ANS and sympathetic division pharm
... principally secreted by the postganglionic sympathetic fibres (red). The two exceptions to this are the adrenal medulla which acts as a postganglonic fibre itself and secretes 80% adrenaline and 20% noradrenaline into the systemic circulation, and sweat glands whose sympathetic postganglionic fibres ...
... principally secreted by the postganglionic sympathetic fibres (red). The two exceptions to this are the adrenal medulla which acts as a postganglonic fibre itself and secretes 80% adrenaline and 20% noradrenaline into the systemic circulation, and sweat glands whose sympathetic postganglionic fibres ...
Is Diabetic Nerve Pain Caused by Dysregulated
... cytokines, increased aldose reductase activity, and oxidative stress, may contribute to the impaired function of sensory neurons in animals with PDN. However, multiple preclinical and clinical studies that aimed to target several of these mechanisms while simultaneously ensuring proper blood glucose ...
... cytokines, increased aldose reductase activity, and oxidative stress, may contribute to the impaired function of sensory neurons in animals with PDN. However, multiple preclinical and clinical studies that aimed to target several of these mechanisms while simultaneously ensuring proper blood glucose ...
Reconstructing the Engram: Neurotechnique Simultaneous, Multisite
... neurons, distributed across up to five distinct neuronal structures that define the rat somatosensory system. In all experiments described here, stainless steel, Teflon-coated microwires (50 mm in diameter, California Fine wire) were used to build different microelectrode matrices, each of which was ...
... neurons, distributed across up to five distinct neuronal structures that define the rat somatosensory system. In all experiments described here, stainless steel, Teflon-coated microwires (50 mm in diameter, California Fine wire) were used to build different microelectrode matrices, each of which was ...
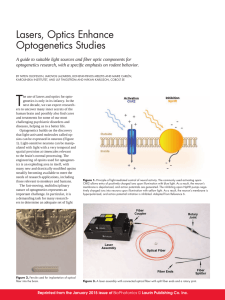
Lasers, Optics Enhance Optogenetics Studies
... assembly and can be fused into one fiber, if needed. To allow for free movement of the animal and to avoid twisting and turning the fiber(s), a rotary joint can be added (Figure 3). Lasers for optogenetics It is a true challenge for neuroscientists to achieve sufficient light exposure in an area of ...
... assembly and can be fused into one fiber, if needed. To allow for free movement of the animal and to avoid twisting and turning the fiber(s), a rotary joint can be added (Figure 3). Lasers for optogenetics It is a true challenge for neuroscientists to achieve sufficient light exposure in an area of ...
optical imaging and control of genetically designated neurons in
... for observing and controlling neuronal function are built, the most fundamental limitations on observability and reachability necessarily derive from them. (As discussed below, the currently available sensor and actuator proteins also impose often considerable constraints on what can be observed and ...
... for observing and controlling neuronal function are built, the most fundamental limitations on observability and reachability necessarily derive from them. (As discussed below, the currently available sensor and actuator proteins also impose often considerable constraints on what can be observed and ...
Questions - rlsmart.net
... cells, neurons have a nucleus, a cell membrane, and cytoplasm. They are different from other cells because the cytoplasm is shaped into a very long thin extension. This is called the axon, and it is how neurons connect different parts of the body. ...
... cells, neurons have a nucleus, a cell membrane, and cytoplasm. They are different from other cells because the cytoplasm is shaped into a very long thin extension. This is called the axon, and it is how neurons connect different parts of the body. ...
presentation-notes-for-brain-power
... Learn the basics of how the brain’s 100 billion nerve cells are born, grow, connect, and function. Neuroanatomy; Cell Communication; Brain Development. ...
... Learn the basics of how the brain’s 100 billion nerve cells are born, grow, connect, and function. Neuroanatomy; Cell Communication; Brain Development. ...
Somatosensory system
... locations in the central nervous system – Several pathways with variable numbers of projection neurons, not a three neuron pathway like fast pain. – The information from the medial pain systems is not somatotopically organized, so slow pain cannot be precisely localized. ...
... locations in the central nervous system – Several pathways with variable numbers of projection neurons, not a three neuron pathway like fast pain. – The information from the medial pain systems is not somatotopically organized, so slow pain cannot be precisely localized. ...
Neil Bossenger - The power of upper cervical
... The unique anatomy of atlas and axis. The relationship of skull to atlas. The relationship of atlas to axis. The neurology of brain (and cerebellum). The neurology of brainstem. The neurological associations between. And basically how the whole body works! ...
... The unique anatomy of atlas and axis. The relationship of skull to atlas. The relationship of atlas to axis. The neurology of brain (and cerebellum). The neurology of brainstem. The neurological associations between. And basically how the whole body works! ...
Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes
... Protein quality-control, especially the removal of proteins with aberrant structures, has an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of non-dividing neural cells1. In addition to the ubiquitin–proteasome system, emerging evidence points to the importance of autophagy—the bulk protein degradati ...
... Protein quality-control, especially the removal of proteins with aberrant structures, has an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of non-dividing neural cells1. In addition to the ubiquitin–proteasome system, emerging evidence points to the importance of autophagy—the bulk protein degradati ...
Body Organization
... anterior/posterior parts • Transverse (horizontal) – divides the body into superior/inferior parts – Also known as a cross-section ...
... anterior/posterior parts • Transverse (horizontal) – divides the body into superior/inferior parts – Also known as a cross-section ...
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
... Peripheral Distribution of Spinal Nerves • Spinal nerves: – form lateral to intervertebral foramen – where dorsal and ventral roots unite – then branch and form pathways to destination ...
... Peripheral Distribution of Spinal Nerves • Spinal nerves: – form lateral to intervertebral foramen – where dorsal and ventral roots unite – then branch and form pathways to destination ...
Pyrokinin/PBAN-like peptides in the central nervous system of
... otherwise noted (Fig. 1). The SEG contained three groups of immunoreactive neurons that putatively correspond to the mandibular, maxillary, and labial neuromeres (Fig. 2a). All three neuromeres contained about 6 neurons each in most preparations. In most preparations the neurons of the mandibular an ...
... otherwise noted (Fig. 1). The SEG contained three groups of immunoreactive neurons that putatively correspond to the mandibular, maxillary, and labial neuromeres (Fig. 2a). All three neuromeres contained about 6 neurons each in most preparations. In most preparations the neurons of the mandibular an ...
Essential circuits of cognition: The brain`s basic operations
... Representation 1. Regularities With this set of processing elements, connected as prescribed in the overall telencephalic architecture, we may ask what it is that is being computed. Perceptual inputs arrive at peripheral structures, e.g., retina, certain thalamic nuclei, and even early sensory corti ...
... Representation 1. Regularities With this set of processing elements, connected as prescribed in the overall telencephalic architecture, we may ask what it is that is being computed. Perceptual inputs arrive at peripheral structures, e.g., retina, certain thalamic nuclei, and even early sensory corti ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
How Opioid Drugs Bind to Receptors
... reach for a cup, electrical signals stream from the brain through the spinal cord, instructing our muscles to move. However, a disruption of the nerve pathways along which these signals travel can cause paralysis, with devastating consequences for the person’s quality of life. So there is growing in ...
... reach for a cup, electrical signals stream from the brain through the spinal cord, instructing our muscles to move. However, a disruption of the nerve pathways along which these signals travel can cause paralysis, with devastating consequences for the person’s quality of life. So there is growing in ...
"I`ll see it when I believe it!"*: Investigating Nervous System
... right mantle flap; T, "tail" (anterior end) of left mantle flap. Horizontal field width = 7 cm. (From Krae- Hydra" organisms? No. Indeed, such invesmer, 1984) tigations now seem to have moved from the quest for understanding of neuronof Burnett and Diehl's experiments showed, making, gamete-making a ...
... right mantle flap; T, "tail" (anterior end) of left mantle flap. Horizontal field width = 7 cm. (From Krae- Hydra" organisms? No. Indeed, such invesmer, 1984) tigations now seem to have moved from the quest for understanding of neuronof Burnett and Diehl's experiments showed, making, gamete-making a ...
[ 181 Dynamic Imaging of Neuronal Cytoskeleton
... The development of green fluorescent protein (GFP) constructs for labeling proteins has made cellular transfection an important strategy for imaging the dynamics and movement of the cytoskeleton.16-z° This approach has the potential advantage of labeling many cells at a time. However, transfection t ...
... The development of green fluorescent protein (GFP) constructs for labeling proteins has made cellular transfection an important strategy for imaging the dynamics and movement of the cytoskeleton.16-z° This approach has the potential advantage of labeling many cells at a time. However, transfection t ...
The peripheral nervous system links the brain to the “real” world
... “Nothing is in the mind that does not pass through the senses” Nervous system Aristotle (~ 350 B.C.) ...
... “Nothing is in the mind that does not pass through the senses” Nervous system Aristotle (~ 350 B.C.) ...
ppt
... 1. Connect the flow of neurotransmitters through an axon to the mechanism of its potential effect on another neuron 2. Outine the steps in chemical synaptic transmission and predict changes in the efficacy of transmission when the system is perturbed (e.g. changes in ion concentrations or addition ...
... 1. Connect the flow of neurotransmitters through an axon to the mechanism of its potential effect on another neuron 2. Outine the steps in chemical synaptic transmission and predict changes in the efficacy of transmission when the system is perturbed (e.g. changes in ion concentrations or addition ...
Chapter 2: Communication Within the Nervous System
... appreciate the importance of biological psychology in its own right. This book is for them, too, but I wrote it so any student who is interested in behavior, including the newly declared sophomore major or the curious student who has wandered over from the history department, could have the deeper u ...
... appreciate the importance of biological psychology in its own right. This book is for them, too, but I wrote it so any student who is interested in behavior, including the newly declared sophomore major or the curious student who has wandered over from the history department, could have the deeper u ...
Word`s - Semiosis Evolution Energy
... embedded in sign-exchanging bodies embedded in sign-exchanging worlds, the eternal interplay of symmetry breaking and of self-organization that characterizes the momentto-moment experience of this recursively interactive system constitutes, in a very real sense, the very essence of ‘the mind.’ Prope ...
... embedded in sign-exchanging bodies embedded in sign-exchanging worlds, the eternal interplay of symmetry breaking and of self-organization that characterizes the momentto-moment experience of this recursively interactive system constitutes, in a very real sense, the very essence of ‘the mind.’ Prope ...
Mike Webster the king of the NFL comes in with all his brute force
... which according to Maureen Courtney ( a neurologist that is focused on hard hits and neuropathological diseases) is not a really understandable condition. “Second impact syndrome happens when a person gets one concussion and in the same week get’s another. This however is a very rare happening a ...
... which according to Maureen Courtney ( a neurologist that is focused on hard hits and neuropathological diseases) is not a really understandable condition. “Second impact syndrome happens when a person gets one concussion and in the same week get’s another. This however is a very rare happening a ...
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT
... instruc7ons coming from higher levels in the motor program • Adjus7ng motor unit ac7vity to local condi7ons (obstacles to movement, pain) • Local control systems use sensory informa7on from sensory receptors ...
... instruc7ons coming from higher levels in the motor program • Adjus7ng motor unit ac7vity to local condi7ons (obstacles to movement, pain) • Local control systems use sensory informa7on from sensory receptors ...
Curriculum Vitae
... My laboratory was set up in March 2005. The long-term goal of the laboratory is to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the proper migration and distribution of different types of neurons in developing brain, one of the key steps for brain morphogenesis. Currently, we focus on the guidance ...
... My laboratory was set up in March 2005. The long-term goal of the laboratory is to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the proper migration and distribution of different types of neurons in developing brain, one of the key steps for brain morphogenesis. Currently, we focus on the guidance ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.