Bio 17 – Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... Sodium/Potassi um Pump Potassium Channels (K+) Sodium Channels (Na+) ...
... Sodium/Potassi um Pump Potassium Channels (K+) Sodium Channels (Na+) ...
Module 9: Synaptic Transmission
... neurons in the substantia nigra • Symptoms include – difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements – tremors at rest – stooped posture – rigidity – poor balance ...
... neurons in the substantia nigra • Symptoms include – difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements – tremors at rest – stooped posture – rigidity – poor balance ...
click - Uplift Education
... 19) Differentiate between continuous conduction and saltatory conduction. Where does each occur? Which is faster and why? ...
... 19) Differentiate between continuous conduction and saltatory conduction. Where does each occur? Which is faster and why? ...
File
... 1. How is it possible for charged ions to move from neuron to neuron if the plasma membrane is impermeable to charged ions? 2. Describe the forces that act upon the potassium ions in and out of the plasma membrane. 3. What is the resting membrane potential charge? 4. At rest, why is the neuron negat ...
... 1. How is it possible for charged ions to move from neuron to neuron if the plasma membrane is impermeable to charged ions? 2. Describe the forces that act upon the potassium ions in and out of the plasma membrane. 3. What is the resting membrane potential charge? 4. At rest, why is the neuron negat ...
Slide 1
... •Significance of them not well understood - important in absence seizures, cognitive performance and regulation of amine release. ...
... •Significance of them not well understood - important in absence seizures, cognitive performance and regulation of amine release. ...
the limbic system
... block the reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic axon terminal, for example fluoxetine (Prozac). • Cocaine, opiates, and alcohol produce rewarding effects by promoting the release or inhibiting the presynaptic re-uptake of dopamine. {addiction is associated with reduced density of dopamine recep ...
... block the reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic axon terminal, for example fluoxetine (Prozac). • Cocaine, opiates, and alcohol produce rewarding effects by promoting the release or inhibiting the presynaptic re-uptake of dopamine. {addiction is associated with reduced density of dopamine recep ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... Neuronal glutamate (Glu) is synthesized de novo from glucose (not shown) and from glutamine (Gln) supplied by glial cells. Glutamate is then packaged into synaptic vesicles by vesicular glutamate transporters (vGluTs). SNARE complex proteins mediate the interaction and fusion of vesicles with the pr ...
... Neuronal glutamate (Glu) is synthesized de novo from glucose (not shown) and from glutamine (Gln) supplied by glial cells. Glutamate is then packaged into synaptic vesicles by vesicular glutamate transporters (vGluTs). SNARE complex proteins mediate the interaction and fusion of vesicles with the pr ...
Endocrine System - Brain Mind Forum
... It functions to regulate appetite, sleep, memory and learning, temperature, mood, behaviour, muscle contraction, and function of the cardiovascular system and endocrine system. It is speculated to have a role in depression, as some depressed patients are seen to have lower concentrations of metaboli ...
... It functions to regulate appetite, sleep, memory and learning, temperature, mood, behaviour, muscle contraction, and function of the cardiovascular system and endocrine system. It is speculated to have a role in depression, as some depressed patients are seen to have lower concentrations of metaboli ...
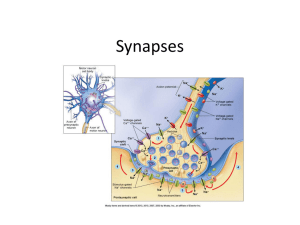
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... • Location where information is transmitted from presynaptic neuron to postsynaptic neuron- gap where axon terminal meets dendrite of next neuron • Neurotransmitter molecules released into this space ...
... • Location where information is transmitted from presynaptic neuron to postsynaptic neuron- gap where axon terminal meets dendrite of next neuron • Neurotransmitter molecules released into this space ...
here
... Each neuron is separated from the next by a tiny gap called a synapse. Signals in the synapse are transmitted chemically. When an electrical impulse reaches the end of the neuron (the pre-synaptic terminal) it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from tiny sacs known as vesicles. These ...
... Each neuron is separated from the next by a tiny gap called a synapse. Signals in the synapse are transmitted chemically. When an electrical impulse reaches the end of the neuron (the pre-synaptic terminal) it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from tiny sacs known as vesicles. These ...
Synaptic Transmission - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... • Plays a dual role in sleep: day – excites the brain, night – slows down the brain. • Huntington’s disease involves loss of neurons in striatum that utilize GABA – Symptoms: • jerky involuntary movements ...
... • Plays a dual role in sleep: day – excites the brain, night – slows down the brain. • Huntington’s disease involves loss of neurons in striatum that utilize GABA – Symptoms: • jerky involuntary movements ...
Neuronal signaling and synapses
... -four main types of changes can occur with the activation of metabotropic receptors -opening specific ion channels through the postsynaptic cell member – e.g. opening of a potassium channel (prolonged opening) -activation of cAMP or cGMP in the neuron can activate metabolic processes that result in ...
... -four main types of changes can occur with the activation of metabotropic receptors -opening specific ion channels through the postsynaptic cell member – e.g. opening of a potassium channel (prolonged opening) -activation of cAMP or cGMP in the neuron can activate metabolic processes that result in ...
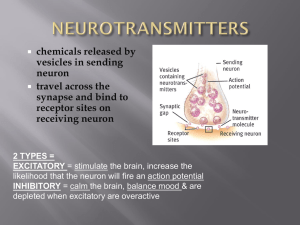
KKDP4: The role of neurotransmitters in the transmission of neural
... NOTE: The effects of a neurotransmitter are not entirely caused by the chemical. Its effects are also due to the receptor to which the neurotransmitter binds. The same neurotransmitter can be excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the properties of the receptor and on the receptor’s location in the ...
... NOTE: The effects of a neurotransmitter are not entirely caused by the chemical. Its effects are also due to the receptor to which the neurotransmitter binds. The same neurotransmitter can be excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the properties of the receptor and on the receptor’s location in the ...
Chapter 2
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a positive value – Potential is restored when other channels open, allowing potassiu ...
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a positive value – Potential is restored when other channels open, allowing potassiu ...
Neural transmission
... GABA (gamma-amino-butyric acid) Glutamate/Glu Norpinephrine /NE Dopamine /DA Enkephalin/Endorphin ...
... GABA (gamma-amino-butyric acid) Glutamate/Glu Norpinephrine /NE Dopamine /DA Enkephalin/Endorphin ...
Synaptic Transmission
... • Excitatory message—increases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will activate (allows + ions to enter) • Inhibitory message—decreases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will activate. (allows – ions to enter) ...
... • Excitatory message—increases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will activate (allows + ions to enter) • Inhibitory message—decreases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will activate. (allows – ions to enter) ...
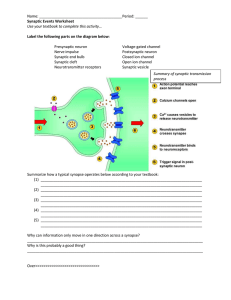
synaptic transmission worksheet
... Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
... Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... causes blood vessels to contract & heart rate to increase GABA Gamma-Amino Butyric Acid An inhibitory neurotransmitter “nature’s VALIUM-like substance” Related probs = anxiety, seizures, Huntington’s disease Valium and similar antianxiety drugs work at GABA synapses ...
... causes blood vessels to contract & heart rate to increase GABA Gamma-Amino Butyric Acid An inhibitory neurotransmitter “nature’s VALIUM-like substance” Related probs = anxiety, seizures, Huntington’s disease Valium and similar antianxiety drugs work at GABA synapses ...
Cognitive Psychology
... currents that can pass through a neuron: • Active currents are ones that are caused by explicit chemical activity (opening and closing of ion channels); ex - at the synapse and across the surface of the axon • Passive currents are ones that simply pass through the cytoplasm, typically as a response ...
... currents that can pass through a neuron: • Active currents are ones that are caused by explicit chemical activity (opening and closing of ion channels); ex - at the synapse and across the surface of the axon • Passive currents are ones that simply pass through the cytoplasm, typically as a response ...
ACh - Perkins Science
... Agonists and Antagonists Agonists: drugs that can stimulate a receptor a)Nicotine for nicotinic ACh receptors b)Muscarine for muscarinic ACh receptors Antagonists: drugs that inhibit a receptor a)Atropine from plants, is an antagonist for muscarinic receptors. ...
... Agonists and Antagonists Agonists: drugs that can stimulate a receptor a)Nicotine for nicotinic ACh receptors b)Muscarine for muscarinic ACh receptors Antagonists: drugs that inhibit a receptor a)Atropine from plants, is an antagonist for muscarinic receptors. ...
Transmission at the Synapse and the
... excitatory neurotransmitter released Voltage-gated potassium channels can open, thus hyperpolarizing the membrane by allowing a stream of potassium to exit, and thusa decreasing the inward calcium stream upon the arrival of the action potential Direct inhibition of neurotransmitter release indep ...
... excitatory neurotransmitter released Voltage-gated potassium channels can open, thus hyperpolarizing the membrane by allowing a stream of potassium to exit, and thusa decreasing the inward calcium stream upon the arrival of the action potential Direct inhibition of neurotransmitter release indep ...
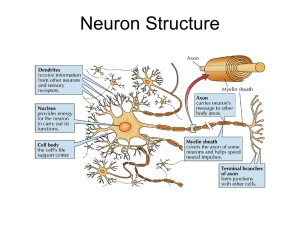
Neurons and Neurotransmission
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
Neurons_and_Neurotranmission
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.