Metabotropic Neurot
... • All 3 classes inhibit L-type voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels • mGluR activation also closes K+ channels, leading to slow repolarization (prolong excitation) HPC and cortex • Opposite effect in cerebellum • Pre-synaptic mGluRs are inhibitory-on both Glutamate and GABA neurons (Ca2+ channel) ...
... • All 3 classes inhibit L-type voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels • mGluR activation also closes K+ channels, leading to slow repolarization (prolong excitation) HPC and cortex • Opposite effect in cerebellum • Pre-synaptic mGluRs are inhibitory-on both Glutamate and GABA neurons (Ca2+ channel) ...
IV. Conduction Across Synapses
... neurotransmitter split by a specific enzyme fragments re-absorbed by presynaptic neuron used to synthesize more neurotransmitter ex: acetylcholine (Ach) split by enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
... neurotransmitter split by a specific enzyme fragments re-absorbed by presynaptic neuron used to synthesize more neurotransmitter ex: acetylcholine (Ach) split by enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
Receptors and Neurotransmitters
... . This neurotransmitter is involved in the control of skeletal muscle action in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), stimulating skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions. It can excite or inhibit ANS synapses. Most of the postganglionic fibers of th ...
... . This neurotransmitter is involved in the control of skeletal muscle action in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), stimulating skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions. It can excite or inhibit ANS synapses. Most of the postganglionic fibers of th ...
Chemistry of Neurotransmitters
... Metabotropic receptors • They are coupled to G proteins, through which they influence the synthesis of second messengers. Receptors that work with type Gs proteins increase the cAMP level in the postsynaptic cell (cAMP), while those that activate Gi proteins reduce it. Via type Gq proteins,other rec ...
... Metabotropic receptors • They are coupled to G proteins, through which they influence the synthesis of second messengers. Receptors that work with type Gs proteins increase the cAMP level in the postsynaptic cell (cAMP), while those that activate Gi proteins reduce it. Via type Gq proteins,other rec ...
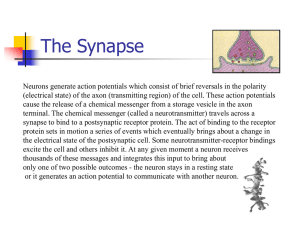
The Synapse
... the limbs, chest, and abdomen and, finally, the diaphragm. Larger doses increase the risk of respiratory depression due to relaxation of the intercostal muscles and diaphragm. Muscle tone returns in the reverse order. ...
... the limbs, chest, and abdomen and, finally, the diaphragm. Larger doses increase the risk of respiratory depression due to relaxation of the intercostal muscles and diaphragm. Muscle tone returns in the reverse order. ...
L23-Neurotransmitter
... hypothalamus also found in gastric mucosa and in mast cells. • Formed by decarboxylation of amino acid histidine with the help of enzyme histaminase. • Three known types of histamine receptors in found e.g. H1, H2, H3. • H3 receptors are presynaptic. Its function in brain is not very certain. Its ma ...
... hypothalamus also found in gastric mucosa and in mast cells. • Formed by decarboxylation of amino acid histidine with the help of enzyme histaminase. • Three known types of histamine receptors in found e.g. H1, H2, H3. • H3 receptors are presynaptic. Its function in brain is not very certain. Its ma ...
jeopardy bio psych review
... Produces hormones insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels ...
... Produces hormones insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels ...
Chapter 48 Worksheet
... 1. The part of a neuron that carries nerve impulses toward the cell body is called _____. a. a nerve b. white matter c. a neurotransmitter d. a dendrite e. an axon 2. Which one of the following statements is not true about the resting potential? a. The neuron's plasma membrane is much more permeabl ...
... 1. The part of a neuron that carries nerve impulses toward the cell body is called _____. a. a nerve b. white matter c. a neurotransmitter d. a dendrite e. an axon 2. Which one of the following statements is not true about the resting potential? a. The neuron's plasma membrane is much more permeabl ...
It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and
... It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and peripheral nervous systems play essential roles in the transmission and assimilation of the information of our environment. This information is processed through neuronal synaptic communications, mediated by excitatory and inhibitory ...
... It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and peripheral nervous systems play essential roles in the transmission and assimilation of the information of our environment. This information is processed through neuronal synaptic communications, mediated by excitatory and inhibitory ...
4-5_Chem_postsyn_KolozsvariB
... First, the receptors may directly open ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic cell membrane, causing ions to enter or exit the cell and changing the local transmembrane potential. The resulting change in voltage is called a postsynaptic potential. In general, the result is excitatory in the c ...
... First, the receptors may directly open ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic cell membrane, causing ions to enter or exit the cell and changing the local transmembrane potential. The resulting change in voltage is called a postsynaptic potential. In general, the result is excitatory in the c ...
Prémio Artigo Destaque SPN_2011 Cellular and Molecular
... Neurons are capable of integrating information spatially and temporally. They can process electrical signals at specific locations called synapses, which can be excitatory or inhibitory. The information can then be built or not into an output signal, the action potential, carried by the axon. The dy ...
... Neurons are capable of integrating information spatially and temporally. They can process electrical signals at specific locations called synapses, which can be excitatory or inhibitory. The information can then be built or not into an output signal, the action potential, carried by the axon. The dy ...
overview of neural f..
... • conditioning produces LTP-like changes in brain. • drugs that block LTP block learning. ...
... • conditioning produces LTP-like changes in brain. • drugs that block LTP block learning. ...
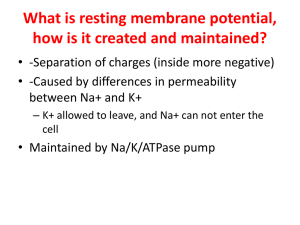
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... • -Separation of charges (inside more negative) • -Caused by differences in permeability between Na+ and K+ – K+ allowed to leave, and Na+ can not enter the cell ...
... • -Separation of charges (inside more negative) • -Caused by differences in permeability between Na+ and K+ – K+ allowed to leave, and Na+ can not enter the cell ...
big
... – Inside myelin, diffusion is fast, but fades out – At nodes, new action potentials are triggered ...
... – Inside myelin, diffusion is fast, but fades out – At nodes, new action potentials are triggered ...
Mind Is Matter
... 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Receptors and ion chan ...
... 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Receptors and ion chan ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... Cell communication: neurotransmitters released at synapses Axon (presynaptic cell) Dendrite (postsynaptic cell) ...
... Cell communication: neurotransmitters released at synapses Axon (presynaptic cell) Dendrite (postsynaptic cell) ...
11- neurotransmitters and receptors
... Can generate an electric signal there (EPSP’s or IPSP’s) These are graded potentials (more channels, more charge flux) Effect depends which ions are allowed to diffuse across membrane, how many and for how long. Effect depends on the selectivity of the channel. What if….. the LGC are….. – Na+ select ...
... Can generate an electric signal there (EPSP’s or IPSP’s) These are graded potentials (more channels, more charge flux) Effect depends which ions are allowed to diffuse across membrane, how many and for how long. Effect depends on the selectivity of the channel. What if….. the LGC are….. – Na+ select ...
Synapses - JNCASR Desktop
... What is a neuron? Neurons are the basic data processing units of the brain. Each neuron receives electrical inputs from about 1000 other neurons. Impulses arriving simultaneously are added together and, if sufficiently strong, lead to the generation of an electrical discharge, known as an action pot ...
... What is a neuron? Neurons are the basic data processing units of the brain. Each neuron receives electrical inputs from about 1000 other neurons. Impulses arriving simultaneously are added together and, if sufficiently strong, lead to the generation of an electrical discharge, known as an action pot ...
Drugs Change the way Neurons communicate
... axon terminals where it enters the vesicles that contain dopamine. This triggers the vesicles to be released, even without an action potential. Combined, this causes a surge of dopamine to be present in the synaptic cleft, leading to overactivation of neurons and an extreme ‘high’. ...
... axon terminals where it enters the vesicles that contain dopamine. This triggers the vesicles to be released, even without an action potential. Combined, this causes a surge of dopamine to be present in the synaptic cleft, leading to overactivation of neurons and an extreme ‘high’. ...
Lecture #21 Date
... A neuron is like a French Fry: high Na+ outside, high K+ (POTassium/potato) inside!!! During the AP, we will turn our axon INSIDE OUT!!! To fire an action potential, we have to be at resting potential (-70 mV), maintained by closed Na+ and K+ channels If enough NT molecules are picked up by dendrite ...
... A neuron is like a French Fry: high Na+ outside, high K+ (POTassium/potato) inside!!! During the AP, we will turn our axon INSIDE OUT!!! To fire an action potential, we have to be at resting potential (-70 mV), maintained by closed Na+ and K+ channels If enough NT molecules are picked up by dendrite ...
Synaptic Transmission Lecture
... • NO PORE, but binding can initiate: • 2nd messenger system • Other products could open ion channels • Modulate enzyme activity • Regulate ion channels in membrane • Initiate gene transcription/translation ...
... • NO PORE, but binding can initiate: • 2nd messenger system • Other products could open ion channels • Modulate enzyme activity • Regulate ion channels in membrane • Initiate gene transcription/translation ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.