The Peripheral Nervous System
... Nervous tissue: Excitable cells (neurons) Nonexcitable (supporting) cells Connective tissue: Meninges in central nervous system Endoneurium Perineurium in peripheral nervous system Epineurium Epithelium found only in blood vessels of PNS Muscle (smooth) ...
... Nervous tissue: Excitable cells (neurons) Nonexcitable (supporting) cells Connective tissue: Meninges in central nervous system Endoneurium Perineurium in peripheral nervous system Epineurium Epithelium found only in blood vessels of PNS Muscle (smooth) ...
Brainstem (Medulla), Brain vasculature & Ventricular system
... Explain how cranial nerves differ from spinal nerves List the cranial nerves that contain parasympathetic fibers, the location of their nuclei, and their function Recognize the major internal and external landmarks on the dorsal and ventral surface of the brain stem, so that you can determine if a g ...
... Explain how cranial nerves differ from spinal nerves List the cranial nerves that contain parasympathetic fibers, the location of their nuclei, and their function Recognize the major internal and external landmarks on the dorsal and ventral surface of the brain stem, so that you can determine if a g ...
Balancing the brain: resting state networks and deep brain stimulation
... are starting to address these shortcomings (Hansen et al., 2010). In fact, combining MEG and DBS may offer new insights into the fine-grained temporal neural dynamics of aberrant brain states, while at the same time providing novel insights into the fundamental principles as first demonstrated in 20 ...
... are starting to address these shortcomings (Hansen et al., 2010). In fact, combining MEG and DBS may offer new insights into the fine-grained temporal neural dynamics of aberrant brain states, while at the same time providing novel insights into the fundamental principles as first demonstrated in 20 ...
tractus corticomuscularis
... different physiological processes. That means that nervous system unites, integrates and subordinates all the parts of human body and provides its connection with environment ...
... different physiological processes. That means that nervous system unites, integrates and subordinates all the parts of human body and provides its connection with environment ...
Reflex Action
... •Small inhibitory interneurons present in AHCs of the spinal cord •Stimulated A.H.C. gives a recurrent collateral branch which stimulates the Renshaw cells. •Renshaw cells in turn inhibits either: stimulated or surrounding A.H.C. ...
... •Small inhibitory interneurons present in AHCs of the spinal cord •Stimulated A.H.C. gives a recurrent collateral branch which stimulates the Renshaw cells. •Renshaw cells in turn inhibits either: stimulated or surrounding A.H.C. ...
Hemichordata and Invertabrate Ch. 17
... Body divided into three sections, a proboscis, a collar and a trunk. ...
... Body divided into three sections, a proboscis, a collar and a trunk. ...
Body Organization/Planes
... and conduct electrical signals in the body. These electrical messages are managed by nerve tissue in the brain and transmitted down the spinal cord to the body ...
... and conduct electrical signals in the body. These electrical messages are managed by nerve tissue in the brain and transmitted down the spinal cord to the body ...
Untitled
... supporting cells (pink), and highly specialized extracellular matrix structures (ECM, green). These components are housed within a fluid-filled spiral labyrinth known as the cochlea. Although all hair cells in the cochlea have similar organization and the same basic function, the broad range of sens ...
... supporting cells (pink), and highly specialized extracellular matrix structures (ECM, green). These components are housed within a fluid-filled spiral labyrinth known as the cochlea. Although all hair cells in the cochlea have similar organization and the same basic function, the broad range of sens ...
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Reflexes
... mediate several autonomic responses • Spinal cord- autonomic responses as the defecation and micturition (urination) reflexes are integrated in the spinal cord – note these can be influenced by the higher brain centers – in severe spinal injuries, these reflexes alone control the elimination of urin ...
... mediate several autonomic responses • Spinal cord- autonomic responses as the defecation and micturition (urination) reflexes are integrated in the spinal cord – note these can be influenced by the higher brain centers – in severe spinal injuries, these reflexes alone control the elimination of urin ...
The Brain and Marijuana - Boston Children`s Hospital
... • Suppresses cannabinoid receptor function; reduces number of receptors and decreases sensitivity to anandamide, so it can’t do it’s job • Causes too much excitation of neurons, leading to “Excitotoxicity” and cell damage/death Source: Bossong MG, Niesink RJM. Adolescent brain maturation, the endoge ...
... • Suppresses cannabinoid receptor function; reduces number of receptors and decreases sensitivity to anandamide, so it can’t do it’s job • Causes too much excitation of neurons, leading to “Excitotoxicity” and cell damage/death Source: Bossong MG, Niesink RJM. Adolescent brain maturation, the endoge ...
Nervous System Cranial Nerves, Spine and Brain
... Dorsal root-contains sensory neuron and interneurons fibers enter the spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion-enlarged area of dorsal root that contains cell bodies of sensory neurons Ventral root-contains axons of motor neurons of somatic nervous system Spinal nerve forms from a fusion of dorsal and ventr ...
... Dorsal root-contains sensory neuron and interneurons fibers enter the spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion-enlarged area of dorsal root that contains cell bodies of sensory neurons Ventral root-contains axons of motor neurons of somatic nervous system Spinal nerve forms from a fusion of dorsal and ventr ...
4-CPG1
... Most rhythmic behavior - „from swimming of a jelly fish to the running of a child chasing a ball“ (F. Delcomyn) – involves a CPG. CPG activity is subject of modulation which is responsible for network flexibility. ...
... Most rhythmic behavior - „from swimming of a jelly fish to the running of a child chasing a ball“ (F. Delcomyn) – involves a CPG. CPG activity is subject of modulation which is responsible for network flexibility. ...
Summary Ch - Dr. Allan N. Schore
... sciences. The continuously developing mind cannot be understood without reference to the continuously developing body. Their continuous interaction becomes an important interface for the organizing self. Self-organization in the context of nonlinear dynamics refers to the emergence of and stabilizat ...
... sciences. The continuously developing mind cannot be understood without reference to the continuously developing body. Their continuous interaction becomes an important interface for the organizing self. Self-organization in the context of nonlinear dynamics refers to the emergence of and stabilizat ...
Synapses and neurotransmitters
... One neuron (usually) has only one type of receptor • Great place for drug interaction ...
... One neuron (usually) has only one type of receptor • Great place for drug interaction ...
Chapter 10 - Dr. Eric Schwartz
... to brainstem nuclei and (by way of the thalamus) to regions of the sensorimotor cortex that give rise to pathways that descend to the motor neurons. • The cerebellum receives information both from the sensorimotor cortex (relayed via brainstem nuclei) and from the vestibular system, eyes, skin, musc ...
... to brainstem nuclei and (by way of the thalamus) to regions of the sensorimotor cortex that give rise to pathways that descend to the motor neurons. • The cerebellum receives information both from the sensorimotor cortex (relayed via brainstem nuclei) and from the vestibular system, eyes, skin, musc ...
Learning, Memory, Amnesia, and Brain
... System • Sensitization is an increase in response to a mild stimulus as a result to previous exposure to more intense stimuli. • Changes at identified synapses include: – Serotonin released from a facilitating neuron blocks potassium channels in the presynaptic neuron. – Prolonged release of transmi ...
... System • Sensitization is an increase in response to a mild stimulus as a result to previous exposure to more intense stimuli. • Changes at identified synapses include: – Serotonin released from a facilitating neuron blocks potassium channels in the presynaptic neuron. – Prolonged release of transmi ...
Spinal Cord Organization
... • Severe damage to ventral root results in flaccid paralysis. • Skeletal muscles cannot move either voluntarily or involuntarily • Without stimulation, muscles atrophy. • When only UMN of primary motor cortex is damaged, spastic paralysis occurs. • Spinal motor neurons remain intact, muscles continu ...
... • Severe damage to ventral root results in flaccid paralysis. • Skeletal muscles cannot move either voluntarily or involuntarily • Without stimulation, muscles atrophy. • When only UMN of primary motor cortex is damaged, spastic paralysis occurs. • Spinal motor neurons remain intact, muscles continu ...
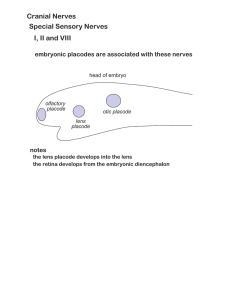
Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII
... vestibular afferents in CN VIII emerge from petrous bone approach rostral medulla/caudal pons rostral medulla/caudal pons superior ...
... vestibular afferents in CN VIII emerge from petrous bone approach rostral medulla/caudal pons rostral medulla/caudal pons superior ...
Document
... Efferent fibers. Efferent fibers are axons that carry impulses away from the CNS to muscles and glands. They also are referred to as motor, or descending, fibers. Afferent fibers are axons that carry impulses toward the CNS. REF: 1-23 40. General sensory (also known as somatic sensory) pathways feat ...
... Efferent fibers. Efferent fibers are axons that carry impulses away from the CNS to muscles and glands. They also are referred to as motor, or descending, fibers. Afferent fibers are axons that carry impulses toward the CNS. REF: 1-23 40. General sensory (also known as somatic sensory) pathways feat ...
Nervous and Muscle Tissue - White Plains Public Schools
... blood tissues regenerate. • Smooth muscle and dense regular connective tissue have a moderate capacity to regenerate while skeletal muscle and cartilage are weak. • Cardiac and nervous tissues have none. ...
... blood tissues regenerate. • Smooth muscle and dense regular connective tissue have a moderate capacity to regenerate while skeletal muscle and cartilage are weak. • Cardiac and nervous tissues have none. ...
1-1 Test Bank Liebgott: The Anatomical Basis of Dentistry, 3rd
... Efferent fibers. Efferent fibers are axons that carry impulses away from the CNS to muscles and glands. They also are referred to as motor, or descending, fibers. Afferent fibers are axons that carry impulses toward the CNS. REF: 1-23 40. General sensory (also known as somatic sensory) pathways feat ...
... Efferent fibers. Efferent fibers are axons that carry impulses away from the CNS to muscles and glands. They also are referred to as motor, or descending, fibers. Afferent fibers are axons that carry impulses toward the CNS. REF: 1-23 40. General sensory (also known as somatic sensory) pathways feat ...
Learning, remembering and forgetting in the mammalian brain
... conditioning in which the underlying mechanisms have been examined. These studies suggest that after recall of a stored memory, biochemical changes in neurons that represent the stored memory are destabilised, and a second round of genetic changes are required for permanent storage. The reasons for ...
... conditioning in which the underlying mechanisms have been examined. These studies suggest that after recall of a stored memory, biochemical changes in neurons that represent the stored memory are destabilised, and a second round of genetic changes are required for permanent storage. The reasons for ...
The Ventrolateral Hypothalamic Area and the Parvafox Nucleus
... LHA without attempting to be exhaustive; several large, reticular areas remain unnamed. The murine parvafox nucleus appears to correspond partially to the paraterete hypothalamic nucleus (PTe) and to be contained within the magnocellular nucleus of the lateral hypothalamus (MCLH; Paxinos et al., 200 ...
... LHA without attempting to be exhaustive; several large, reticular areas remain unnamed. The murine parvafox nucleus appears to correspond partially to the paraterete hypothalamic nucleus (PTe) and to be contained within the magnocellular nucleus of the lateral hypothalamus (MCLH; Paxinos et al., 200 ...
Thyroid Hormones
... Some years later a certain power of movement is acquired, but the gait is waddling and clumsy. Speech is long delayed, or in bad cases may be almost entirely lacking. The voice is usually harsh and unpleasant. Of the senses smell and taste are but slightly developed, more or less deafness is general ...
... Some years later a certain power of movement is acquired, but the gait is waddling and clumsy. Speech is long delayed, or in bad cases may be almost entirely lacking. The voice is usually harsh and unpleasant. Of the senses smell and taste are but slightly developed, more or less deafness is general ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.