Shape of Thought
... 96 percent of the measurable universe is invisible, to us at least. Linger with that thought a moment, picturing the infinities of space-a carbon-paper night struck through with countless stars. Then picture the microscopic hubbub in one brain' A typical brain contains about 100 billion neurons, con ...
... 96 percent of the measurable universe is invisible, to us at least. Linger with that thought a moment, picturing the infinities of space-a carbon-paper night struck through with countless stars. Then picture the microscopic hubbub in one brain' A typical brain contains about 100 billion neurons, con ...
New Neurons Grow in Adult Brains
... If the results are confirmed in humans, they could have major implications for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, or Alzheimer’s disease. In these diseases, neurons either die or lose their normal function. When a critical number of cells have been lost, symp ...
... If the results are confirmed in humans, they could have major implications for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, or Alzheimer’s disease. In these diseases, neurons either die or lose their normal function. When a critical number of cells have been lost, symp ...
Homeostasis Test%28CNS%29-Tawsif Hossain
... case of the reflex arc. In the reflex arc a stimulus causes the body to react fast to prevent damage. For eg: if the sensory system detected a large rise in temperature of the skin surface. A nerve impulse would be sent through the sensory neurons to the interneurons and finally the motor neurons. I ...
... case of the reflex arc. In the reflex arc a stimulus causes the body to react fast to prevent damage. For eg: if the sensory system detected a large rise in temperature of the skin surface. A nerve impulse would be sent through the sensory neurons to the interneurons and finally the motor neurons. I ...
CNS Cellular Components - Johns Hopkins Medicine
... Axonal Pathologies include axonal degeneration following neuronal cell death and axon reaction. When neurons are killed by infarction or other processes their axons degenerate. This can be useful diagnostically. For example, degeneration of the crossed and uncrossed corticospinal tracts as evidenced ...
... Axonal Pathologies include axonal degeneration following neuronal cell death and axon reaction. When neurons are killed by infarction or other processes their axons degenerate. This can be useful diagnostically. For example, degeneration of the crossed and uncrossed corticospinal tracts as evidenced ...
central nervous system ppt
... Development of the CNS Appears as neural tube on dorsal median plane 4th week brain formation begins at anterior end of the neural tube Remaining portion of neural tube becomes spinal cord ...
... Development of the CNS Appears as neural tube on dorsal median plane 4th week brain formation begins at anterior end of the neural tube Remaining portion of neural tube becomes spinal cord ...
bio4161
... 44. Cerebellar lesions usually do not result in paralysis. 45. Equilibrium sensory input is not restricted to the various proprioceptors, but includes visual signals as well. ...
... 44. Cerebellar lesions usually do not result in paralysis. 45. Equilibrium sensory input is not restricted to the various proprioceptors, but includes visual signals as well. ...
Nervous System 1
... • When an impulse reaches the end of an axon, a chemical is produced. The chemical diffuses across the gap. It starts off an impulse in the next neuron . • Only one end of a neuron can make this chemical. So synapses make sure an impulse can only travel in one direction. • Synapses have two other fu ...
... • When an impulse reaches the end of an axon, a chemical is produced. The chemical diffuses across the gap. It starts off an impulse in the next neuron . • Only one end of a neuron can make this chemical. So synapses make sure an impulse can only travel in one direction. • Synapses have two other fu ...
PG1006 Lecture 2 Nervous Tissue 1
... • Neurones communicate through electrical and chemical signalling • Synap4c input to dendrites results in graded poten4als • Large graded poten4al can trigger ac4on poten4als in the axon hillock • Ac4on poten ...
... • Neurones communicate through electrical and chemical signalling • Synap4c input to dendrites results in graded poten4als • Large graded poten4al can trigger ac4on poten4als in the axon hillock • Ac4on poten ...
L8_Nerve_tissue_and_organs
... • Multipolar neurons have one axon and two or more dendrites • Bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite • Unipolar (pseudounipolar) neurons have one process, that divides close to the cell body into two long processes – axon and dendrite ...
... • Multipolar neurons have one axon and two or more dendrites • Bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite • Unipolar (pseudounipolar) neurons have one process, that divides close to the cell body into two long processes – axon and dendrite ...
Characterization of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
Lecture3
... – Axon, threshold, dendrite, integrate and fire, neurotransmitter, excitation, inhibition, synapse, weight ...
... – Axon, threshold, dendrite, integrate and fire, neurotransmitter, excitation, inhibition, synapse, weight ...
CNS
... Central Nervous System Spinal Cord Design & Function Efferent Tracts (red) 1.Pyramidal Tracts 1a. Lateral corticospinal tract 1b. Anterior corticospinal tract 2.Extrapyramidal Tracts 2a. Rubrospinal tract 2b. Reticulospinal tract 2c. Vestibulospinal tract 2d. Olivospinal tract ...
... Central Nervous System Spinal Cord Design & Function Efferent Tracts (red) 1.Pyramidal Tracts 1a. Lateral corticospinal tract 1b. Anterior corticospinal tract 2.Extrapyramidal Tracts 2a. Rubrospinal tract 2b. Reticulospinal tract 2c. Vestibulospinal tract 2d. Olivospinal tract ...
What a Frog s Eye tells the Frog s brain
... Between the Rods & Cones (~1million) and the Ganglion Cells (~ 0.5 million; whose axons form the optic nerve) there is: A layer of connecting Neurons (bipolar, horizontal & Amacrines) (~3million) o Each Rod/Cone connects to many Ganglia & each Ganglia connects to many Rod/Cone Does not make for ...
... Between the Rods & Cones (~1million) and the Ganglion Cells (~ 0.5 million; whose axons form the optic nerve) there is: A layer of connecting Neurons (bipolar, horizontal & Amacrines) (~3million) o Each Rod/Cone connects to many Ganglia & each Ganglia connects to many Rod/Cone Does not make for ...
Researcher studies nervous system development
... neurodevelopmental disorders, like multiple sclerosis or epilepsy, occur. Multiple sclerosis is a disease that damages the myelin sheath on the nerve cells, creating problems for the transmission of the electrical signals. ...
... neurodevelopmental disorders, like multiple sclerosis or epilepsy, occur. Multiple sclerosis is a disease that damages the myelin sheath on the nerve cells, creating problems for the transmission of the electrical signals. ...
NEUROGLIA (Glial cells) Supporting cells of the CNS and PNS
... •Phagocytize necrotic tissue, microorganisms and foreign substances ...
... •Phagocytize necrotic tissue, microorganisms and foreign substances ...
CHAPTER 46 NEURONS AND NERVOUS SYSTEM
... 1) A fast-acting nerve net enables major responses, particularly in times of danger. 2) Another nerve net coordinates slower and more delicate movements. 4. The planarian nervous system is bilaterally symmetrical. a. It has two lateral nerve cords that allow rapid transfer of information from anteri ...
... 1) A fast-acting nerve net enables major responses, particularly in times of danger. 2) Another nerve net coordinates slower and more delicate movements. 4. The planarian nervous system is bilaterally symmetrical. a. It has two lateral nerve cords that allow rapid transfer of information from anteri ...
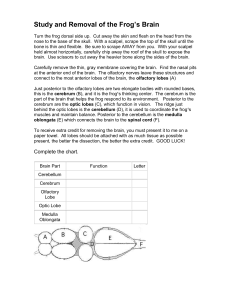
Study and Removal of the Frog`s Brain
... at the anterior end of the brain. The olfactory nerves leave these structures and connect to the most anterior lobes of the brain, the olfactory lobes (A) Just posterior to the olfactory lobes are two elongate bodies with rounded bases, this is the cerebrum (B), and it is the frog¹s thinking center. ...
... at the anterior end of the brain. The olfactory nerves leave these structures and connect to the most anterior lobes of the brain, the olfactory lobes (A) Just posterior to the olfactory lobes are two elongate bodies with rounded bases, this is the cerebrum (B), and it is the frog¹s thinking center. ...
Methods and Strategies of Research
... Computerized tomography (CT) uses an x-ray beam to scan the brain from all angles, these scans are then summarized in an image of the skull and brain (in a horizontal plane) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses a magnetic field and radio waves to excite hydrogen molecules, the resulting informati ...
... Computerized tomography (CT) uses an x-ray beam to scan the brain from all angles, these scans are then summarized in an image of the skull and brain (in a horizontal plane) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses a magnetic field and radio waves to excite hydrogen molecules, the resulting informati ...
Bio Bases 2014 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... follow the text In this case, it is integrating your sensory experiences (seeing) with muscle movements (tilting your head) o Forebrain Where the magic of thought and reason occur It is what makes humans, human Composed of the: Thalamus ...
... follow the text In this case, it is integrating your sensory experiences (seeing) with muscle movements (tilting your head) o Forebrain Where the magic of thought and reason occur It is what makes humans, human Composed of the: Thalamus ...
3 Medical Terminology - MedicalScienceTwoCCP
... 2. Why is the autonomic division of the nervous system important? Give an example 3. Using a soccer player as an example, give an example of 8 different things that the nervous system does to help the player perform. ...
... 2. Why is the autonomic division of the nervous system important? Give an example 3. Using a soccer player as an example, give an example of 8 different things that the nervous system does to help the player perform. ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVE 5: Explain how an injured nerve fiber may
... Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines 1. Illustrate the structure of a typical motor neuron. Label the major structures such as dendrites, myelin sheath, cell body, neurilemma, Schwann cell, Nodes of Ranvier, axon, and synapse. 2. Describe the structures of a neuron cell body, including the cytoplasm, ...
... Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines 1. Illustrate the structure of a typical motor neuron. Label the major structures such as dendrites, myelin sheath, cell body, neurilemma, Schwann cell, Nodes of Ranvier, axon, and synapse. 2. Describe the structures of a neuron cell body, including the cytoplasm, ...
Sermon Presentation
... • The property of the mind that encompasses many related abilities, such as the capacities to reason, to plan, to solve problems, to think abstractly, to comprehend ideas, to use language, and to learn. • The number of those cognitive abilities available for use and the extent to which one is capab ...
... • The property of the mind that encompasses many related abilities, such as the capacities to reason, to plan, to solve problems, to think abstractly, to comprehend ideas, to use language, and to learn. • The number of those cognitive abilities available for use and the extent to which one is capab ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.