BIOLOGY 3201
... 6. _?_ carry information from receptor cells to the CNS. 7. _?_ carry information from the CNS to effectors like muscles. 8. Modulators of the CNS are composed of these type neurons. 9. Nerves always fire with the same intensity. Either they fire or they don’t. This notion is referred to as the ___? ...
... 6. _?_ carry information from receptor cells to the CNS. 7. _?_ carry information from the CNS to effectors like muscles. 8. Modulators of the CNS are composed of these type neurons. 9. Nerves always fire with the same intensity. Either they fire or they don’t. This notion is referred to as the ___? ...
Action Potential
... Why an EPSP or an IPSP ? 1. neurotransmitter. acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, glutamate, GABA 2. specific type of receptor one neurotransmitter can produce an EPSP or an IPSP, depending on receptor ...
... Why an EPSP or an IPSP ? 1. neurotransmitter. acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, glutamate, GABA 2. specific type of receptor one neurotransmitter can produce an EPSP or an IPSP, depending on receptor ...
Neuroscience in PT: Introduction and Review
... • The same neurotransmitter may bind to several types of receptors, e.g. Serotonin • The effect of neurotransmitters on a postsynaptic neuron is determined by the type of receptors present on its membrane, e.g. Ach, Norepinephrine ...
... • The same neurotransmitter may bind to several types of receptors, e.g. Serotonin • The effect of neurotransmitters on a postsynaptic neuron is determined by the type of receptors present on its membrane, e.g. Ach, Norepinephrine ...
File
... called a terminal button which contains neurotransmitters. B. Neurotransmitters are any chemical involved in synaptic transmission. Examples of neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin. C. When an action potential reaches the terminal button of an axon, it signals synaptic tr ...
... called a terminal button which contains neurotransmitters. B. Neurotransmitters are any chemical involved in synaptic transmission. Examples of neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin. C. When an action potential reaches the terminal button of an axon, it signals synaptic tr ...
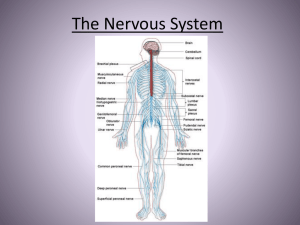
The Nervous System
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
File
... • IPSP: Transient hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential caused by presynaptic release of neurotransmitter. E.g. Glycine- and GABAgated channels cause IPSPs ...
... • IPSP: Transient hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential caused by presynaptic release of neurotransmitter. E.g. Glycine- and GABAgated channels cause IPSPs ...
Lecture 5 Transmitters and receptors lecture 2015
... Nitric oxide is made from L-arginine and a cofactor, citrullline by the enzyme nitric oxide synthase. Stimulation of a postganglionic parasympathetic neuron can cause complex effects on vascular smooth muscle cell. The first phase in this example is mediated by both nitric oxide (NO) and acetylcholi ...
... Nitric oxide is made from L-arginine and a cofactor, citrullline by the enzyme nitric oxide synthase. Stimulation of a postganglionic parasympathetic neuron can cause complex effects on vascular smooth muscle cell. The first phase in this example is mediated by both nitric oxide (NO) and acetylcholi ...
Powerpoint
... Pharmacology of receptors Nicotinic ACh receptor agonist - nicotine, succinylcholine antagonist - curare, bungarotoxin ...
... Pharmacology of receptors Nicotinic ACh receptor agonist - nicotine, succinylcholine antagonist - curare, bungarotoxin ...
neurotransmitter
... • There are dozens of different neurotransmitters (NT) in the neurons of the body. • NTs can be either excitatory or inhibitory • Each neuron generally synthesizes and releases a single type of neurotransmitter • The major neurotransmitters are indicated on the next slide. ...
... • There are dozens of different neurotransmitters (NT) in the neurons of the body. • NTs can be either excitatory or inhibitory • Each neuron generally synthesizes and releases a single type of neurotransmitter • The major neurotransmitters are indicated on the next slide. ...
`synapse`.
... receiving neurons. ► It is the presence of the NT 'keys' opening the receptor 'locks' on the surface of the dendrites of the post-synaptic neurons (and not any electrical signal that jumps the synapse) that excites or inhibits the postsynaptic neurons into activating or not. ...
... receiving neurons. ► It is the presence of the NT 'keys' opening the receptor 'locks' on the surface of the dendrites of the post-synaptic neurons (and not any electrical signal that jumps the synapse) that excites or inhibits the postsynaptic neurons into activating or not. ...
General design of the nervous system
... The somatic nervous system includes all nerves controlling the muscular system and external sensory receptors. External sense organs (including skin) are receptors. Muscle fibers and gland cells are effectors (since they prerform the functions dictated by the nerve signals). The autonomous nervous s ...
... The somatic nervous system includes all nerves controlling the muscular system and external sensory receptors. External sense organs (including skin) are receptors. Muscle fibers and gland cells are effectors (since they prerform the functions dictated by the nerve signals). The autonomous nervous s ...
Neurotransmitters
... • Sometimes there is a decrease in the number of receptors for a neurotransmitter on the postsynaptic neuron due to long-term exposure to the neurotransmitter. This is called downregulation. • Neurotransmitters can be classified into 4 major groups: 1. Amino acids (eg, glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric ...
... • Sometimes there is a decrease in the number of receptors for a neurotransmitter on the postsynaptic neuron due to long-term exposure to the neurotransmitter. This is called downregulation. • Neurotransmitters can be classified into 4 major groups: 1. Amino acids (eg, glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric ...
File
... feeling of pleasure and rewards particular behaviour in the reward pathway include Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases ...
... feeling of pleasure and rewards particular behaviour in the reward pathway include Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases ...
Psychopharmacology and Other Biologic Treatments
... • Present in the presynaptic terminal • Released into the synaptic cleft, causing a particular effect on the postsynaptic receptors • An exogenous form of the chemical is administered as a drug causes identical action. • Chemical is removed from the synaptic cleft by a specific mechanism. ...
... • Present in the presynaptic terminal • Released into the synaptic cleft, causing a particular effect on the postsynaptic receptors • An exogenous form of the chemical is administered as a drug causes identical action. • Chemical is removed from the synaptic cleft by a specific mechanism. ...
AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 9
... MULTIPLE ANSWER: Biological psychologists study behavior and mental processes from multiple levels, noting how____________________, ______________________________and ______________________-_____________________________ systems work and interact. (0.5 pt each) ...
... MULTIPLE ANSWER: Biological psychologists study behavior and mental processes from multiple levels, noting how____________________, ______________________________and ______________________-_____________________________ systems work and interact. (0.5 pt each) ...
Document
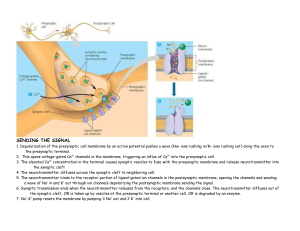
... the synaptic cleft, OR is taken up by vesicles at the presynaptic terminal or another cell, OR is degraded by an enzyme. 7. Na+-K+ pump resets the membrane by pumping 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ into cell. ...
... the synaptic cleft, OR is taken up by vesicles at the presynaptic terminal or another cell, OR is degraded by an enzyme. 7. Na+-K+ pump resets the membrane by pumping 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ into cell. ...
Nervous System
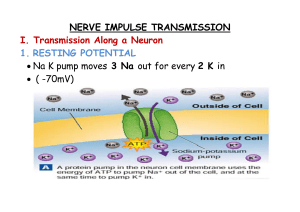
... • Voltage- potential energy stored in a charge disparity over distance • Nervous system uses ions (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++) to send signals from one neuron to another ...
... • Voltage- potential energy stored in a charge disparity over distance • Nervous system uses ions (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++) to send signals from one neuron to another ...
Nervous System
... • Voltage- potential energy stored in a charge disparity over distance • Nervous system uses ions (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++) to send signals from one neuron to another ...
... • Voltage- potential energy stored in a charge disparity over distance • Nervous system uses ions (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++) to send signals from one neuron to another ...
steps in nerve impulse transmission
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
Animal Nutrition
... As the membrane potential heads back toward resting, the K+ channels have not had a chance to close. The membrane is hyperpolarized and membrane potential dips slightly below -70mV: ...
... As the membrane potential heads back toward resting, the K+ channels have not had a chance to close. The membrane is hyperpolarized and membrane potential dips slightly below -70mV: ...
Action Potentials
... “Each neuron continuously integrates signals over both time and space as it is continually bombarded with stimuli through the thousands of synapses covering its dendrites and cell body. Remember that, although schematic diagrams of neural circuitry rarely show neurons with more than a few representa ...
... “Each neuron continuously integrates signals over both time and space as it is continually bombarded with stimuli through the thousands of synapses covering its dendrites and cell body. Remember that, although schematic diagrams of neural circuitry rarely show neurons with more than a few representa ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission - Milton
... “One-third of humanity has perished from the plague. 2.3 billion people have died, and countless more are quickly moving towards the final stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, a ...
... “One-third of humanity has perished from the plague. 2.3 billion people have died, and countless more are quickly moving towards the final stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, a ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.