability to RESPOND to a stimulus is common to _______ living things !!! ...
... EX- light, gravity, food, etc. *The ability to RESPOND to a stimulus is common to _______ living things !!! ...
NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS TEST PREVIEW
... 2. What’s the function of the nervous and endocrine systems? 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an ...
... 2. What’s the function of the nervous and endocrine systems? 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an ...
Lab 8: Muscle and Nervous Tissue
... NOTE: For the following you may substitute use of the HistoWeb site images for the microscope work. Go to the HistoWeb Nerve site. (link from “Project Info” on PhysioWeb) 4. Obtain a prepared slide of spinal cord smear. Using low power magnification, search the slide and locate the large, deeply sta ...
... NOTE: For the following you may substitute use of the HistoWeb site images for the microscope work. Go to the HistoWeb Nerve site. (link from “Project Info” on PhysioWeb) 4. Obtain a prepared slide of spinal cord smear. Using low power magnification, search the slide and locate the large, deeply sta ...
The Nervous System
... the brain to the body The Spinal cord has 31 pairs of spinal nerves exiting it to enervate the trunk, arms, and legs. It runs down the arch of the Vertebra behind the Body Spinal cord ends near L1. The Spinal Cord ends there and becomes the Cauda Equina “Horse Tail” in Latin ...
... the brain to the body The Spinal cord has 31 pairs of spinal nerves exiting it to enervate the trunk, arms, and legs. It runs down the arch of the Vertebra behind the Body Spinal cord ends near L1. The Spinal Cord ends there and becomes the Cauda Equina “Horse Tail” in Latin ...
The Nervous System
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
Chapter 5 - Metropolitan Community College
... Basic Brain Structures, cont. • Each neuron has a single axon (nerve fiber) that extends from it and meets the dendrites of other neurons at intersections called synapses - axons and dendrites don’t actually touch at synapses - electrical impulses trigger brain chemicals called neurotransmitters, w ...
... Basic Brain Structures, cont. • Each neuron has a single axon (nerve fiber) that extends from it and meets the dendrites of other neurons at intersections called synapses - axons and dendrites don’t actually touch at synapses - electrical impulses trigger brain chemicals called neurotransmitters, w ...
TECHNIQUES2001
... • Computer combines a series of contrast XRays taken from circling around head to create a CT scan of one 2-D horizontal section of the brain. • 1 regular X-RAY would not work. ...
... • Computer combines a series of contrast XRays taken from circling around head to create a CT scan of one 2-D horizontal section of the brain. • 1 regular X-RAY would not work. ...
Slide 1
... • List the different parts of a neuron? • What are the functions of a neuron? • List the different types of glia cells and name one function for each? ...
... • List the different parts of a neuron? • What are the functions of a neuron? • List the different types of glia cells and name one function for each? ...
Psychology Brain Body Behavior Chapter Syllabus
... Brain, Body, and Behavior Learning Objectives: In this section of the course, students are introduced to the history of the study of the brain, the parts and functions of the human brain, various methods for studying the human brain, the role of neurons and neurotransmitters on brain communication, ...
... Brain, Body, and Behavior Learning Objectives: In this section of the course, students are introduced to the history of the study of the brain, the parts and functions of the human brain, various methods for studying the human brain, the role of neurons and neurotransmitters on brain communication, ...
Additional Science B6 Module – What You Should Know
... a. sensory neurons carrying impulses from receptors to the CNS b. motor neurons carrying impulses from the CNS to effectors I understand that within the CNS, impulses are passed from sensory neurons to motor neurons through relay neurons I describe the nervous pathway of a spinal reflex arc to inclu ...
... a. sensory neurons carrying impulses from receptors to the CNS b. motor neurons carrying impulses from the CNS to effectors I understand that within the CNS, impulses are passed from sensory neurons to motor neurons through relay neurons I describe the nervous pathway of a spinal reflex arc to inclu ...
The Nervous System
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
Vertebrate Nervous System
... Optic nerves one of the cranial nerves, Part of the Peripheral Nervous system but considered to be still part of central nervous system Still covered in same meninges or layers that cover the brain Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses Nerve cell body called perikaryon sometimes the soma wh ...
... Optic nerves one of the cranial nerves, Part of the Peripheral Nervous system but considered to be still part of central nervous system Still covered in same meninges or layers that cover the brain Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses Nerve cell body called perikaryon sometimes the soma wh ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... The brain can be divided into three main regions: hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain. HINDBRAIN 1. Medulla: has charge of largely unconscious, but vital functions, including circulating blood, breathing, maintaining muscle tone, and regulating reflexes such as sneezing, coughing, and salivating. 2. ...
... The brain can be divided into three main regions: hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain. HINDBRAIN 1. Medulla: has charge of largely unconscious, but vital functions, including circulating blood, breathing, maintaining muscle tone, and regulating reflexes such as sneezing, coughing, and salivating. 2. ...
The Nervous System
... • However, dendrites and somata typically lack voltagegated channels, which are found in abundance on the axon hillock and axolemma. – So what cannot occur on dendrites and somata? ...
... • However, dendrites and somata typically lack voltagegated channels, which are found in abundance on the axon hillock and axolemma. – So what cannot occur on dendrites and somata? ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.